There are three levels of Processor Cache viz; L1, L2, and L3. The more of L2 and L3 cache your system has, the faster will the data be fetched, the faster will the program be executed and the more accurate will be the output. In this post, we will show you how to check Processor Cache Memory Size in Windows 11/10.
Compared to the main memory (RAM), the Processor Cache provides faster access to information, resulting in faster processing of programs and data on a computer – also it should be noted that Processor Cache Memory is more expensive than RAM.
Check Processor Cache Memory Size in Windows 11/10
The following are the three types of Processor Cache Memory:
- L1 cache: This is the primary cache embedded in the processor chip. This type of Cache is fast, but it offers very limited storage capacity. Processors, nowadays, no longer come with the L1 cache.
- L2 cache: This secondary cache can either be embedded on the processor chip or made available on its own separate chip with a high-speed bus connecting it to the CPU.
- L3 cache: This type of processor cache is designed to serve as a backup for L1 and L2 caches. While L3 Cache is slower compared to L1 and L2 Caches, it is faster than RAM and offers significant boost to the performance of L1, L2 Cache.
We can check Processor Cache size in Windows 10 in 4 quick and easy ways. We’ll explore this topic under the methods outlined below in this section as follows.
1] Via Command Prompt
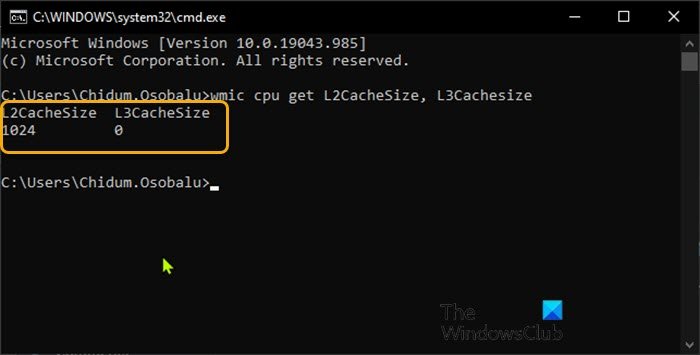
To check Processor Cache size via Command Prompt in Windows 10, do the following:
- Press Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box, type cmd and hit Enter to open Command Prompt.
- In the command prompt window, type the command below and hit Enter.
wmic cpu get L2CacheSize, L3Cachesize
This command when executed will return the corresponding size of L2 and L3 caches in a message format. As you can see from the image above, the processor has sizes 1024KB and 0KB for L2 and L3 caches respectively.
- Exit CMD prompt when you’re done reviewing.
2] Via Task Manager
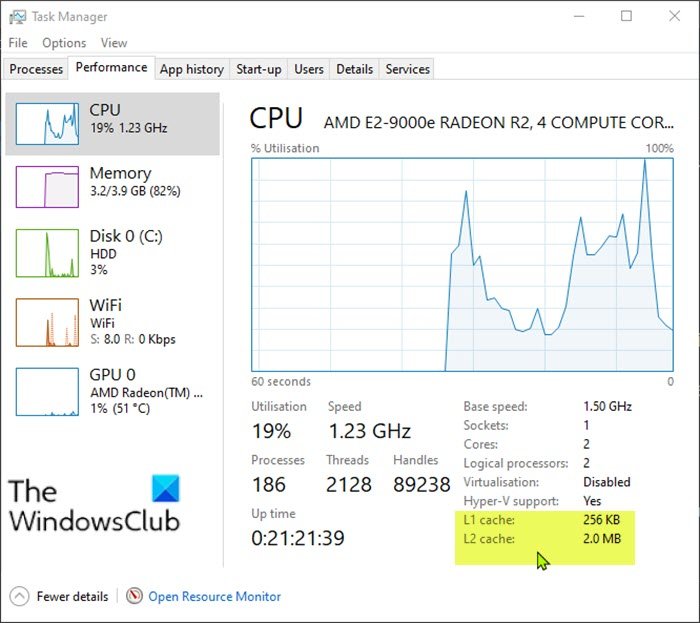
To check Processor Cache size via Task Manager in Windows 10, do the following:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys to open Task Manager. If Task Manager opens in compact mode, click or tap on More details.
- In Task Manager, click the Performance tab.
- Click on CPU in the left pane.
- In the right-pane, you will see L1, L2 and L3 Cache sizes listed at the bottom.
- Exit Task Manager when done reviewing.
Read: How to check RAM speed on Windows 11.
3] Via Web Search
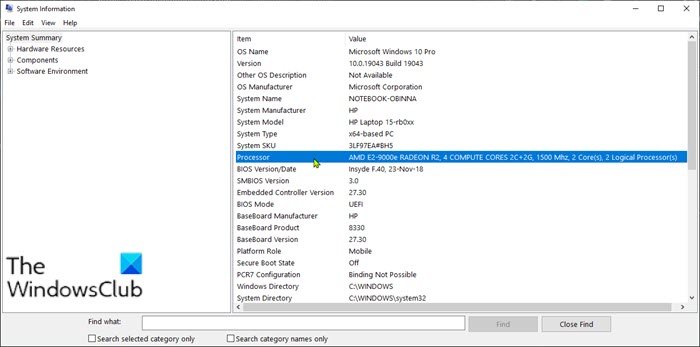
To check Processor Cache size via Task Manager in Windows 10, do the following:
- Press Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box, type msinfo32 and hit Enter to open System Information.
- In the window that opens, on the right pane, you will find an item named Processor. You can find the model of your processor just next to it.
Alternatively, you can get the processor information on the About page in Settings app.
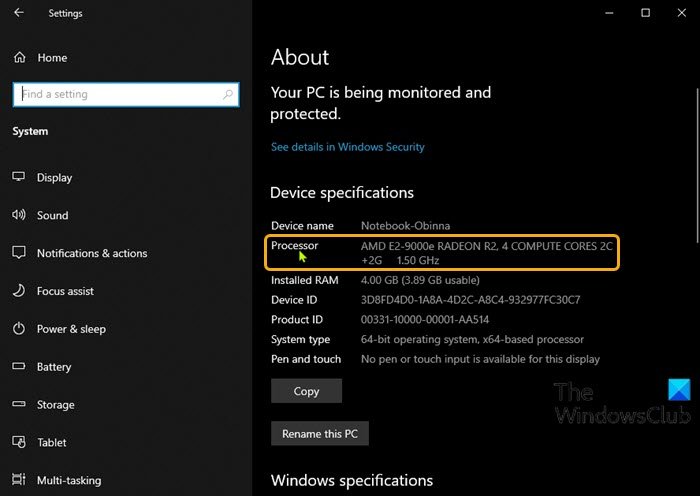
- Press the Windows key + I to open Settings.
- Click System.
- Scroll down on the left pane, and click About.
Tip: You can also launch the About page by pressing Windows key + X, and then tap Y on the keyboard.
- Now, open up your web browser and search for the details of your processor model.
4] Using third-party app
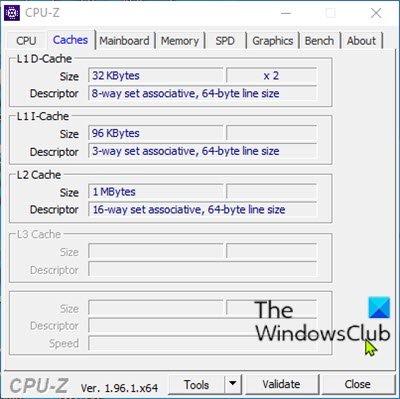
Here you can use a nifty app called CPU-Z. The app provides you with the information on the processor, motherboard and RAM.
To check Processor Cache size using CPU-Z in Windows 10, do the following:
- Download CPU-Z.
- Install and then open the app.
- Click the Cache tab. Here, you can get more detailed info about the cache in your system.
- Esit the app when done reviewing.
That’s it on the 4 ways to check Processor Cache Memory Size in Windows 10!
Leave a Reply