802.11 is a set of IEEE standards that control wireless networking transmission methods. They are used today in the following versions to offer wireless connectivity in different environments (home/business): 802.11b, 802.11a, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac, 802.11ax, and 802.11be.
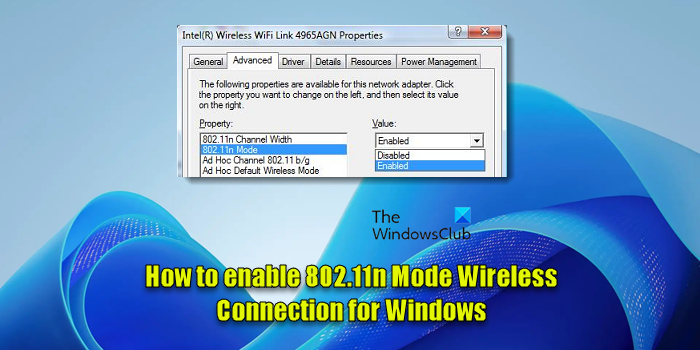
The 802.11n standard uses multiple antennas to increase data rates. The performance of this version is influenced by network setup, interference from other nearby networks, frequency (2.4GHz or 5GHz), and more. If you find it disabled for some reason, here are the steps you can follow to review the recommended settings for 802.11n connectivity and enable it in Windows 11/10 if needed.
Update: After 802.11n, 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) emerged primarily operating in the 5 GHz band, delivering higher speeds and increased capacity. This was followed by 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6), which brought even greater speed, efficiency, and performance, especially in crowded environments, and extended to the 6 GHz band as Wi-Fi 6E. The latest, 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7), promises even higher throughput, lower latency, and better handling of multiple simultaneous connections, further advancing wireless networking capabilities in the Windows environment.
How to install 802.11n driver in Windows 11/10
To enable 802.11n Mode Wireless Connection for Windows 11/10, do the following:
- Open Control Panel
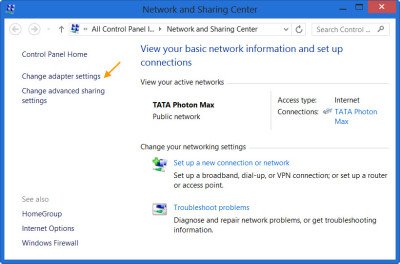
- Choose Open Network and Sharing Center
- Click Change Adapter Settings
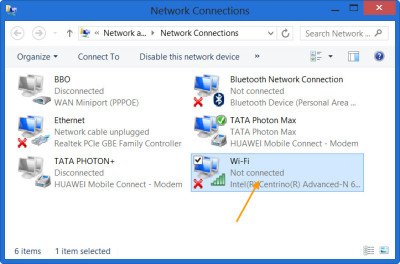
- Right-click the Wi-Fi adapter and select Properties
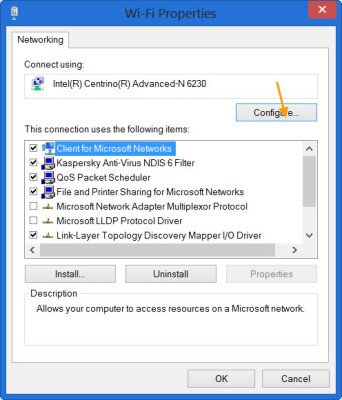
- From Properties page, select Configure
- Switch to Advanced Tab and search for the 802.11n Mode under the Property
- Change its Value to Enabled.
Read on to get a detailed perspective.
For this, we assume a Wireless-N (802.11n) network adapter is installed on the computer.
From the Start search, search for and open Control Panel. Then choose Network and Sharing Center applet.
Next, click ‘Change Adapter Settings’ link.
Then, right-click the Wi-Fi adapter and select the ‘Properties’ button.
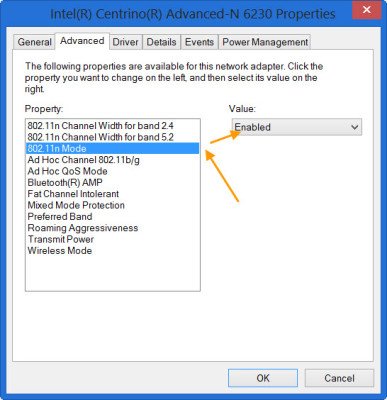
This will open the Properties box. From the ‘Properties’ page that shows up on your screen, select ‘Configure’ option.
Switch to ‘Advanced Tab’ and search for the 802.11n Mode under the Property, select it and change its Value to “Enabled“.
If for some reason, the 802.11n version doesn’t show there, update your driver and firmware.
When done, hit the ‘OK’ button to apply the final changes.
As the last step, establish a re-connection with the WiFi router.
Read: WLAN extensibility module has stopped [Fix].
What is 802.11 n mode in router?
802.11n mode in a router refers to a wireless networking standard that utilizes multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technology to significantly boost data transfer rates, offering theoretical speeds up to 600 Mbps. This mode operates on both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands, allowing for greater flexibility and reduced interference compared to previous standards.
Why is my 802.11n not working?
If 802.11n is not working on your Windows PC, verify that 802.11n mode is enabled on your router (access your router’s settings through a web browser and navigating to the wireless settings section). Also, ensure that 802.11n mode is enabled in the wireless adapter settings on your Windows 11/10 PC and your router’s firmware and wireless adapter’s drivers both are up to date.
Read Next: How to tell if my PC has Wi-Fi 6.
Hi.
Nice and informative blog………………….you can post your comments and suggestion on my blog also….
http://respondindia.com
Rajesh
Join to new experience of social media Deshimukh is here for you. You want to promote your company, you want to know new people you want the new experience???Join to our family…https://www.facebook.com/deshimukh
i already updated my driver and firmware, but this option still shown,