In Windows, the humble defragmentation tool has evolved to carry on other roles, apart from its disk defragmentation role. While in Windows 7 and Windows Vista, the Disk Defragmenter tool did improve, it continued only to defragment the fragmented files and data. In Windows 11/10, however, it optimizes your storage in Thinly Provisioned environments – using Storage Optimizer. The Defragment tool is now called Defragment and Optimize Tool in Windows 11/10/8 and includes the Storage Optimizer.
Defragment and Optimize Tool in Windows 11/10
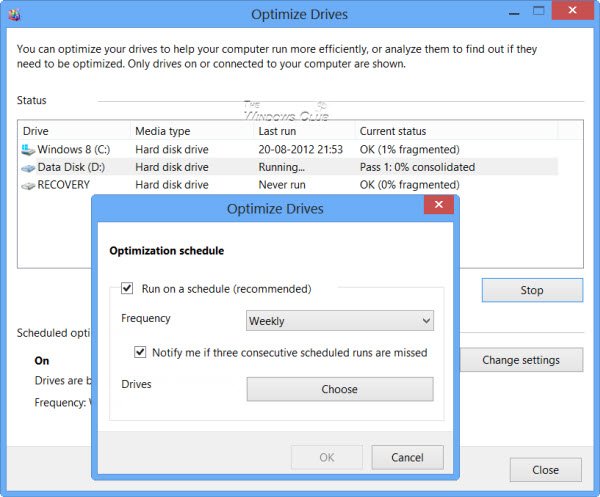
What is Storage Optimizer in Windows 11/10
The Storage Optimizer in Windows 11/10 now takes care of maintenance activities like compacting data and complying with file system allocation to enable capacity reclamation on thinly provisioned disks. If your storage platform supports it, Storage Optimizer will consolidate lightly used ‘slabs’ of storage and release those freed storage ‘slabs’ back to your storage pool for use by other Spaces or LUNs. It does so periodically, without any user intervention from the user, and completes the task provided the task is not interrupted by the user.
In Windows 8, when the Storage Optimizer detects that the volume is mounted on an SSD – it sends a complete set of TRIM hints for the entire volume again – this is done at an idle time and helps to allow for SSDs that were unable to clean up earlier – a chance to react to these hints and cleanup and optimizer for the best performance.
Read: How to use Disk Defragmenter or Optimize Drives Tool in Windows 11
What is TRIM
TRIM is a storage level hint, NTFS sends for some normal inline operations such as “deletefile.” NTFS will send such trim hints when files are deleted or moved from those regions; SSDs consume these hints to perform a cleanup in the background called as ‘reclaim’ that helps them get ready for next writes. The SSD may choose to perform the optimization immediately, store the information for later optimization or throw away the hint completely and not use it for optimization since it does not have time to perform this optimization immediately.
In short, TRIM, introduced in Windows 7, is a way of communicating with SSDs about sectors that are not needed anymore. You can learn more about it at TechNet.
Read: How to check, disable, and enable TRIM support.
Solid State Drives and Windows 11/10
Solid State Drives or SSDs are flash memory based block-erased devices. This means that when data is written to the SSD, it cannot be over-written in place and must be written elsewhere until the block can be garbage collected – ie they can be written to at a byte level but need to erased at a block level. Since the SSD has no internal mechanism for determining that certain blocks are removed and others are needed. The only time the SSD can mark a sector ‘dirty’ is when it is over-written. In other cases, such as when a file is deleted, the SSD retains these sectors because the deletion is performed as a MFT change only, and not as an operation to all the sectors of the file.
In Windows 7, Microsoft had turned off defragmentation for Solid State Disks. In Windows 11/10/8, however, since the tool has changed into a general disk optimization tool, you will see it enabled by default for SSDs too.
In this scenario, where an SSD is present, the tool sends ‘TRIM’ hints for the entire volume. A traditional defrag is not performed on SSDs, says Microsoft.
Read here about the Storage Diagnostic Tool in Windows 11/10.
Does defragging speed up the computer?
If you are using an HDD, i.e., a storage device that came with a mechanical head and disks, then yes, you can speed up the computer using defragmentation. During fragmentation, Windows rearranges data, so they are easy to fetch, and there is the least movement of the mechanical head. In turn, this method increases the life of the HDD.
How often should you defrag?
Usually, one month is enough. However, if the volume of data copying and moving is high, you can defrag in 15 or 20 days. This will ensure faster data fetch.