The main security measure on any operating system is the privileges. This means that the execution of any process or simply a program can be done at various stages. Mostly, this decision is taken care of by the operating system itself because it is the supreme authority to do so. But sometimes, running additional scripts or programs requires higher privileges. This is because these programs need access to system files and APIs that are embedded into the operating system and solely the higher authority in the privileges hierarchy to have access to. This is usually the Administrator. Similarly, users often have an issue running the PowerShell scripts as an administrator. Because this is a whole lot big procedure, so, we will be adding an option Run as Administrator to the PS1 File Context Menu.
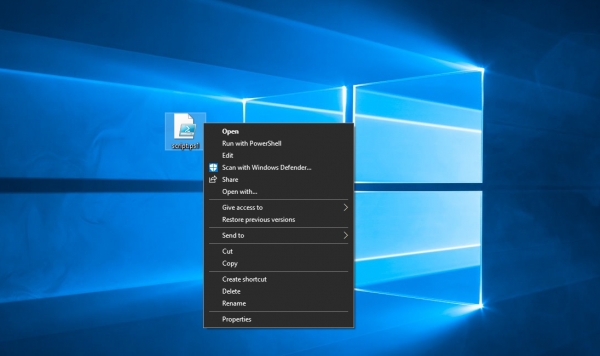
Add Run as Administrator to PS1 File Context Menu
Please create a system restore point before commencing. Having done this, start by opening Registry Editor. To do this, search for regedit in Cortana Search Box or hit WINKEY + R button combo to launch Run and type regedit and hit Enter.
Now navigate to the following path,
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Microsoft.PowerShellScript.1\shell
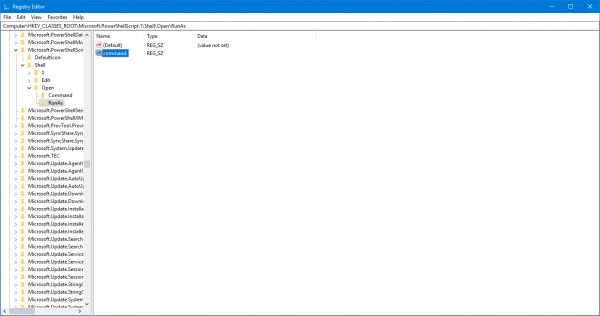
Now, right-click on left side panel. Hover and Select New > Key.
Now rename it to RunAs.
Under it, create a new String by right-clicking on the right side panel and clicking on String.
Name that new string at HasLUAShield. Select Yes to any UAC or User Account Control prompts.
Under the Run key, create another key and name it command.
Inside it, you will find a default subkey named as Default.
Right-click and modify it and sets it’s Value Data to this,
powershell.exe "-Command" "if((Get-ExecutionPolicy ) -ne 'AllSigned') { Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope Process Bypass }; & '%1'"
Finally, Reboot your computer.
Now after it boots, check if you can run any PowerShell script with Administrator privileges from the right-click context menu.
How to undo all these changes
In order to undo these changes, navigate to the following path,
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Microsoft.PowerShellScript.1\shell
Now, delete the subkey named as RunAs.
Reboot your computer.
Use our readymade files
Alternatively, you can just use the Add Run As Administrator PS.reg file that we created for your use and skip all the instructions above. Double click on it to run it. Now, in order to Merge it, hit Yes for all the prompts that you get including the UAC prompt. Reboot your computer.
To undo the changes, double-click on the Remove Run As Administrator PS.reg file and reboot the changes.
You can download the files from our servers by clicking here.
Leave a Reply