Here are some basic Command Prompt Tricks and Tips to help a Windows user, while using the CMD in Windows 11 or Windows 10. To begin, first, launch Command Prompt. These tips will also work on Windows Terminal.
Command Prompt Tips for Windows users
Here is the list which you should try and know more about it.
- Customize CMD window
- Copy or Paste in CMD
- Adjust the size of the Prompt window
- Use Drag and Drop in Command Prompt
- Auto-complete file paths in CMD
- CMD Help
- Make the Command Prompt transparent
- CMD Keyboard Shortcuts
- Command Prompt History
If you open a Command prompt with admin privileges, you will not see anything different. The customization is the same for all.
1] Customize CMD window
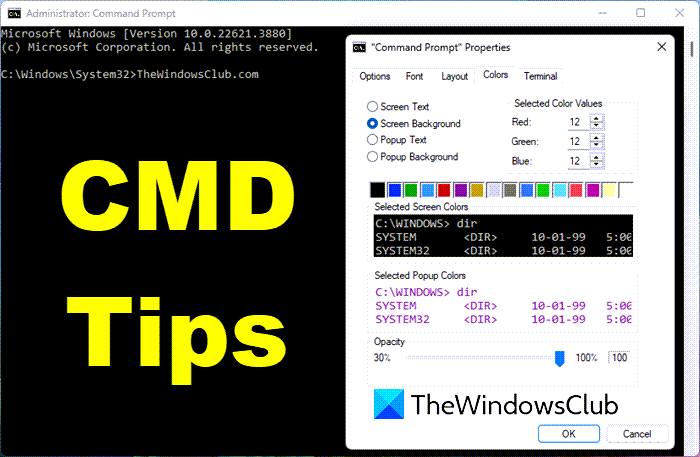
You can customize your black CMD window any way you want. Click on the black CMD icon which appears on the top left side of the title bar and select Properties. Here you can change options, fonts, layout, and colors too.
You can also change the colors using the syntax: color [attr].
This post will show you how to add Custom Fonts to Command Prompt. and this one to change the Background and Foreground Color.
2] Copy or Paste in CMD
You cannot use Ctrl+C to copy. To copy, you have to right-click inside the CMD, select Mark, and then drag the highlighted box to the text you want to copy. Right-click on the text. It will automatically get copied.
To paste your Clipboard contents, you can right-click in the CMD and select Paste to paste the copied text. Or you may use Ctrl+V.
Alternatively, open the Properties box, and from the Options tab, select the Quick Edit option. Now you will be able to copy as usual.
Read: How to clear CMD screen?
3] Adjust the size of the Prompt window
You can adjust the size of the Prompt window by using the following syntax:
Syntax: mode [width], [height]
4] Use Drag and Drop in Command Prompt
Rather than typing the full path of a file, you can simply drag and drop the file. The full path will get entered.
5] Auto-complete file paths in CMD
To auto-complete file paths, type the first part of the path, say E:\ . Now click on Tab. All available file names & folders will be cycled.
6] CMD Help
Need help with CMD? If you know a command but aren’t sure how it works, suffix the command with ‘/’ or ‘?’ and execute it. If the command is valid, the command prompt will give you all the information related to it.
7] Make the Command Prompt transparent
To quickly see what is behind your CMD window in Windows 10, press Ctrl+Shift+- to increase transparency. To make it opaque again, press Ctrl+Shift++.
8] CMD Keyboard Shortcuts
These Command Prompt keyboard shortcuts will help you work faster with it.
9] See Command Prompt History
Pressing the arrow up selects a previous command from your command history; similarly, the arrow down selects the next command. To see your complete command prompt history, press the F7 key.
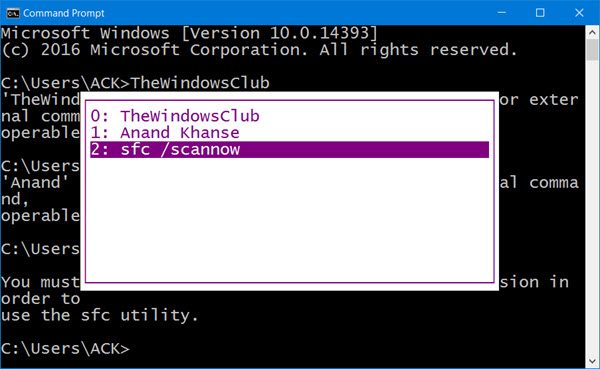
You can see the Command history in a session, by pressing the F7 key. You can also type doskey /history in the CMD window, to see the command history in the command prompt itself.
Incidentally, running CMD in full-screen mode, by pressing Alt+Enter, is no longer supported, from Windows Vista onwards. But you can check this post for a workaround of sorts.
Looking for more? Check out these Advanced CMD Tricks for Windows 11/10.
How do I get a list of command prompts?
The easiest way to do this is to type Help and press enter on the Command Prompt, and it will list all the tools and commands available. If the list is too long, you can save the output into a text file and then open it with your favorite editor to view them one by one.
What does * do in the command line?
It is a wildcard which means ALL. It can be all files, all conditions, or anything but the entire. So it will depend on where and how it is used. If you use it with the Directory command, then it will reveal all the files in the directory.
How to save command prompt output in a text file?
To save the output of a command you plan to execute in a text file; you can use the > operator. For example, if you want to save the list of all commands in a text file, then use Help > Output.txt. Similarly for saving all files in a directory into a text file, then use dir > output.txt.
I already knew most of these tricks.
Nice for you.