We all know that Windows 11/10 comes with multiple sign-in options available. This is possible due to the presence of various Credential Providers in the operating system. In earlier versions of Windows such as Windows XP, Windows Vista, etc., the password credential provider was the only option. After Windows 8, there were some new additions to the credential providers family – and now we have many members in it.
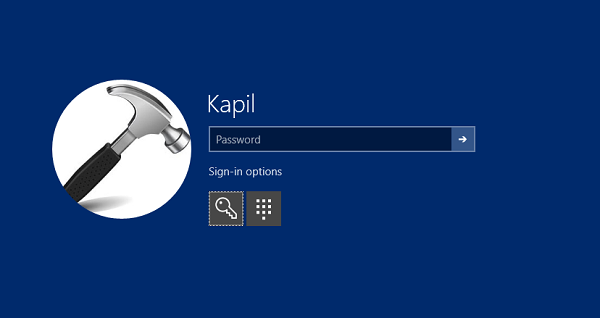
The above-shown screen illustrates the importance of credential providers. Here you can see two sign-in options available to the user. Now he can select either of them. If you minutely observe this login screen, you’ll find that the Password sign-in icon is selected by default, when you would have to click the Sign-in options link. This is because the password sign-in provider is the default credential provider here.
In this article, we’ll show you how to assign a default credential provider to user accounts in Windows 11/10. You may need to sign in as an administrator to follow these steps.
Assign default Credential Provider in Windows 11/10
While the default in Windows OS is the Password Credential Provider, administrators or developers can change this to a different one if needed, such as a custom provider for biometric authentication or third-party security solutions. This involves modifying the registry or group policies on a Windows 11/10 PC.
1. Press the Windows Key + R combination, type regedit in the Run dialog box, and hit Enter to open the Registry Editor.
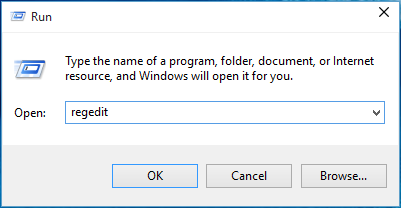
2. Navigate here:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Authentication\Credential Providers
The list of registered credential providers and their GUIDs can be found here.
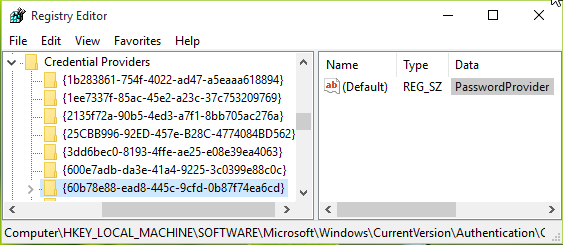
3. In the above-shown window, expand the Credential Providers key and you’ll see some long-named sub-keys. These long sub-keys with their name as CLSID, correspond to a specific credential provider. You’ve to highlight these sub-keys, one by one, and in the corresponding right pane, check out the Data for (Default) registry string. This will help you to identify which CLSID is for which provider. In this way, pick the default credential provider’s CLSID and note down it.
4. Now press the Windows Key + R combination, type gpedit.msc in the Run dialog box, and hit Enter to open the Local Group Policy Editor.
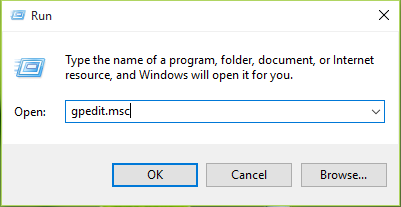
5. In the Local Group Policy Editor window, go to:
Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Logon
6. In the right pane of the above-shown window, look for the policy setting named Assign a default credential provider. The policy is Not Configured by default. Double-click on it to get this window:
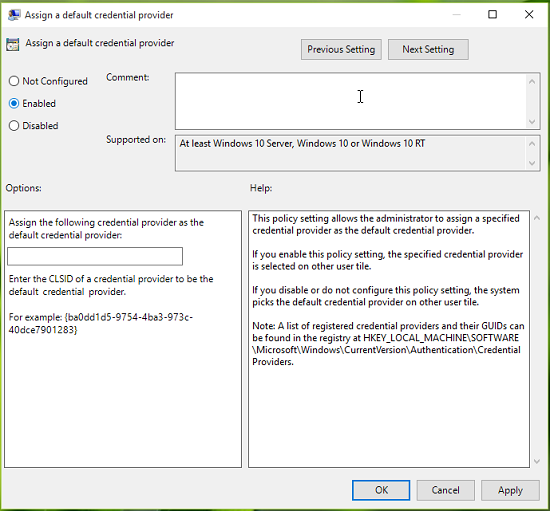
This policy setting allows the administrator to assign a specified credential provider as the default credential provider. If you enable this policy setting, the specified credential provider is selected on other user tile. If you disable or do not configure this policy setting, the system picks the default credential provider on other user tile.
7. Finally, set the policy to Enabled state, and in the Assign the following credential provider as the default credential provider input box, type the CLSID we noted down in step 3.
Click Apply followed by OK. You can close the Group Policy Editor and reboot to make changes effective.
I hope you find the article useful!
Read: Custom credential providers fail to load on Windows.
What is the default credential provider?
The default Credential Provider refers to the Password Provider in Windows 11/10. It is responsible for handling the traditional password-based authentication users encounter when logging into their computers. Microsoft offers several other built-in credential providers to handle various authentication methods and user interactions, such as PIN, smartcard, and Windows Hello (Fingerprint, Face, and Iris recognition), as well as custom credential providers developed by third-party vendors for specific or enhanced authentication solutions.
How do I manage my credentials in Windows 11?
You may use the built-in Credential Manager to manage your credential in Windows 11. It securely encrypts and stores your login credentials for different websites, network connections, and applications and provides a centralized platform to view, add, edit, and delete saved credentials. You can also use your Microsoft account to manage passwords and sign-in methods across various Microsoft services and devices.
Read Next: CredentialUIBroker.exe Remote Desktop error in Windows.
I thought this would help simplify users logging into Windows 10 on a domain but it doesn’t. I did copy the GUID from the Password Policy credential provider, and restarted. On this test laptop I have here it still does not show any fields under “Other User”. You have to click Local or Domain account” in the lower left corner and then you can type your username and password to get on.
The GPO in the domain is already set to not show last user name and requires username and password to log on after accepting an AUP message. It seems Windows 10 has mixed issues with this.
Is there a way to achieve the same on Windows 8? We need to set our own credential as the default one for “Other User” tile if it’s used for previous logon. The “Other User” tile cannot “remember” what’s the credential it used last time, and local user/domain user tiles work fine in this scenario.