If your 5G Wi-Fi keeps dropping on Windows 11/10, this post will help you fix this problem. This issue can be frustrating because it can hamper your work and affect your productivity. Usually, the router and driver issues are responsible for this problem.

Fix 5G Wi-Fi keeps dropping on Windows 11/10
5G Wi-Fi dropping issues can also be caused by temporary glitches in your PC. Before you proceed, we suggest you restart your computer and router to fix temporary glitches. If your 5G Wi-Fi still keeps dropping on Windows 11/10, use the following suggestions:
- Power cycle your router
- Run Network and Internet troubleshooter
- Update your Network driver
- Roll back your Network driver
- Change the Power Management settings of your Network adapter (if available)
- Reset TCP/IP, flush DNS cache, reset Windows sockets
- Enable IPv6 in the Network adapter settings
- Reset network
Let’s start.
1] Power cycle your router
The first step you should do is power cycle your router. This will fix the temporary glitches. To do so, use the following instructions:

- Turn off the switch and unplug the power adapter from the wall socket.
- Wait for a few minutes.
- Plug the power adapter back into the wall socket and turn on the switch.
- Wait for the router to start up and connect to the internet.
Check if it brings any changes.
Read: WiFi keeps disconnecting in Windows
2] Run Network and Internet troubleshooter
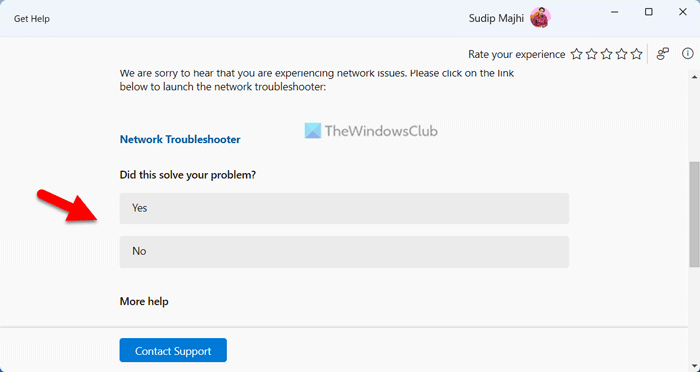
Windows 11/10 has automated troubleshooting tools. You can run a dedicated troubleshooter on your system depending on the problem you are experiencing on your Windows device. Network and Internet Troubleshooter helps you resolve network problems. Run the Network and Internet Troubleshooter via the Get Help app in Windows 11.
3] Update your Network driver
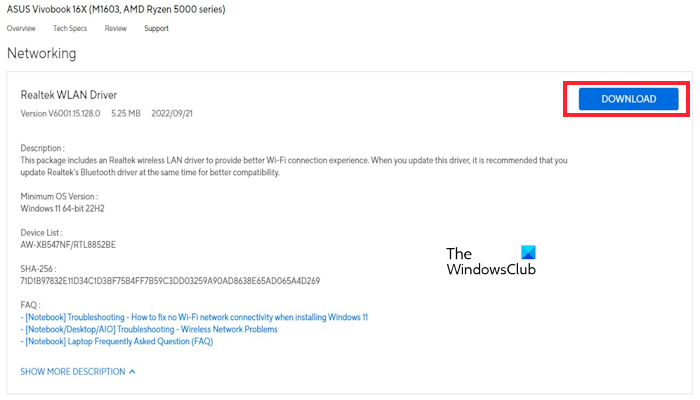
An outdated or corrupted Network driver can cause the WiFi dropping issue. Make sure your Network driver is up to date. You can update the driver from the manufacturer’s website or use free driver updater software. After updating drivers, check if the issue is resolved.
4] Roll back your Network driver
Windows Updates also update the outdated drivers. In this case, you can install the previous version of the driver by using the Roll Back option. We suggest you check if the Roll Back Driver option is available for your Network driver. If yes, use it to install its previous version. To do so, use the below steps:
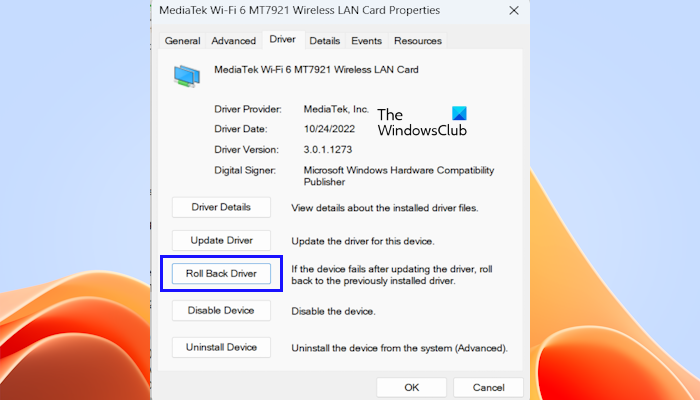
- Go to the Device Manager.
- Expand the Network adapters section.
- Right-click on your Network driver and select the Properties option.
- Select the Driver tab.
- Check if the Roll Back Driver button is clickable or not. If yes, click on that button to roll back your Network driver.
- Follow the on-screen instructions.
- Restart your computer.
Now, check if it brings any changes. You can also try uninstalling the recent Windows Update.
5] Change the Power Management settings of your Network adapter (if available)
If you enable your Network adapter’s Power Management settings, Windows puts your Network card to sleep when your laptop goes into sleep mode. There is a possibility that your WiFi drops due to this setting. We suggest you disable this setting (if available) and check if it brings any changes. To do so use the below steps:
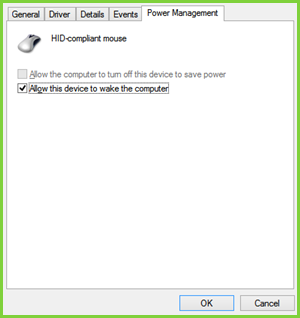
- Go to the Device Manager.
- Expand the Network adapters.
- Double-click on your Network adapter and click on the Power Management tab (if available).
- Clear the check box to “Allow the computer to turn off the device to save energy.”
- Click OK to save the changes.
Related article: Power Management tab missing in Device Manager of Windows.
6] Reset TCP/IP, flush DNS cache, reset Windows sockets
Connectivity issues can also occur due to the corrupt TCP/IP or Internet Protocol, corrupt DNS cache, and corrupt Windows Sockets. We suggest you reset TCP/IP, flush your DNS cache, and reset Winsock. You have to execute the required commands in the elevated Command Prompt window. However, if you do not want to execute the commands, you can also use our FixWin11 utility for the same.
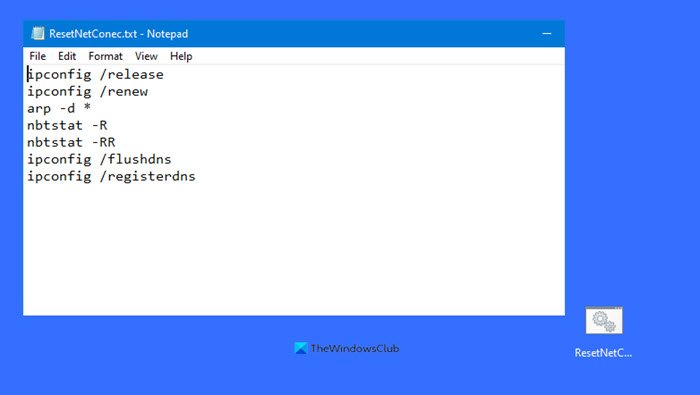
Alternatively, you can create a batch file to perform all the above-mentioned actions with a single click.
7] Reset network
Sometimes resetting your Network can help fix this issue. This will resolve any network-related issues. To do so, use the following steps:
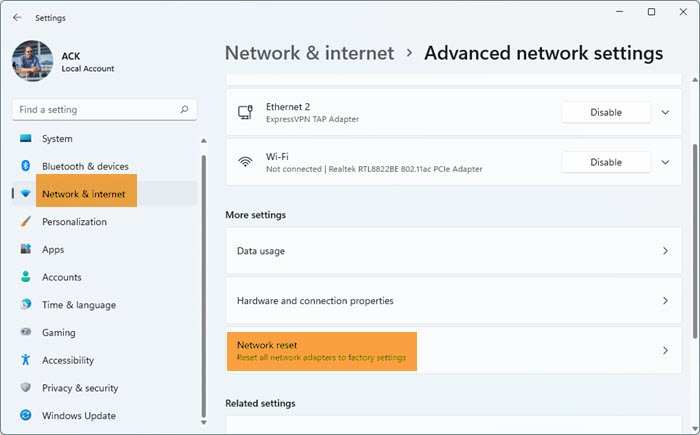
- Open the Windows Settings.
- Click on Network & internet.
- Now, click on Advance network settings.
- Click on Network reset and select Reset now.
When you perform a Network reset, you have to wait for 5 minutes. After 5 minutes, Windows will restart automatically.
8] Enable IPv6 in the Network adapter settings
If IPv6 is disabled on your system, you may experience issues while connecting to the 5 GHz WiFi band. Use the below steps to enable IPv6:
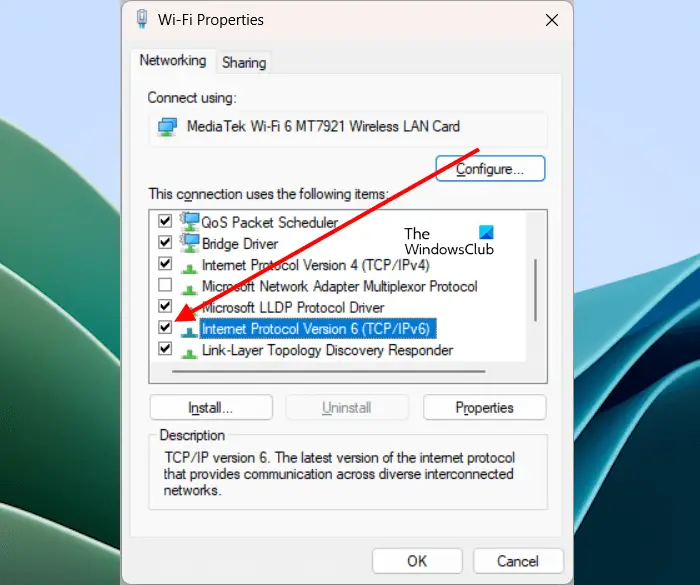
- Open the Control Panel.
- Select Category in the View by mode.
- Go to Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center.
- Click on your network. A new window will open in which you have to click Properties. This will open your network properties.
- Now, select the Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) checkbox.
- Click OK to save the changes.
Now, check if your 5 GHz WiFi band is stable or not.
Why does my 5G Wi-Fi keep dropping?
There can be a few reasons why your 5G Wi-Fi keeps dropping. Some of the most common reasons are outdated drivers, corrupted DNS cache, router issues, temporary glitches, etc.
Does Windows 11 support 5G Wi-Fi?
Yes, Windows 11 supports the 5GHz WiFi band. But it is not enough to get a 5GHz WiFi connection on your system. Your computer should also have the supported hardware for this. If your WiFi card does not support the 5GHz WiFi band, you can’t connect to the 5GHz WiFi band. Therefore, consider upgrading your network card if you want to use high-speed internet connectivity through the 5G WiFi.
Read next: Low Wi-Fi signal strength on Windows.
Leave a Reply