In this post, we will see what causes the Blue Screen of Death and how to fix it on a Windows 11/10 PC. Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), often referred to as a ‘Blue Screen‘ or a ‘Stop Error‘ screen is a screen that a Windows device displays when it encounters a fatal error from which it cannot recover safely. When such an error occurs, the system halts all its operations to prevent data corruption or further damage to the hardware.

As a Windows user, it is likely that you have, at some point, encountered the Blue Screen of Death. When it occurs, the entire screen turns blue, and a white text is displayed detailing the error message and technical information about the cause of the crash. The error message often includes a specific error code, such as Stop code: 0xc00002e3.
While it can be disruptive and alarming to see a BSOD, it is essentially a safety mechanism designed to protect your system from further damage in case of a critical error.
Blue Screen of Death Causes and Solutions
Various hardware, software, or driver-related issues can trigger the Blue Screen of Death. Identifying the specific cause often requires analyzing the error message displayed on the screen, examining system logs, and performing diagnostic tests on hardware components. Once the cause is determined, appropriate steps can be taken to troubleshoot the underlying issue and prevent future BSOD errors.
Here are the main causes of a Blue Screen of Death:
1] Hardware Issues
A] Faulty RAM
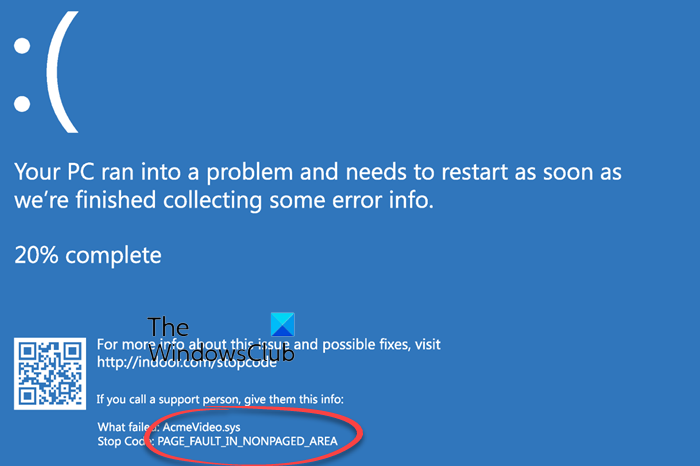
RAM stores data that needs to be used quickly while a computer runs. If there’s a fault in the RAM module, it may corrupt this data, leading to system instability or crashes, including BSODs. Faulty RAM can also produce random bit flips or may not respond properly to memory allocation requests, triggering a BSOD.
A few BSOD error codes that can be caused by faulty RAM are:
- MEMORY_MANAGEMENT (0x0000001A)
- PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED_AREA (0x00000050)
- IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL (0x0000000A).
To check for faulty RAM, you may run the Windows built-in Memory Diagnostic tool or use third-party tools such as Memtest86+. Once identified, you need to replace the faulty RAM to fix the BSOD issue.
TIP: If you want the error code, you may have to force Windows to display Stop Error details.
B] Failing or Corrupted hard drive or SDD
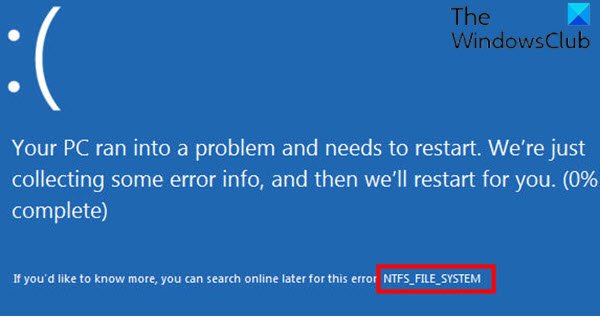
HDDs and SSDs can develop bad sectors over time due to dust intrusion, physical damage, or wear and tear. Attempts to read or write data to bad sectors can cause the system to freeze or become unresponsive. If critical system files are located in these areas, the system may crash, leading to a BSOD. Additionally, if critical system files stored on the HDD or SSD become corrupted, the operating system may fail to boot properly, leading to a BSOD.
A few BSOD error codes that can be caused by issues related to a hard drive are:
To troubleshoot such issues, ensure that all cables connecting the hard drive to the motherboard and power supply are securely connected, use the Windows built-in CHKDSK tool to scan and repair disk errors, and use a disk diagnostic tool to identify any bad sectors. We recommend replacing the hard drive if bad sectors are found.
C] Faulty power supply
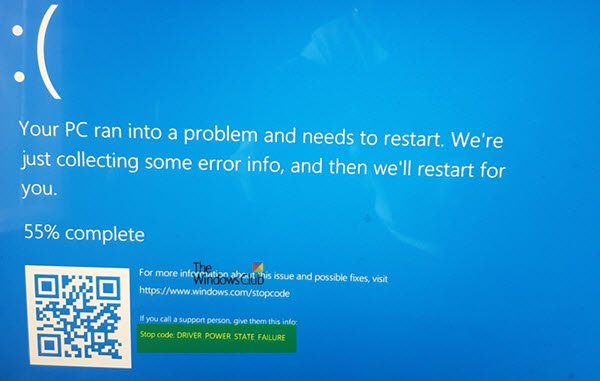
Fluctuations in voltage levels such as sudden spikes or drops caused by a faulty power supply can corrupt critical system data or result in the malfunctioning of hardware components, indirectly contributing to BSOD errors, such as DRIVER_POWER_STATE_FAILURE.
Also, a failing power supply may not provide sufficient power to peripheral devices such as graphics cards or hard drives. This can lead to instability in these devices, resulting in BSODs or system crashes.
Make sure that the power supply is adequately cooled and not obstructed by dust or debris. Check for loose connections or damaged cables between the power supply and other system components. Replace the power supply with a known working unit if you suspect that a faulty power supply is causing BSOD errors.
D] Overheating processor

Modern processors come with a built-in thermal protection mechanism known as thermal throttling. However, it may not work if the processor consistently operates at high temperatures due to heavy workload or inadequate cooling. This can cause instability in the processor’s operation, leading to delays or failures in interrupt handling, memory corruption, and data loss. As a result, critical system processes or drivers fail to execute properly, exacerbating existing hardware or software issues. This can trigger or worsen various types of BSOD errors, such as:
To prevent the processor from overheating, ensure adequate cooling and ventilation in the computer case. Use third-party software to monitor and manage CPU temperatures and adjust overclock settings to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
E] Faulty motherboard components

Faulty or degraded motherboard components such as broken capacitors or corroded PCB traces might corrupt the data during its transmission or storage. If the corrupted data includes critical system files, BSOD errors may occur. Additionally, if the BIOS/UEFI firmware stored on the motherboard gets corrupted or misconfigured, it may fail to initialize hardware components during system boot-up, leading to BSOD errors.
For example, issues with the motherboard’s memory controller or chipset can contribute to memory corruption and trigger the PFN_LIST_CORRUPT (0x0000004E) BSOD error.
To troubleshoot such errors, ensure that your motherboard’s BIOS/UEFI firmware is up-to-date and the motherboard and its components are adequately cooled. Physically inspect the motherboard for any signs of damage and perform diagnostic tests on hardware components to identify any faults, bad sectors, or corruption. If any faults are found, consider replacing the affected components or the entire motherboard if required.
Read: How to fix Blue Screen in Windows 11
2] Software Issues
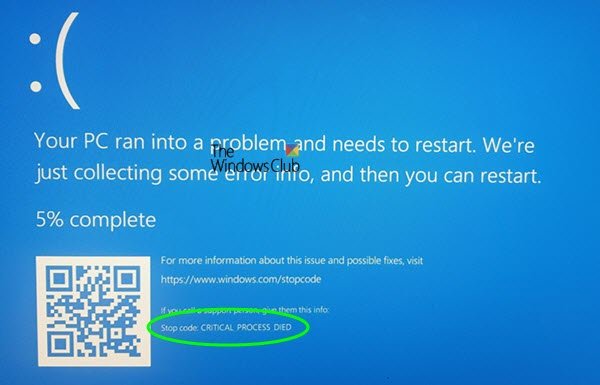
Incompatible or poorly coded third-party software may interfere with critical system processes or other software components, resulting in BSOD errors. Also, corrupted system files, faulty device drivers, and updates to the Windows operating system may sometimes introduce bugs or compatibility issues, leading to error codes 0x000000EF, 0x0000009F, and other BSOD errors.
Always keep your system and device drivers up-to-date. If the BSOD started occurring after a recent change, such as software installations, driver updates, or hardware upgrades, consider rolling back the change. Run System File Checker (SFC) to scan and repair corrupted system files.
3] Driver Issues
Incompatible device drivers cannot work with a specific hardware configuration or operating system version. As a result, they may conflict with system components, causing instability or crashes. Faulty drivers may attempt to overwrite critical system data structures in the Windows kernel or access invalid memory addresses, further leading to a BSOD. Here are some BSODs caused by driver issues.
When a faulty or incompatible device driver causes a BSOD, Windows generates a crash dump file that contains information about the error. Analyzing this dump file can help identify the specific driver that caused the crash. Once you’ve identified the problematic driver, you may try updating or rolling back the driver to the previous version. If the BSOD continues to show up, try uninstalling the faulty driver.
This post will show you how to find which Driver is causing the Blue Screen.
4] Malware or Virus Infections
Malicious software can corrupt system files, interfere with drivers, compromise system stability, and cause various issues, including BSOD errors.
Never download and install software from untrusted sources or click on suspicious links or attachments in emails. Regularly scan your system for malware infections. For added security against malware attacks, enable built-in security features such as Windows Defender or Firewall.
Read: How to open and read Small Memory Dump (DMP) files
5] Other Factors
Other factors such as overclocking hardware components beyond their rated specifications and physical damage to components such as the motherboard, CPU, or RAM can cause BSOD errors.
To troubleshoot BSODs caused by overclocking, revert overclocked settings to default in BIOS. For hardware damage, replace or repair the affected component.
I hope this helps.
Troubleshoot: Common Windows Blue Screen Errors
Can RAM cause Blue Screen?
Yes, faulty RAM modules or incorrect memory configurations can lead to system instability, data corruption, and other memory-related errors. When the system attempts to read or write data in a faulty RAM, a critical system error may occur, leading to a Blue Screen of Death.
Read: Purple, Brown, Yellow, Orange, Red Screen of Death explained.
Can Overheating cause Blue Screen?
Yes, when GPU, CPU, or other system components exceed their safe operating temperatures, they become unstable or fail to function normally. Overheating compromises system stability and leads to crashes or blue screen errors. Regular cleaning of cooling components and ensuring proper airflow can help prevent overheating-induced BSODs.
Can GPU cause Blue Screen?
Yes. Issues such as outdated or incompatible drivers, faulty hardware, overheating, or overclocking can lead to instability in the Graphics Processing Unit. When a malfunctioning GPU encounters errors or fails to handle graphics processing tasks properly, it can trigger system crashes and blue screen errors.
Can a bad SSD cause Blue Screen?
Yes, a bad SSD can cause blue screen errors, typically storage access errors. Issues such as NAND flash wear-out, physical damage, and firmware corruption can cause system instability or problems accessing or writing data to the SSD. As a result, critical system errors or blue screen crashes may occur.
Can PSU cause Blue Screen?
Yes, a faulty power supply unit can cause blue screens of death. When the PSU fails to deliver adequate power to system components, or when power fluctuations, voltage drops, or overloading of the PSU occurs, it can result in system instability, triggering BSODs and crashes.
Can CPU cause Blue Screen?
CPU issues such as hardware faults, overheating, or incompatibility with other components can lead to system instability or crashes. Critical system errors can occur when a malfunctioning CPU fails to execute processing instructions correctly, further triggering blue screens of death.
Can Dust cause Blue Screen?
Dust buildup can block airflow to crucial system components, such as CPU or GPU, leading to overheating issues. As a result, hardware malfunctions or data corruption may occur, triggering system instability and potentially causing blue screen errors. Regular computer system cleaning and maintenance can help mitigate the risk of duct-induced blue screens.
Can a bad laptop battery cause Blue Screen?
Yes, a faulty or failing laptop battery can induce power-related issues that cause blue-screen errors. When the laptop battery is not able to supply consistent power to the system or when there are sudden power fluctuations, system errors can occur, leading to BSOD errors.
Can BIOS cause Blue Screen?
Yes, BIOS issues can contribute to blue-screen errors during system boot or operation. Incorrect BIOS settings, incompatible configurations, and outdated firmware can trigger blue screen crashes. Furthermore, a failed BIOS update or incorrect flashing procedure might leave the machine unbootable, resulting in blue screen issues.
Read Next: Recover Data after a Blue Screen of Death in Windows.
Leave a Reply