Microsoft has made Windows 11 available for all users. Windows 10 users can upgrade their computers to Windows 11 for free, provided their computers meet the hardware requirements. One of these hardware requirements is that your system’s firmware should be capable of Secure Boot. Therefore, if you are going to upgrade your Windows 10 operating system to Windows 11, you should enable Secure Boot. Some users are complaining that their computer does not boot after enabling the Secure Boot. In this article, we will provide some solutions that may help you fix this problem.

Secure Boot is a feature of UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) that ensures that a device uses the startup software developed only by OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer). By doing so, Secure Boot protects the device from being taken control of by malware or other unauthorized software during the boot process. When we start our computer, the firmware validates the signature of the boot software. If the signatures are found valid or legit, the firmware gives control to the OS.
If we compare UEFI with the Legacy BIOS, the Secure Boot feature is not available in the latter one. Another factor on which the Secure Boot depends is the drive partition type. Some of you may probably know that there are two types of formats used to define drive partitions, namely, MBR and GPT. Both MBR and GPT contain information about the beginning and the end of the partitions on a physical disk. This information lets the operating system know which partition on a hard disk is bootable.
If we compare MBR with GPT, the former one has some limitations, like:
- MBR works with disks of size up to 2 TB.
- MBR supports only a maximum of four primary partitions.
Windows computer won’t boot after enabling Secure Boot
Is your Windows computer not booting after enabling Secure Boot? If yes, the following solutions may help you fix it:
- Check the file format used to define your drive partition
- Disconnect external hard disks and other storage devices
- Try to boot your computer from bootx64.efi file or bootia32.efi file manually
Now since you cannot boot Windows normally to the desktop, you may have to try and boot in Safe Mode or into the Advanced Startup options screen to be able to carry out the fixes. You will need to make use of the Command Prompt. For some strange reason if you can boot in Safe Mode but cannot access the Advanced Startup Options screen, when in Safe Mode, you may use the Command Prompt to boot Windows directly to the Advanced Startup Settings screen.
1] Check the file format used to define your drive partition
If your computer does not boot after enabling Secure Boot mode, the first thing that you should do is check your drive is partitioned by using which format, GPT or MBR. You can check this in the Disk Management app. The following steps will help you with that:
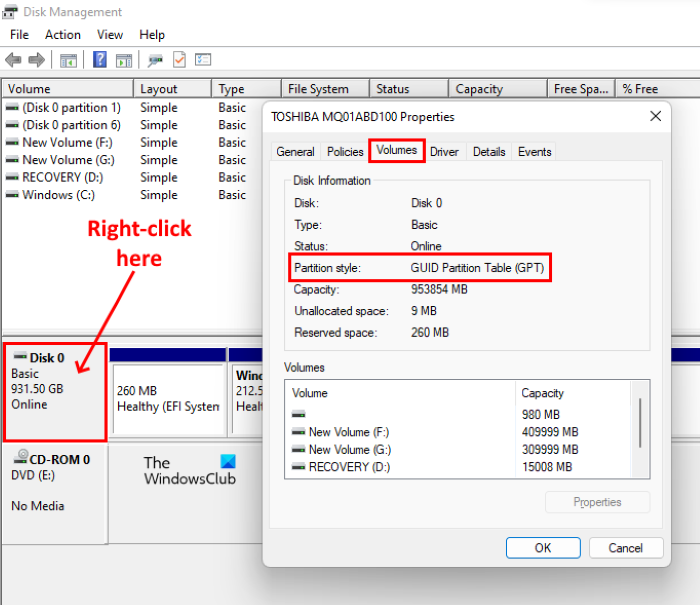
- Right-click on the Start Menu and select Disk Management.
- Now, right-click on your hard disk and select Properties. Remember, you have to open the properties of your hard disk and not of the disk partitions.
- In the Properties window, click on the Volumes tab. There, you will see the partition style of your hard disk.
If the partition style of your hard disk is MBR, you should convert it into GPT. After converting MBR into GPT, boot your PC with Secure Boot enabled. It should work.
2] Disconnect external hard disks and other storage devices
If you have connected external hard disks or any other storage devices to your computer, disconnect them and then boot your PC. See if it helps.
3] Try to boot your computer from bootx64.efi file or bootia32.efi file manually
Some users have reported that the issue was fixed after manually booting their computer from bootx64.efi file. The files with the EFI extension are the boot loaders. In most cases, these files are located on a specific system partition. This system partition does not have any drive letter and is usually hidden. If you have a UEFI based system, you may find the EFI file located at the following location under the Windows Boot Manager:
\EFI\boot\bootx64.efi
\EFI\boot\bootia32.efi
If you have a 64-bit version of Windows OS, you will see the bootx64.efi file on your firmware. On the other hand, 32-bit Windows OS users will find bootia32.efi file on their firmware.
Try to boot your computer manually from bootx64.efi file or bootia32.efi file and see if it works. To boot your computer manually from EFI files, you have to enter into the boot options in BIOS. There, you will find all the boot options available on your computer. The key to enter into the boot options menu is different for different computer brands. Therefore, you have to refer to your user manual. See whether bootx64.efi or bootia32.efi file is available there. If yes, boot your computer from that file.
Related read: Windows PC will not boot up or start.
What happens if I turn on Secure Boot?
Secure Boot is a security standard that makes sure your computer uses only the software from the OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturers) by validating the digital signatures at the time of startup. This avoids the risk of being hijacked by malware or other unauthorized software at the time of startup. Hence, by turning on the Secure Boot, you will increase your device security.
How do I know if my Secure Boot is disabled?
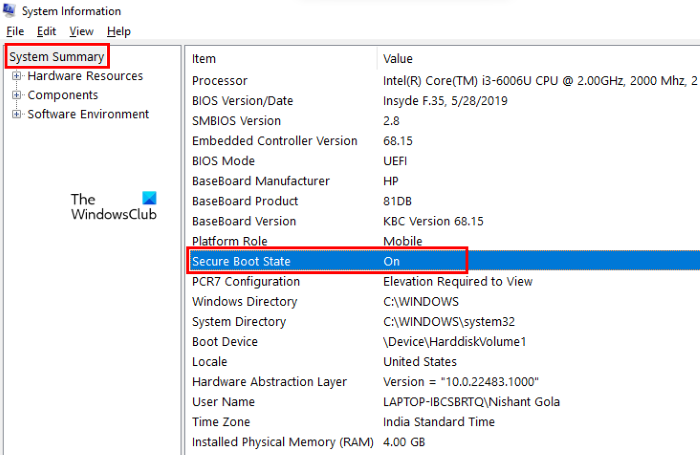
The following instructions will help you know if Secure Boot is disabled on your system:
- Click on the Windows 11/10 Search and type System Information.
- Select the System Information tool from the search results.
- Select the System Summary from the left side.
- Take your cursor on the right pane and scroll down to find Secure Boot State. If its Value is off, Secure Boot is disabled and vice-versa.
Why won’t my PC boot after enabling Secure Boot?
There are numerous things involved in this error. For example, if the file format used to define your drive partition doesn’t match, you can encounter this problem. For your information, this is the most common reason since people often get conflicts between GPT and MBR. On the other hand, you can get the same issue when an external hard drive is connected to your PC as well.
Hope this helps.
Read next: The value is protected by Secure Boot policy and cannot be modified or deleted.
Leave a Reply