A new technology that is slowly picking up in the online world is Blockchain technology. It is basically a distributed ledger technology that keeps a record of transaction data and online assets. Blockchain can be either private or public. An example of a widely popular public blockchain is ‘Bitcoin’. Business establishments mainly invest in private blockchains that are used for keeping a record of transaction data in virtual environments (Cloud), accessible only to a defined or known network. Processes carried out within this infrastructure/network are tamper-proof.

What is Blockchain technology
To put it very simply, Blockchain technology is a distributed database that is used to manage & maintain a growing list of data blocks, using a P2P network collectively. These data blocks may be situated in different locations and not connected to the same Processor. A database is a collection of records. A distributed database is one that may be located in different locations and not be attached to a common Processor – but it may be located in the same or different physical locations and dispersed over a computer network. In a Blockchain, once a piece of data is recorded, it cannot normally be edited or changed.
Building this infrastructure, however, requires expertise in back-end cloud-computing capacity which Microsoft offers as BaaS or Blockchain as a Service. Giants like IBM too, offer this service but under a different name – IBM Blockchain.
In the case of Microsoft, the back-end infrastructure on Microsoft Azure is capable of meeting all the business needs. An added advantage, it offers- interoperability with other blockchains. Companies of any size benefit from the collaborative economy with its Azure Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) program.
Read: What is Hashgraph? How is it different from Blockchain?
This video gives you a basic visual introduction to SHA256 Hash and the concept behind a Blockchain.
Microsoft Azure’s Blockchain Strategy
At its core, a blockchain is a data structure used to create a digital transaction ledger. This ledger does not rest with a single provider but shared among a distributed network of computers and is completely secure. How? It uses cryptography to create transactions that are impervious to fraud. Moreover, Blockchain value is directly linked to the organizations that participate in them.
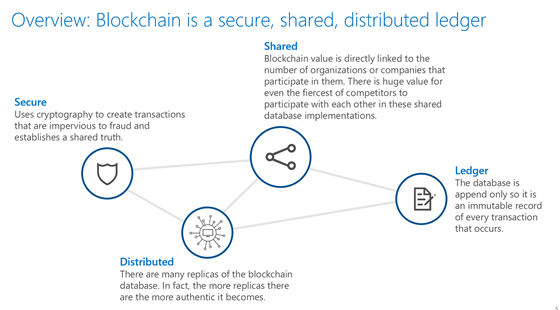
The blockchain uses a distributed ledger to track transactions. It’s a write-only database used in accounting. The distributed ledger creates the same copy of data across all participating nodes. A node is a person, thing or entity that has decided to take part in the Blockchain.
If you don’t know this technology was initially designed to power Bitcoin. Participants in the blockchain can verify the transaction if it is valid and then write it to the ledger. Once this is done, transactions are then connected within a chain of blocks. All the transactions are grouped together in blocks. These blocks represent the order of transactions.
When these blocks are linked to previous blocks, it represents a chain of blocks hence, originally known as Blockchains.
The transaction can then track how the ownership changes. Transactions within the same blocks are considered to occur at the same time.
Read: What are Cryptocurrencies?
Traditional ledgers are centralized. Some person owns it. Blockchain safely distributes it across multiple parties. This negates the need for middlemen that makes it probably, one of the best innovations of a blockchain. Also, the technology helps in maintaining the multiple replicas of the file chain system. So, multiple copies of the ledger are available. Changes made to one ledger cannot be effected to other unless accepted.
The process of decentralization as highlighted above has multiple benefits. One, it eliminates intermediaries. This helps industries to redefine their business models. Secondly, it reduces fraud by making the network highly secure and transparent. All this makes it difficult to change the historical records.
Finally, it increases speed and efficiency and also revenue and savings. Having said that, if there’s no central authority, how does one create an encryption algorithm that ensures no manipulation occurs. Well, Blockchain solves all these problems and many others by replacing central authority with cryptography.
Its solution is based on a simple logic – develop an electronic payment system that completely relies on cryptographic proof instead of trust that allows two parties to transact directly with each other without the need of a trusted third party. Microsoft Azure BaaS is just based on the same solution. This breakthrough is, however, a culmination of 6 steps,
- New transactions are broadcast to the bitcoin network.
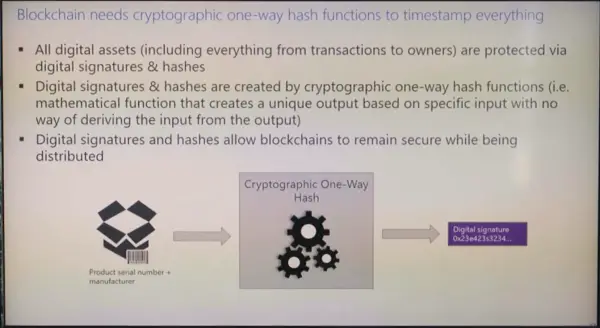
- Each participant collects new transactions into a block and timestamps them. (this is also known as hash )
- Each node works on finding a difficult proof of work.
- When a participant finds proof of work, it broadcasts the block to all nodes. The first individual who successfully manages to find the proof wins the right to write the block to the permanent chain and also gets rewarded for his work later.
- The participants in the node can accept the block only if all the transactions in it are valid and not already spent. This, like in normal cases helps in developing a consensus (also the name given to the algorithm) and prevents participants from cheating.
- Finally, participants express their acceptance of the block by working on creating the next block in the chain, using the hash of the accepted block as the previous hash.
All the digital assets you create remain protected via digital signatures and hashes. This, in turn, is created via a one-way hash function – a mathematical function that creates a unique output based on specific input with no way of deriving the input from the output.
In this way, Microsoft plans to grow the blockchain marketplace ecosystem with our partners & customers and develop key Azure blockchain middleware as a service.
Blockchain Ecosystem – Blockchain 2.0 and Smart Contracts
Originally, Blockchain was advertised as a simple ledger that could record transactions in sequence. Later, it was realized that the Blockchain Ecosystem could have more applications in domains other than transacting payments. Thus, evolved the idea of Blockchain 2.0 and Smart Contracts.
Blockchain 2.0 expands the power of the ledger to include other utilities like agreements, proposals, documents, codes, and more. Basically, this includes an additional logic a.k.a. code, through ‘Smart Contracts’.
Smart Contracts contain a code and execute various terms written or explicitly mentioned in a contract. Similar to normal contracts, these ‘Smart Contracts’ are based on reaching agreed-upon conditions. These Smart Contracts are stored in Blockchain 2.0 distributed ledger. Contracts can be as simple as recording a loan or making payments or as complex as ‘Swaps’.
How Blockchain 2.0 is different from Blockchain 1.0
Blockchain 1.0 was primarily a Bitcoin blockchain, whereas Blockchain 2.0 has many different blockchains such as Ethereum, Corda, and Hyperledger. This is not the end. There are many others in the loop and in different stages of development.
Blockchain 2.0 also marks a change in its functioning, i.e., it moves from simple transactions to multiple transactions. Previously, we had mentioned blockchains could be public or private. Blockchain 1.0 was limited to the public only. Blockchain 2.0 expands its reach and includes consortium, domain-specific apart from the public and private.

The benefits that are associated with Blockchain 2.0. First, Blockchain 1.0 always remained open and distributed. This is not the case with blockchain 2.0. Secondly, it solves many regulatory and privacy needs, can handle more complex needs and is not locked into one vendor. Apart from these, Blockchain 2.0 overcomes some of the existing blockchain issues such as speed and computational cost.
How Microsoft intends to develop Blockchain Ecosystem
Microsoft is implementing a three-part strategy for this:
- Build and learn from key partner-driven POCs built on top of various Blockchain technologies
- Grow the blockchain marketplace ecosystem & artifacts together with our partners & customers
- Develop key Azure blockchain middleware services to ensure the infrastructure is enterprise-ready
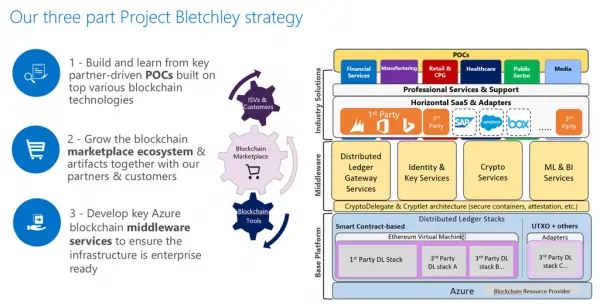
Microsoft also plans to extend blockchain by creating both new middleware as well as secure ‘scriptlets, a project it names as Project Bletchley for extending blockchain. In addition to this, the company is attempting to connect to many different ledgers and existing external and internal services to enable a robust blockchain ecosystem for the enterprise since it realizes the technology has some great applications.
The potential applications of Blockchain technology include:
- Financial – Trading, dealing, equities, Derivatives Trading, Compliance Reporting, etc
- Media – Digital Rights Management, Game Monetisation, Art Authentication, Purchase and Usage monitoring and more
- Computer Science – Micronization of work (pay for algorithms, tweets), Expanse of Marketplace, Disbursement of Work
- Medical – DNA Sequencing, Personalized medicine
- Government – Voting, vehicle Registration, Licensing, and identification.
So, depending on your industry, there are lots of solutions available. Most of the customers embracing Blockchain technology are new to Microsoft Azure service. You need to sign up for an Azure account to use the blockchain technology offered by Microsoft.
Blockchain as a Service is available within Microsoft Azure DevTest Labs. So, you need to use Azure Dev test lab to use Blockchain as a service. Azure DevTest Labs is a service that helps developers and testers quickly create environments in Azure while minimizing waste and controlling cost. To get started, simply search for the keyword “Blockchain” and you will see Blockchain Labs in the list of available resources.
Read: What is Web3 technology?
Select Create and fill in the details of your lab, and you should be good to go. Do not forget to select your open-source stacks and third-party offerings before proceeding further. Now, to set up Blockchain as a Service hosted on Azure, navigate to portal.azure.com and enter the credentials for your Microsoft Azure account. Once authenticated, you will be redirected to the Azure portal. Thereafter, follow the steps outlined in this post in sequence to create a new DevTest Lab Instance, create a new virtual machine, and acquire a personal access token from GitHub.
Leave a Reply