Users of Windows 11/10/8 may have noticed that Disk Error Checking is a bit different from the earlier versions of Windows. Checking your hard disk, every once in a while for errors – usually caused due to improper or sudden shutdowns, corrupted software, metadata corruption, etc., – in Windows 7 and earlier is always a good practice as this can help solve some computer problems and improve the performance of your Windows computer.
Disk Error Checking in Windows 11/10
Microsoft has redesigned chkdsk utility – the tool for detecting and fixing disk corruption. Microsoft introduced a file system called ReFS, which does not require an offline chkdsk to repair corruptions – as it follows a different model for resiliency and hence does not need to run the traditional chkdsk utility.
The disk is periodically checked for file system errors, bad sectors, lost clusters, etc., during Automatic Maintenance and you now no longer need to really go and run it. In fact, Windows now even exposes the state of the file system and disk via the Action Center or under the Drive properties in File Explorer. If potential errors are found, you will be informed about it. You can continue to use the computer while the scan is carried out in the background. If errors are found, you may be prompted via a notification to restart your computer.
Read: How to cancel ChkDsk in Windows.
Windows found errors on this drive that need to be repaired
You may sometimes see a message – Windows found errors on this drive that need to be repaired. If you see it, you may want to run a scan manually. Earlier, you had to schedule Disk Error Checking for the system drive and for drives that had files or processes or folders opened. In Windows 11/10, error checking starts right away, even on the system drive – and it no longer needs to be scheduled at start-up. Only if some errors are found will you have to restart to let Windows 11/10 fix the errors.
How to run CHKDSK in Windows 11/10
To begin the scan, right-click on the Drive which you wish to check and select Properties. Next, click on Tools tab and under Error-checking, click on the Check button. This option will check the drive for file system errors.
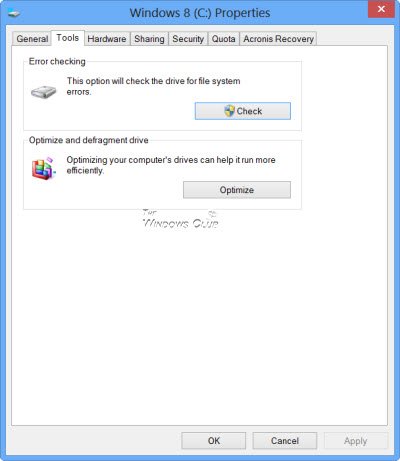
If the system detects that there are errors, you will be asked to check the disk. If no errors are found, you will see a message – You don’t need to scan this drive. You can, nevertheless, choose to check the drive. Click on Scan drive to do so.
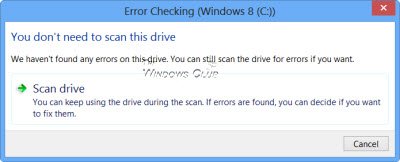
The scanning starts. I found that the process ran quite fast and the scanning was over in less than 5 minutes.
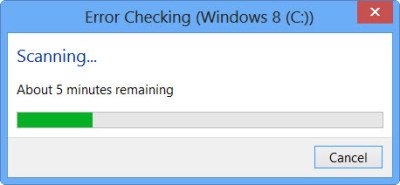
On completion, Windows will display a message. If no errors are found it will say so.
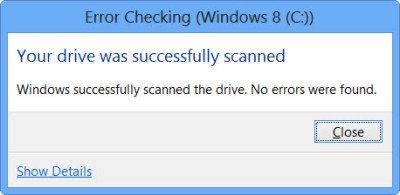
If errors are found, you will see the following message:
Restart your computer to repair the file system. You can restart right away or schedule the error fixing on the next restart.
When I clicked on Show Details, the Event Viewer sprang to life, showing me the relevant log.
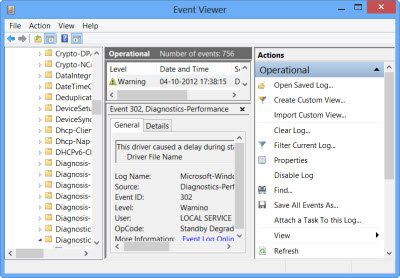
In Windows 11/10, Microsoft has made the Disk Error detection and correction of file system errors less intrusive so that users can carry on working on their computers without worrying about such error.
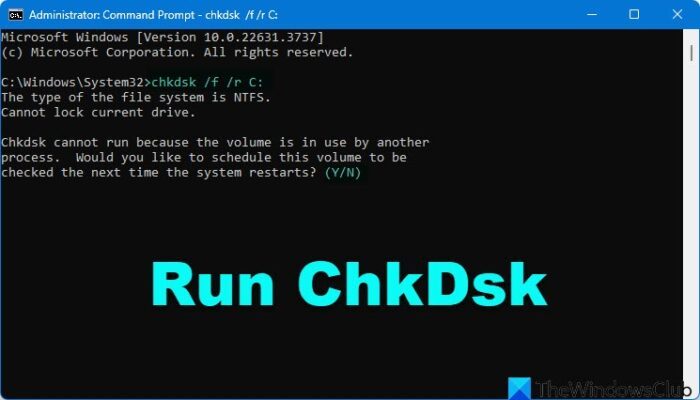
To run Check Disk on your System Drive (C), using the command line, type the following and hit Enter:
chkdsk /r C:
If required, restart your computer.
Note:
- ChkDsk /f scans for and attempts to repair errors in the file system.
- ChkDsk /r includes /f, but it also scans the entire disk surface for physical errors and attempts to repair them as well.
Read next: Command Line ChkDsk Options, Switches, Parameters in Windows
Will chkdsk fix corrupt files?
No, CHKDSK will not fix corrupt or damaged files. It only checks if the file system is in good condition and that the data on the disk is in a consistent and safe state. If files are damaged, the CHKDSK attempts to separate the damaged files and save the remnants in .chk file format.
These links may also interest you:
This new Error Correction tool in Windows 8 sounds great. This kind of utility would have been extremely useful with the Vista and 7 OS’s.
this tool is their in windows from the version of DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 and in Windows 8
windows 2000 & windows millennium edition too :)
Yes it was, but “In Windows 8, Microsoft has redesigned chkdsk utility”
Mybad, but the shit doesnt work :-)
I have here a 3 months old lenovo pc which doesent run (freeze even after restoring factory default). Windows 8 says disk ok, but lenovo has provided a system cmd promt. When running chkdsk /r it finds bad clusters.
Try the /f parameter. More at https://www.thewindowsclub.com/command-line-check-disk-windows-7
/r implies /f
great tool!
Visit http://www.lahabrahome.com to search for homes
or for a FREE market analysis of your current homes value!
Carlos Amador
BRE 01881631
It worked perfectly, thanks so much
Great article, well done.
i just did the checking of error in my hard disk …but during pluging this did not show progessing after 8 hr ..
but as i uplug my extrnal harddisk …it shows the progress in 10 or 15 % …
this is not working ….what can i do now…it may be crrupted due to sudden shut down of system ….plz help me
what happens when check disc deletes files, I need to get them back where do they go where do I look
Disk Error Checking will not delete files. If the disk was already corrupted, then you may have lost those files. But you may try some of these to recover files: https://www.thewindowsclub.com/7-free-data-recovery-software-to-recover-deleted-files-in-windows-7
In Windows 10 I’ve found the following to be better:
chkdsk C: /scan /offlinescanandfix /R
/R is probably redundant… but it gets me what I want.
This schedules the scan to be done with file system offline at the next reboot.
I don’t see any process to chkdisk for windows 10.
“In Windows 8, Microsoft introduced a file system called ReFS, which does not require an offline chkdsk to repair corruptions – as it follows a different model for resiliency and hence does not need to run the traditional chkdsk utility.”
Windows 8 and 10 still use NTFS by default. You can right click your drive and see what it says for “File system.”
But self-healing NTFS was introduced in Windows Vista and it fixes file system errors on the fly and no longer requires offline chkdsk.
what to do when the repair fails and shows a dialog to rescan and repair again but nothing happens
Why my disk utilization is 100 on Windows 10 always?
Try https://www.thewindowsclub.com/fix-100-disk-usage-windows-10
How thorough is the Windows 8 CHKDSK?
Does it write data to the all the sectors and make sure that they read back properly?
Hello TWC,
I uninstalled my AVG antivirus and my system was working fine. Even restarted it and it was okay. I connected it to my projector this morning and it was okay. after a while, i was getting a black page with a white line. I use easy worship. I went on to restart the system since restarting the projector did not change a thing and ever since its been stuck on the welcome page. I use a hp pavilion 15 note book. Windows 8. 750 hd, 4 g ram amd… kindly advise accordingly please
Need more information… Look in the Task manager, what’s the top process using your disk?
it wont run a scan or a repair im in dire need for help pls