Domain Fronting can be used to bypass censorship by ISPs and governments. Hackers can also use Domain Fronting to obtain the information they want from you. What is domain fronting? This article briefly explains domain fronting and lets you decide if it is good or bad by presenting both the advantages and dangers of domain fronting.
What is Domain Fronting?
Domain fronting, in short, is changing the destination of an internet connection midway using encryption. If you want to browse a restricted website, you can use one of the following methods to reach it:
- Proxy
- VPN
- TOR
- Domain Fronting
The problem is that many governments are banning or restricting VPN and TOR traffic on different ISP networks. ISPs have specific orders from such governments to ban one or more website of any nature. Earlier, eight to ten years ago, we could easily use a proxy and reach the restricted website. Technology changed, and now it is easier than ever to detect traffic that is using a proxy. Not only that, but TOR (The Onion Router) can also be cracked now with some military grade techniques. Those two are no more viable methods to access restricted websites.
Thus, we are left with VPN and Domain Fronting. In an attempt to censor and to keep an eye on what its citizens are doing, many countries are banning/restricting VPNs too. They do not want encrypted traffic so that they know what is going on. The ISPs cannot rebel against the government of any country that restricts or bans VPN. They have to oblige.
The last method to access a restricted website is to apply domain fronting. You, as a user, cannot apply domain fronting though. You have to use an app that employs domain fronting. One such app is Telegram, which is a chat app banned by Russia and many other countries.
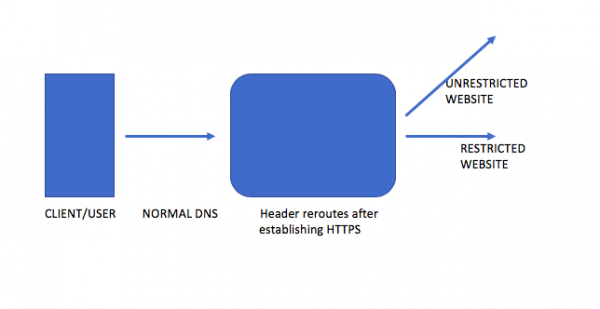
These apps have built-in algorithms that allow users to access restricted websites or websites banned in the particular country where the user is located. This is done by altering the code in the header in the host websites. For invigilators, it generally shows that it is connecting to an innocent website, probably without HTTPS too. In the middle of the handshake between the website and app, the app first establishes an encrypted connection (could be as simple as HTTPS) and then switches route to another website. That website may be banned or restricted.
Thus, it is possible to cheat the invigilators at ISP and government levels by contacting a restricted website while the Internet police think you are connected to some other website when you were communicating with the banned website all the time.
Domain Fronting can be used to circumvent any type of censorship. That’s the good part. The next section talks about the dangers of domain fronting.
Dangers of Domain Fronting
While domain fronting is being used to let users access restricted websites and services, there is a good chance that hackers might use the same technique to mislead users and mine the data they want.
Both the namesake domain and the restricted website (or infected website, in case of hackers) are hosted on the same set of servers. When one tries to connect to the namesake domain, its header sends another GET request that gives it the address of the restricted website. Now, this could be a simply restricted-by-government website or a computer infected by hackers.
Domain fronting can be advantageous or dangerous, depending on who is using it. While mostly private messaging apps were using the technique, Google and Amazon dumped Telegram, saying it violated their Terms and Conditions. Currently, Telegram is looking for another cloud service that would provide them with the ability to domain front.
There are several other cases where the use of domain fronting was genuine—to allow free speech. But it seems that world governments are closing all routes to freedom of expression. In the same breath, domain fronting has its own dangers because if it can replace destination, it may lead you to fake sites, and you won’t ever know.
Does domain fronting still work?
Domain fronting is largely unsupported by major cloud providers like Google and Amazon. However, some smaller CDNs may still allow it. While it’s less common, it’s essential to be cautious, as domain fronting can be misused for malicious activities.
What is the difference between domain fronting and CDN?
Domain fronting disguises the true endpoint of network packets by using a different hostname, often leveraging CDNs. In contrast, a CDN (Content Delivery Network) distributes content across various servers to improve accessibility and load times, without hiding the destination server.
What is the difference between proxy and domain fronting?
Proxy servers route traffic through a single intermediary to bypass censorship, while domain fronting disguises the true destination by using a different hostname in the HTTP request. This technique evades blocks more effectively, as the censor sees only the benign fronting domain, not the real target.
Now read: What is a Cold Boot Attack?