Consider your own mini manufacturing plant that does not require any license to set up. Of course, you have seen many home-based manufacturing industries that don’t require a license. You won’t need a license to buy and use a juicer. If you want to go for commercial usage of a 3D printer, we got the news that a few manufacturing units applied for a license for bulk sales. However, that is the case for commercial production and for the output of the printer. You don’t need a license to own a 3D printer and to print things for personal usage.
What Is A 3D Printer
3D printing is the process of converting your digital designs into solid three-dimensional objects. This idea might seem novel to some but it was actually developed in the late nineteenth century and has been widely used for prototyping in several industries. Although what has changed is that this technology has finally opened up to the consumer market and is no longer restricted to manufacturing industries.
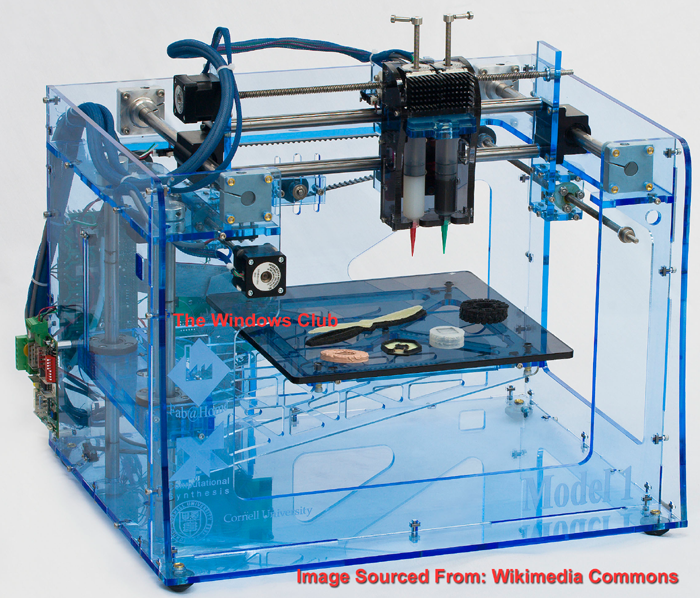
How Does A 3D Printer Work
A set of simple steps must be followed to print a three-dimensional prototype.
The first step is digitally modeling your idea using computer-aided design (CAD) software. Once a blueprint has been created the application breaks it down into multiple horizontal digital cross-sections in a manner that the printer can understand and reproduce in the exact defined specifications. The completed design is then sent to the 3D printer.
Interestingly, 3D printing actually employs the “additive” manufacturing process, which means that the solid object is created by adding layers of the raw material, as opposed to the “subtractive” process used in conventional manufacturing, through which an object is built by selectively removing the raw material to obtain a pre-defined structure.
After this, a material is selected that the printer will use to print the object. This can be chosen from a plethora of options, including plastic, rubber, or metal. The printing process consists of creating the object layer by successive layer. Different printers employ different techniques for creating these layers. The printer continues to deposit a layer on top of the previous layer until it is completed. The various layers are automatically amalgamated to create the three-dimensional prototype.
The printing process can typically take anywhere between a few hours to entire days depending on the complexity and size of the object to be printed.
What Can A 3D Printer Make?
Theoretically, anything that can be digitally visualized can be printed. The only limitation at present is the restriction on size and material that can be employed for 3D printing. It is being extensively used in art, industries, space research, health care, and several other varied industries.
Here are some examples of what a 3D printer can make:
1. In the health care domain, 3D printing has been employed to create hearing aids, prosthetic limbs, and dental fixtures. Researchers are working on printing human tissues that could be transplanted into humans.
2. NASA has employed 3D printing to build parts of rockets and spaceships. Scientists are already working on 3D printers that can be used in zero gravity on the International Space station.
3. Companies like Boeing are actually using 3D printing to build parts for an actual airplane. Automotive companies are extensively using 3D printing to build prototypes for engines and other parts of vehicles.
4. Hobbyists and artists are using 3D printing to express themselves creatively and to create shapes and structures that were previously considered impossible to implement. Toys, sculptures, gifts, and jewelry have been created using 3D printing in all shapes and colors.
5. Disturbingly, 3D printing has been employed to create prototypes of guns capable of firing actual bullets. It can also be used for forging jewelry and art.
The Future Of (3D) Printing
3D printing is a disruptive technology that has the potential to transform multiple aspects of several industries. The possibilities of 3D printing are limitless. The innovation 3D printing can spur in engineering, healthcare, architecture, construction, consumer electronics, and space research is mind-boggling.
It is true that 3D printing can be used to create weapons in bulk or even to forge high-value art and jewelry. One way to contain illegal usage is to make a manufacturing license mandatory for those buying 3D printers. However, several regulations are also in place for anti-piracy.
BOTTOMLINE: The constructive applications (advantages) of 3D printing far outweigh the negative usage possibilities (disadvantages and dangers of 3D printers). I leave it up to you to decide how the industry can be used for more good than bad.
Please let us know your point of view on the 3D printers in the comment boxes below.
ASSISTED BY: Swagat Karnany.

Microsoft has been using 3 D printing since long. It has a Model shop where prototypes have been regularly printed in 3D. Mouse, Phone prototypes and other parts have been regularly printed & tested using this technique. Even recently, Surface prototypes were prepared using this tech.
I find the statement, “Disturbingly enough 3D printing has been employed to create prototypes of guns”, disturbing! I read the article to learn about 3d printing, not the authors opinions on gun control
And so, then, max, you’re, obviously, a gun rights person who abhors anyone’s challenging your Second Amendment rights…
…by challenging their First Amendment ones.
Do I have it about right? (a rhetorical question; don’t bother answering)
Here’s a question, max, that you actually CAN answer (though I already know you won’t do so truthfully): Did you even KNOW anything about 3D printing before the recent news about how plastic guns capable of getting through airport security could be made using it? And so isn’t it true that THAT’s why you came here to learn about it?
You, me, and God all know that you did; and so, that being the case, how is that one can make a gun using 3D printing — and, worse, that it could end-up in the hands of YOUR likes — not disturbing?
Hmm?
Gregg L. DesElms
Napa, California USA
gregg at greggdeselms dot com
Actually Greg, when they were talking about a 3D gun printed, I was thinking of something in terms of z angle. It was only after they said it fired real bullets, I understood this is much more than just an extra angle. A research showed both how useful as well as dangerous this could be. Then, the point that came into mind was how to control and use it for good.
Don;t know about Max but I sure dug into the topic only after the gun thing made news!
TO: Arun Kumar
I appreciate that which has now made the subject interesting to you; and I agree.
My comment was aimed entirely at “max” and his obvious position against gun control in the US which I am likely better able to recognize than you might be, simply because I’m in the US where the gun control debate rages — and I’m embroiled in said debate — and you’re not. I recognize max’s words in a way that may not be as obvious to those outside the US; and that’s fine: I’m now simply trying to make clear, here, why I so called him on his words.
To be clear, I’m in favor or gun control; and am, in fact, an activist for it in the US. Those like, clearly, max, who abhor gun control have become ultra sensitive to calls for it, of late, because of the US citizenry’s generally negative reaction a new spate of shootings in the US, from just this past Sunday’s rampage in New Orleans…
http://bit.ly/18LM7K2 (Wikipedia)
…back to last December’s shooting at Sandy Hook Elementary School in Newtown, Connecticut…
http://bit.ly/10GQTSC (Wikipedia)
…and everything both in between, and dating back to long before. Just in the past few months, though, gun rights proponents, like, obviously, max, are feeling pressure being placed on those alleged rights (which I argue don’t really exist; see my Newsvine article linked to near the end of this comment) by a public call for increased US governmental control of gun ownership.
So sensitive have people like max become about it that they cannot tolerate even the slightest negative comment — or even hint of one — about guns. Max, who’s obviously a gun rights proponent, clearly interpreted your “[d]isturbingly enough 3D printing has been employed to create prototypes of guns” to be negative regarding guns. And so he chastised you for even writing it…
…and recognizing that as the very sort of intolerance that’s typical of gun-rights proponents, I called him on it. Because you’re not in the US, and so may not fully grasp all the subtleties and nuance of the debate, you may not have recognized that that’s what was going on, there. Again, that’s okay; and now that I’ve explained it, here, it will hopefully be at least a LITTLE bit more clear to persons outside the US. If it felt like I was attacking max, it’s because I sorta’ was; but only because he attacked you, first.
One refreshing thing that your reaction reveals to me, though, is how wonderful it must be to live someplace, such as where you live, where no one’s arguing about it! [grin]
Now, just watch, though: the typical anger and back-handed arguing technique of such as max will cause either him or another of his compadres, here, to respond that if I’m so impressed with living in such a place as that, then maybe that’s where I should go live. Such is all part of the “love America or leave it” both attitude and argument of conservatives (usually Republicans, in the US) who don’t realize that dissent, as a means of contributing to the democratic process of being an American citizen, is one of the most patriotic things we can do.
But refusing to see that, and demanding that anyone who doesn’t like how things are in America should just leave it, is how intolerant and unfair such as max tend to be; and it’s a classic example of how they argue. Of course, now that I’ve predicted that that’s what they’ll chime-in and write about me, here, they probably won’t. They hate it when we can either predict or recognize their arguments, and then call them on it. That’s probably, in fact, why max hasn’t responded, because he, I and God all know that I’m right.
To learn more about where I stand on guns, and why, see my August 2012 article on the NBC-owned “Newsvine” website:
http://bit.ly/13vtoPJ (Newsvine article)
Gregg L. DesElms
Napa, California USA
gregg at greggdeselms dot com
Wow. I did not know there was a larger canvas to all that above. Thank you for explaining it to me. And sure I will go through your Newsvine article to know more about the issue. Thanks again :)
This article is sensationalized. Here is the origin of the image above – only parts of the gun were printed using a 3D printer:
http://www.wired.com/dangerroom/2012/08/3d-weapons/
You can say that. Every machine – from pen to cars to jet and nuclear missiles – are assemblies. But then, no machine is shown disassembled because then, people won’t understand what is that screw/nut for – will it be used in a calculator or a remote bomb detonator?
And it is not impractical for the 3D printer to print the case if that is what you are referring to. If it can make parts, it can make cases too! BTW, talks are on about the Star Trek replicator that can print food. Looking forward to install one in my home – for coffee, chocolate and orange soda.
The image has been sourced from Wikimedia Commons and acknowledged too.
Life Saving aspect of 3D Printers – not taken up mainstream media. Via (Techland)
Doctors saved a baby’s life using 3D printer. The baby’s breathing tubes were weak. They got clearance to create an artificial airway that would keep the baby’s breathing tubes open so that it can breathe. The media that made much noise about 3D guns, should have reported this highly positive story but most of them chose to ignore the story. Here is the link to full story:
http://techland.time.com/2013/05/23/an-airway-created-with-a-3d-printer-saved-this-babys-life/
Another example of 3D Printing: Low cost fingers for people who lost their fingers… check this out:
http://news.cnet.com/8301-17938_105-57587027-1/3d-printed-robohands-help-kids-without-fingers
There’s always a good and bad side to everything – 3D printers included. I agree. Instead of worrying about making gun parts, tell about the good that can be done. By the way, some of the gun still has to be metal. The printer can’t do it all – yet.
Great! Another great innovation in technology gets taken over by politics! To begin with the statement of licensing for buyers of 3D printers – you may as well call it another tax or better another attempt to kill the “free enterprise spirit” in the United States.
Will we need a license to own a milling machine, how about a metal lathe, hell a hand file. All of these can produce a gun. How about a license to buy a piece of metal water pipe. You can make a single shot , shotgun with that. What about a machete, you can kill quite a few people with those. Man this ridiculous liberal world we live in. Every tool can be used for good or evil. Its evil in the heart of man that needs to be controlled, not tools. Hell I saw a guy kill 3 men with a pencil, a pencil ! Just kidding, that was from the movie John Wick ;-)
Pencil? Haha. You hv to see a South India movie where the actor cuts off ppl using a banana. Seriously. However, ur message is right. Anything, physical or abstract, can b used for both good and bad. Depends on person wielding that thing. Wishing u a Merry Christmas n a happy new year :)
Thanks man, you too, Merry Christmas :-)