Windows Services Manager (services.msc) allows you to create and manage long-running executable applications that run in their own Windows sessions. Windows services can start without user intervention and it may continue to run long after the user has logged off. The services will automatically start when the user boots the system and the services will run long until the system shuts down. By default, the Windows Services Manager is not present in the Control Panel. In this post, we will show you how to add or remove Services.msc on the Control Panel in Windows 11/10.

Add Services.msc to Control Panel in Windows 11/10
To add Services.msc to the Control Panel in Windows 11/10, you need to use the Registry Editor. Since this is a registry operation, it is recommended that you back up the registry or create a system restore point as necessary precautionary measures.
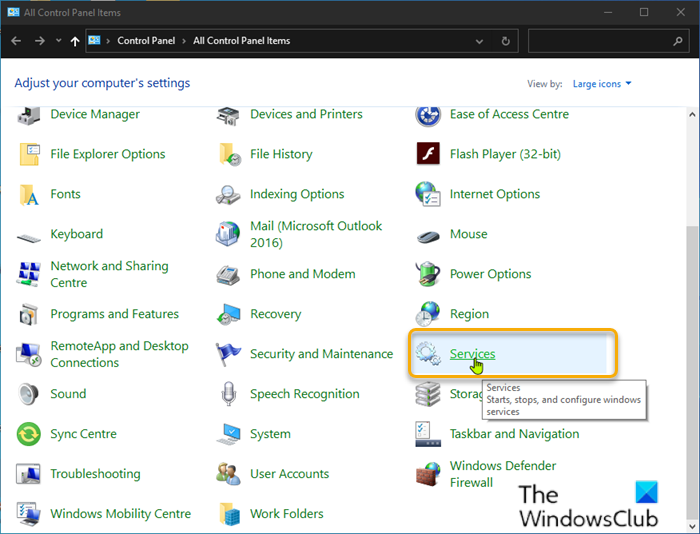
To add Services to Control Panel in Windows 11/10, do the following:
Press Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
In the Run dialog box, type notepad and hit Enter to open Notepad.
Copy and paste the syntax below into the text editor.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{0f51e197-1c99-4c39-9c76-a8db4f79baa9}]
@="Services"
"InfoTip"="Starts, stops, and configure windows services"
"System.ControlPanel.Category"="5"
"System.ControlPanel.EnableInSafeMode"="3"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{0f51e197-1c99-4c39-9c76-a8db4f79baa9}\DefaultIcon]
@="%WinDir%\\System32\\filemgmt.dll,-236"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{0f51e197-1c99-4c39-9c76-a8db4f79baa9}\Shell]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{0f51e197-1c99-4c39-9c76-a8db4f79baa9}\Shell\Open]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{0f51e197-1c99-4c39-9c76-a8db4f79baa9}\Shell\Open\command]
@="mmc.exe services.msc"
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\ControlPanel\NameSpace\{0f51e197-1c99-4c39-9c76-a8db4f79baa9}]
@="Services"

Now, click the File option from the menu and select Save As button.
Choose a location (preferably desktop) where you want to save the file.
Enter a name with .reg extension (eg; Add-Services-To-ControlPanel.reg).
Choose All Files from the Save as type drop-down list.
Double-click the saved .reg file to merge it.
If prompted, click on Run > Yes (UAC) > Yes > OK to approve the merge.
You can now delete the .reg file if you like.
Remove Services.msc from the Control Panel
To remove Services from Control Panel in Windows 11/10, do the following:
Open Notepad.
Copy and paste the syntax below into the text editor.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
?[-HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{0f51e197-1c99-4c39-9c76-a8db4f79baa9}]
?[- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\ControlPanel\NameSpace\{0f51e197-1c99-4c39-9c76-a8db4f79baa9}]
Now, click the File option from the menu and select Save As button.
Choose a location (preferably desktop) where you want to save the file.
Enter a name with .reg extension (eg; Remove-Services-To-ControlPanel.reg).
Choose All Files from the Save as type drop-down list.
Double-click the saved .reg file to merge it.
If prompted, click on Run > Yes (UAC) > Yes > OK to approve the merge.
You can now delete the .reg file if you like.
That’s it on how to add or remove Services.msc on Control Panel in Windows 11/10!
How to enable services.msc in Windows 11?
Services.msc is a command in Windows 11/10 computers that is used to launch the Services Manager app. You can type this command in the Run command box or Command Prompt. After typing this command, hit Enter. This will launch the Services Manager app on your system. Now, you can manage services.
How do I remove unwanted services in Windows?
In Windows 11/10, there are two types of services, Microsoft Services and third-party Services. You cannot remove Microsoft Services because they are a part of the operating system. However, the third-party Services can be removed. Third-party services are associated with their respective programs. When you uninstall the third-party program, the services associated with that program are also removed automatically.
Read next: How to enable God Mode in Windows.
Leave a Reply