You don’t need to have 3rd Party Partition Manager Software to achieve resize partitions in Windows 11 or Windows 10. The operating system includes a very useful Disk Management Tool that lets you resize partitions and more. In this post we will see how to resize a partition in Windows, using the built-in Disk Management Tool.
To use the Disk Management Tool, follow these steps: Click Start > Right-click on Computer > Select Manage.
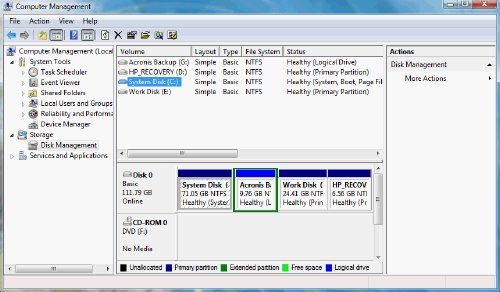
In the left pane, under Storage category, click on Disk Management. Now select and right-click on the partition you wish to modify. In the context menu, you will see options to Extend, Shrink, or Delete the partition. Select the option you want.
You cannot merge partitions in Windows with this utility. If your second partition is empty, you can delete it and then extend the first partition to use the freed-up space. Also, note that you can extend only to the right; if you want to extend the partition to the left, you may have to use a third-party tool. You can read more here about the Disk Management Tool.
Sometimes one or more options may be grayed out and thus unavailable. If this happens, it could mean that such a step may not be physically possible.
Using the DISKPART and FSUTIL command-line tools for Windows 10, you can resize a partition even if disk management fails.
Resize a Partition in even if Disk Management fails
It may happen that the Disk Management tool may fail to complete an operation successfully. Should you wish to continue, nevertheless, please first backup your important data should anything go wrong. You may have to use diskpart.exe.
Diskpart Utility
The Diskpart utility can do everything that the Disk Management console can do, and more! It’s invaluable for scriptwriters or anyone who simply prefers working at a command prompt.
Among several other things, you can use Diskpart to do the following:
- Convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk
- Convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk.
- Create a partition at an explicit disk offset.
- Delete missing dynamic disks.
Enter diskpart in the Start search bar and hit Enter. A ‘command prompt’ like window will open. Type list disk and hit Enter. This will show you a list of all your hard disks. Now type select disk <disk number> to select the disk you want to work with.
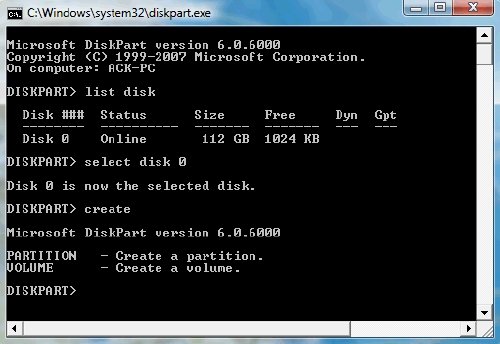
If you want to create a partition. Type ‘create‘ and a set of options will appear. Choose one, and type create <new option>.
There are two types of partitions you can create: Primary and Extended. Only a Primary partition can be made bootable, so if you are planning to install an OS, you will have to select this option. For backup purposes, you may opt for Extended partitions.
Now, to see which number is associated with the volume you are planning to work with, type: list volume.
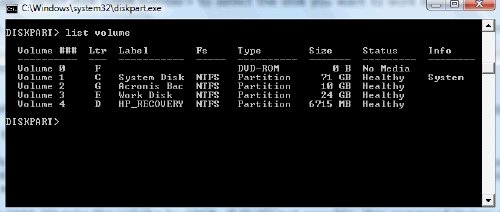
You will get a list. To select one type: select volume <number> (or select partition <number> as the case may be).
Depending on what you want to do to the partition you can select any of the following commands. Typing help and hitting Enter enumerates the options.
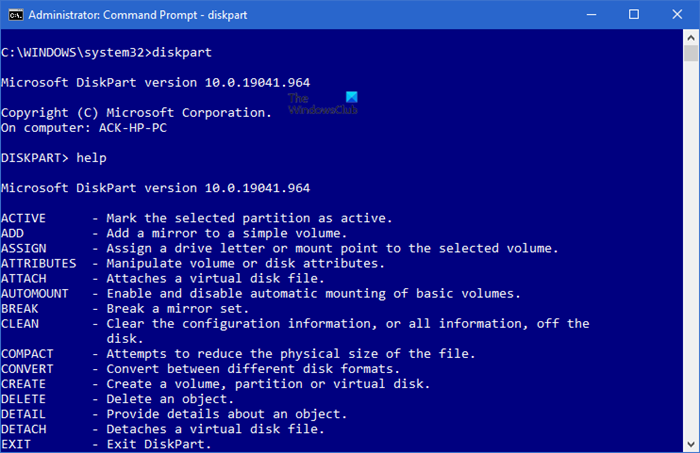
Example :
To extend size by 5GB, type Extend size=5000 To shrink the volume by minimum 1GB, up to a maximum of 5 GB, type, Shrink desired=5000 minimum=1000 You can even delete a partition by typing, Delete Partition and hitting Enter.
Fsutil Utility
Windows also includes an additional command-line tool for file, system, and disk management, called Fsutil. This utility helps you to change the short name of a file, find files by SID’s (Security Identifier) and perform other complex tasks.
FSUtil and Diskpart are powerful, but not for inexperienced Windows user. So do be careful, please.
There is not enough space available on the disk(s) to complete this operation
What do you do if you get the message – There is not enough space available on the disk(s) to complete this operation?
Most new computers with OEM Windows pre-installs come with 4 partitions. Hard disks configured as basic disks are limited to 4 primary partitions or 3 primary partitions and 1 extended partition and multiple logical drives. And as such, if you try to shrink the OS partition, you may find that you cannot create a 5th partition due to this limit.
There could be two possible solutions for this issue:
- As the disk pre-configured by OEM may have conflicts with the disk management tool in Windows, you should try some 3rd party tool to re-partition the disk.
- You may try to delete a less important partition created already and merge the space to create a new partition with a proper drive letter.
Deleting the partitions created by the OEM is often impossible due to how the OEMs configure the partitions. Therefore the option then is to extend the operating system partition back to the original size to regain use of the unallocated space. If additional storage is needed, consider adding an external USB hard disk.
Hello , I have C(primary-system),D (primary),E(primary), and f(logical)rive in my system running on Windows 8. My C drive has very less available space.I want to increase the size of C drive. I have 11 gb of unallocated space. When I am making the 11 gb as a new partiton and trying merging thorugh EaseUs Partition tool that doesnt works. Please help me how can i increase my c drive space.
if your unallocated space is contiguous behind the c drive, you can use disk management to extend c drive. if you can’t satisfy the precondition. i suggest another third-party software to extend your c drive.
more detail you may need
http://www.disk-partition.com/resource/resize-system-drive-partition-c.html