You must have heard about these terms – Partition, Volume, and Logical Drive. And, if you wonder what these terms actually mean, then this post will help you throw some light on them. We will help you understand the difference between Partition, Volume and Logical Drive on a Windows 11/10 computer by explaining their meanings and other information related to them in simple words.
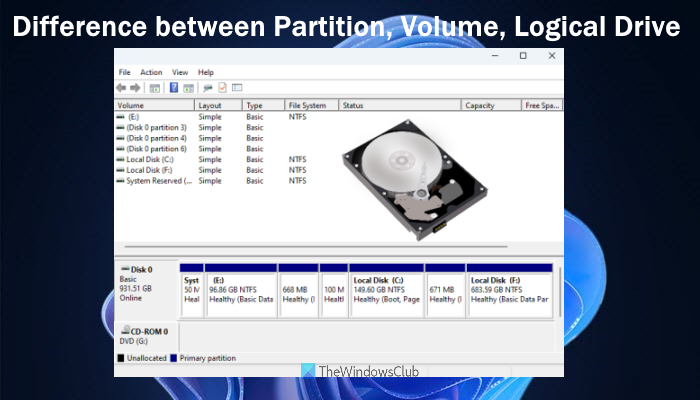
Difference between Partition, Volume, and Logical Drive
All these terms i.e., partition, volume, and logical drive are data storage units. But there are differences that we have tried to cover in this post below. Let’s learn about them one by one.
What is a Partition in a Windows computer?
A physical hard disk (say HDD) can be divided into different storage units and those storage units are known as partitions. Thus, dividing a hard disk drive into different parts is known as partitions for that particular hard disk.
For example, if you have a 1TB hard disk drive, and you divide it into 4 parts (say 250GB each), those parts are called partitions. You can create four primary partitions or three primary partitions and one extended partition. Here is what that means:
- Primary partitions are those where you can install Windows and put other data. For example, if you have installed Windows 11/10 on a C drive, then the C drive is a primary partition
- Extended partition works as a container that you can use to create multiple logical partitions
- Logical partitions are those where you can create folders, add your media files, and other personal data you want.
You can easily create new, resize, and extend partitions on a Windows 11/10 computer using the built-in Disk Management tool or some free third-party Disk and Partition Manager software.
What is a Volume on a Windows computer?
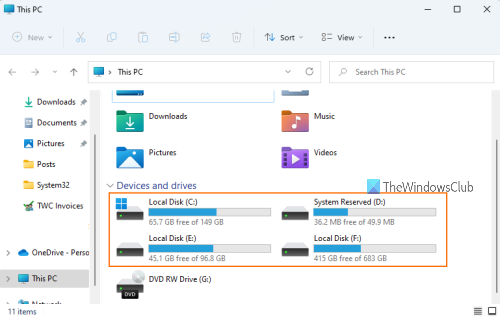
Unless you format a partition, a volume (or logical volume) cannot be created. And, until a volume is not created, you won’t be able to install Windows and add your data. Thus, once you format a partition for a file system (say NTFS file system for Windows), it becomes a volume.
In other words, once you format a partition to create a hard drive and assign a letter (say D, E, etc.) to that drive, it is known as volume. You can also extend, shrink, or delete a volume.
Related: How to re-partition a hard drive on Windows without erasing data.
There are 5 logical volume types which are as follows:
- Simple Volume: This type of volume can have single or multiple regions on a hard disk. You can create a simple volume for the entire hard disk or set the volume size of your choice (not exceeding the total size of the hard disk)
- Spanned Volume: In this volume type, the unallocated space of multiple hard disks is combined or merged into a single logical volume. So, let’s say you have 5GB of unallocated space on one hard disk and 15GB of unallocated space on another, then you can create a 20GB spanned volume
- Striped Volume: This volume type is created by combining the free space available on two or more hard disks in one logical volume using RAID-0 technology. Such volume types are not fault-tolerance. That means, if a disk that contains the strip data fails, then the entire striped volume is failed
- RAID-5 Volume: Also known as striped with parity volume (created with free space available in three or more hard disks) offers fault tolerance. If a part of a hard disk fails and the data present in that portion is gone, then the same data can be re-created from the remaining data
- Mirrored Volume: As the name indicates, this type of volume stores an exact copy of the same data on two physical disks. This is also a fault tolerance volume. Even if one physical disk fails or corrupts, the mirrored data present on the second disk can be used by the system.
What is a Logical Drive?
A logical drive (or logical volume) is a drive space created logically on top of a physical hard disk. Once you format a partition and assign a letter to it like D, E, etc., (as explained above), it becomes a logical drive that can be used to store files, folders, and other personal data. When you open File Explorer on a Windows 11/10 computer, the logical partitions (such as Local Disk (D:), Local Disk (E:), etc.) present under This PC section are examples of logical drives. So, basically, logical drive and volume are the same terms.
Hope this helps.
What is the difference between a Partition and a Logical drive?
Partition (when it comes to a hard disk drive) is a part of a hard disk that you create for installing Windows OS and storing your personal data. There is a primary partition that you can use for installing an operating system. Apart from that, there is an extended partition that you can further divide into multiple logical partitions for storing your data (images, audio-video files, documents, etc.). On the other hand, a logical drive is created when you format a partition and assign a drive letter (including the file system) to it.
Should I use Primary or Logical partition?
Although there is no difference between primary and logical partition in order to store data, it is idle to create a primary partition where you can install Windows and boot your computer. Primary partitions are mainly used for installing an operating system. On the other hand, logical partitions are used for storing your personal data.
Read next: Difference between NTFS, FAT32, FAT, and exFAT File Systems.