In an Enterprise environment, hard drive failure can affect several users simultaneously who are trying to access their files on the drive and this can be a big blow for the entire stream of operation that is supposed to run uninterrupted in an organization. With time, everything ages and the same goes for that hard drive as well. Sooner or later, the hardware wears out and your data is lost.
Backing up the data on a hard drive or having a secure way to access it, if and when things go south is crucial, given the importance of the data. In this post, we will talk about Hard Drive Mirroring – real-time data replication of original disk volumes onto a separate secondary volume, which is an immensely popular backup solution, and learn how to create a Mirrored Volume for a Hard Drive in Windows 10.
What is Hard Drive Mirroring
Hard drives are more prone to failures than other computer components. Drive Mirroring is a technique for overcoming such hard drive failures by automatically creating multiple copies of the data stored on the drive in question.
This way you have the data always at your disposal – even in a case of unfortunate drive failures. Hard Drive Mirroring sits at RAID-1 on the standard RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) levels, where an exact and reliable copy of data is kept on two or more disks. Once mirroring is active, files between these drives are automatically kept in sync so that you always have a real-time replica of your data.
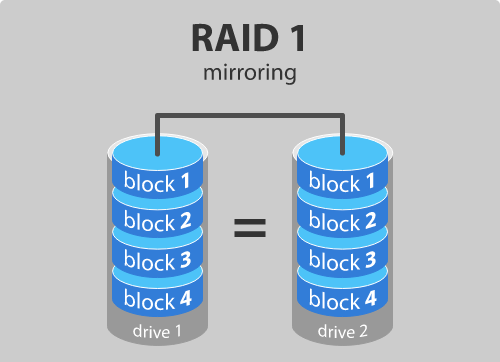
Image Credit: prepressure.com
Create a Mirrored Volume in Windows 11/10
In order to proceed with creating a mirrored drive, you’d need two distinct physical drives. The targeted mirror drive should have equal or larger size than the original drive and it should represent unallocated disk space. If it comprises of any data, you can right click and select Delete Volume – assuming that you have Disk Management tool open – to wipe any data present and mark it unallocated. Once you’re ready with the pre-requisites, follow the below steps to create a mirrored volume:
1. Hit Windows Key + R on your keyboard to launch Run tool. Input diskmgmt.msc in here and hit Enter. This should open up Disk Management tool.
2. In Disk Management tool window, right-click on the empty unallocated disk and select New Mirrored Volume.
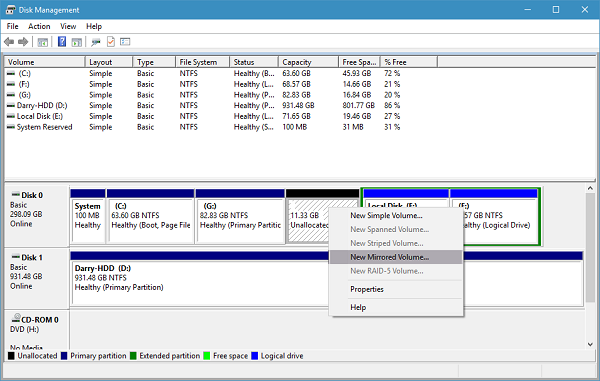
3. In the next window, select the disk from available ones and add it on the right. Select the amount of space you want to dedicate to the mirrored volume and click Next.
4. In the next window, you can assign a drive letter of your choice or leave it with default settings. Once you’ve done this, click Next.
5. Next, you’ll be asked if you want to format the disk before usage. Select Format this volume with the following settings option, select the File system as NTFS, Allocate unit size as Default, and assign a volume label of your choice for the disk. Also, check the Perform a quick format option. Click Next and Finish the process.
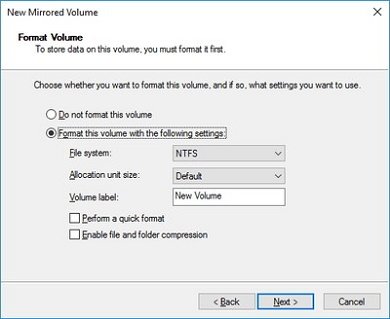
If your drive is set to Basic Disk, you’d need to convert it to Dynamic Disk before adding it as mirrored drive, otherwise, the option for setting it up as mirror grays out.
Read: Fix Mirrored Volume missing after reinstalling Windows.
Pros & Cons of Drive Mirroring
- Random disk read operations on mirrored volumes are more efficient than on a single volume, and recovery from a disk failure is very rapid.
- Disk write operations are less efficient and Mirrored volumes are the least efficient in terms of space utilization.
Mirroring is often confused as a backup strategy. Let me clarify—it is not! The main principle behind mirroring is different from that of backup. While backup focuses on full data protection and accessibility reliability in case of any drive failure event, mirroring is all about keeping your system fully operational with real-time data replication, which comes in handy in case of drive failure.
So, you see, when and if the original hard drive fails to perform read operation, the system automatically fetches the data from mirrored drive and you’d not have to waste your time. Mirroring helps recover data much faster while impacting the system performance least.