If Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) is not responding or is slow to load on Windows Server or Windows 11/10 client machines, the solutions provided in this post can be applied to successfully resolve this issue on affected systems.

When you try to start the Active Directory Users and Computers tool, you may receive the error message along the following similar lines:
Naming Information cannot be located because:
The specified domain either does not exist or could not be contacted.
Contact your system administrator to verify that your domain is properly configured and is currently online.
Some affected users reported when they try to open from the icon (or run dsa.msc from command prompt), there are no errors at all – it just doesn’t open. No screen comes up and goes away, it’s like nothing was launched.
Active Directory Users and Computers not responding
If Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) is not responding or is slow to load when you try to open the snap-in on a Windows computerC, you can try our recommended solutions below in no particular order to resolve the issue on the machine.
- Change DNS to server IP or Localhost
- Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP
- Run DCdiag
- Flush DNS
- Configure TCP/IP filtering
Let’s take a look at the description of the process involved concerning each of the listed solutions.
1] Change DNS to server IP or Localhost
The Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) is not responding or is slow to load issue could be issue with the DNS server or the primary DNS has been changed to something else, consequently causing ADUC to not respond. In this case, to resolve the issue, you can run a DNS check on the server and see if it resolves. If it doesn’t, simply change DNS to server IP or Localhost.
Try the next solution if this task didn’t work.
2] Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP
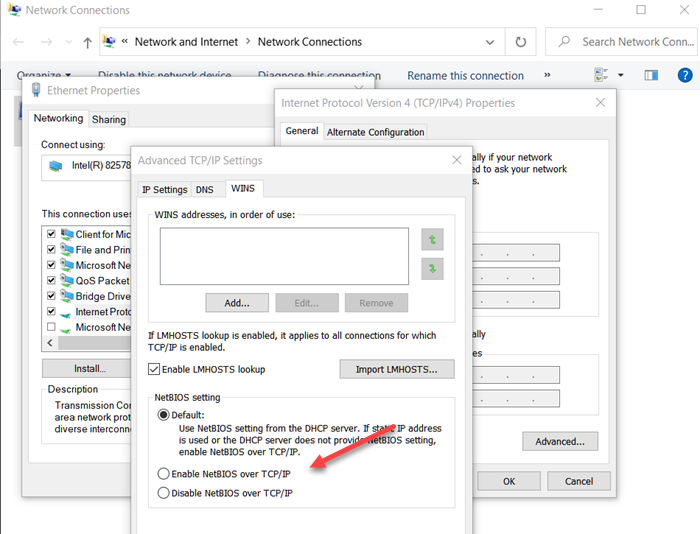
This solution requires you to disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP and then launch the ADUC snap-in and see if the issue in hand is resolved or not. If the latter is the case, you can continue with the next solution.
3] Run DCdiag
DCdiag is a Microsoft Windows command line utility that can analyze the state of domain controllers in a forest or enterprise. You can choose to analyze a single domain controller or all DC’s in a forest. Essentially, the dcdiag command line utility performs a domain controller health check.
To use dcdiag, you must run the dcdiag command from an elevated command prompt. If you have the AD DS server role installed then dcdiag is already installed. If you have the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) tools installed then you already have dcdiag installed.
4] Flush DNS
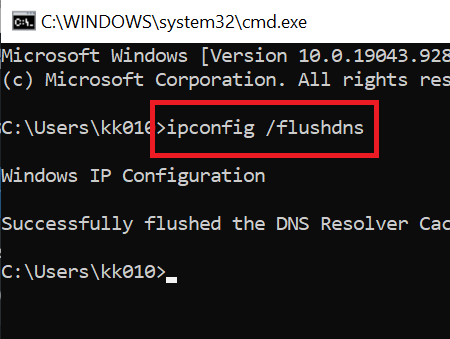
Domain Name System (DNS) settings might interfere with Active Directory. If the DNS settings are corrupted, you may encounter the issue in focus. In this case, you can flush the DNS.
The following are aspects of DNS functionality:
- Connectivity
- Essential services
- DNS client configuration
- Resource record registrations
- Zone and start of authority (SOA)
- Root zone
Flushing DNS will clear any IP addresses or other DNS records from your cache. This can help resolve security, internet connectivity, and other issues.
5] Configure TCP/IP filtering
The issue in hand may occur if TCP/IP filtering is configured to permit only port 80 for TCP/IP traffic. Port 389 used for Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) connections will be blocked if TCP/IP filtering is configured incorrectly. By default, TCP/IP filtering is configured with the Permit All setting.
To verify TCP/IP filtering setting is configured correctly, do the following:
- Right-click My Network Places on the domain controller on which you cannot start ADUC.
- Click Properties.
- Click Internet Protocol.
- Click Properties.
- Click Advanced.
- Click Options.
- Click TCP/IP Filtering.
- Click Properties.
- For the TCP/IP Port setting, click Permit All.
- Restart the computer.
Now all TCP ports, including port 389 should be open.
Hope this post helps!
Related post: Fix The Active Directory Domain Services is currently unavailable
How to enable Active Directory Users and Computers?
To enable or install Active Directory Users and Computers in Windows 11/10, do the following:
- From the Start menu, select Settings > Apps.
- Click the hyperlink on the right side labeled Manage Optional Features and then click the button to Add feature.
- Select RSAT: Active Directory Domain Services and Lightweight Directory Tools.
- Click Install.
What are the common issues in Active Directory?
Top 8 Active Directory performance problems includes the following:
- Active Directory Replication Issues.
- User Account Lockouts.
- Group Policy Issues.
- DNS / DHCP Issues.
- FSMO Roles.
- Logon Failures.
- Active Directory Database Issues.
- Kerberos Issues.
How do I fix Active Directory problems?
You can try the following simple procedures as part of the process to troubleshoot Active Directory:
- Run diagnostics on domain controllers.
- Test DNS for signs of trouble.
- Run checks on Kerberos.
- Examine the domain controllers.
Why is Active Directory so slow?
If Active Directory is slow to respond, it could be due to a number of reasons, including DNS misconfiguration, NIC binding issue, server performance issue, AV scanning causing the delay, AD database corruption, third-party applications installed on the server, etc.
Read next: Free Microsoft Active Directory Alternative software.