A multi-core processor has more than one core, which are considered independent processing units (IPUs). Multiple independent processing units enhance system performance. This article discusses configuring multi-core settings in Windows 11/10.
Multi-Core Settings and Support in Windows 11/10
Now the following question arises:
- Does Windows 11/10 support only a single-core processor?
- Does there exist any method by which we can configure other cores for Windows 11/10?
- If Windows 11/10 is multi-core supported, then how could we prove or configure this?
In this article, we’re going to discuss these questions.
First of all, let us make it clear that Windows 11/10 is already configured for multi-core support.
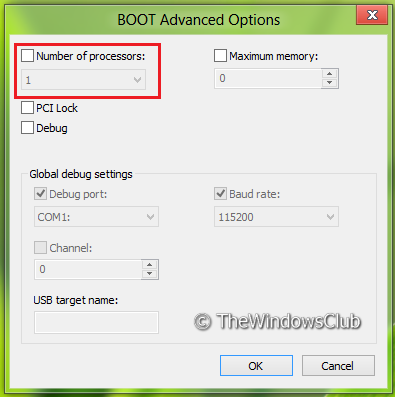
The setting for the second processor is optional. If you configure it, as shown in the image below, there won’t be any noticeable changes.
There is also another setting that lies in the all-new Task Manager of Windows. All you need to do is to open the Task Manager and click on Performance. You will obviously see the processing graph for a single processor.
But I wanted to see the graph for multi-core. Since Windows 11/10 supports multi-core, it must be able to display processes for each processor individually. Click on the graph and select Change graph to and then Logical processors.

After selecting Logical processors in the above graph, the graph splits into two processors and shows that Windows 11/10 is already supporting multicore processing. The individual display for each of the processors can be seen.
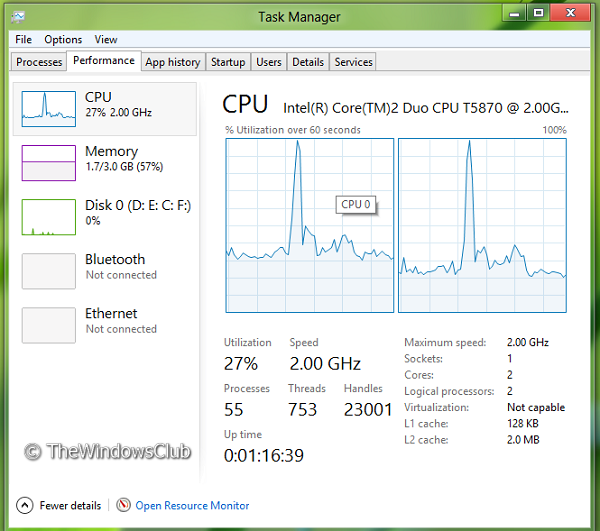
Here the CPU 0 and CPU 1 are the pre-defined cores and do not depend on whether you configure them or not. But we may see some changes for tablets.
In conclusion, we have to say that Windows 11/10 natively supports multi-core by default, and you do not need to configure it. It is configured optimally.
That’s it. I hope this helps.
How many CPU cores does Windows 11 need?
Windows 11 has some hardware requirements. If you want to upgrade your system to Windows 11 or install Windows 11, your computer should have compatible hardware. According to Microsoft, the minimum system requirements to install or upgrade to Windows 11 are a 1 GHz clock speed processor with two or more cores, 4 GB RAM, 64 GB space on a hard disk, TPM version 2.0, etc. It is also possible to bypass some of these hardware requirements and install Windows 11 on a computer with unsupported hardware. However, you will experience performance issues if you install Windows 11 on a computer with unsupported hardware.
How do I know if multithreading is enabled in Windows?
If your CPU supports multithreading, it is enabled by default. You can check this in the Task Manager. Open the Task Manager and select the Performance tab. Now, select CPU and view the number of Cores and Logical processors on the right side. If multithreading is enabled, the Task Manager will show the Logical processors 2 times the number of Cores.
Read next: Fix new CPU Black screen, No beep problem.