In today’s post, we will detail the steps to enable or disable debug logging of the Netlogon service on Windows 11/10 to monitor or troubleshoot authentication, DC locator, account lockout, or other domain communication-related issues.
Netlogon is a Windows Server process that authenticates users and other services within a domain. Since it is a service and not an application, Netlogon continuously runs in the background unless it is stopped manually or by a runtime error. Netlogon can be stopped or restarted from the command-line terminal.
Netlogon starts running in the background after the Workstation service has started. The Workstation service controls all network connections and shared devices using the Server Message Block protocol, a standard Windows network protocol. In addition to Netlogon, the Workstation service manages the Computer Browser and Remote Desktop Configuration services. This hierarchy of network services ensures reliable communication and security across all nodes on a network.
The Netlogon service focuses specifically on verifying user credentials and other services, while Computer Browser maintains a list of computers on the network and Remote Desktop Configuration manages all remote desktop processes. If Netlogon is stopped, many Windows Server functions will be affected as users can no longer log in to their accounts, and the domain controller will not automatically register Domain Name System records, which contain user login information.
Enable Debug logging for Netlogon service
The procedure to enable or disable debug logging for Netlogon service requires registry modification. So, it’s recommended you back up the registry or create a system restore point as a precautionary measure in case the procedure goes wrong.
The version of Netlogon.dll that has tracing included is installed by default on all currently supported versions of Windows. To enable debug logging, set the debug flag that you want by using Nltest.exe via command prompt or registry.
Enable or disable Debug logging via command prompt
To enable, do the following:
- Launch Command Prompt (Click Start and type cmd, then hit Enter).
- In the command prompt window, copy and paste the command below and hit Enter:
Nltest /DBFlag:2080FFFF
To disable it, do the following:
- Launch Command Prompt (Click Start and type cmd, then hit Enter).
- In the command prompt window, copy and paste the command below and hit Enter:
Nltest /DBFlag:0x0
Enable or disable Debug logging via the Registry
To enable it, do the following:
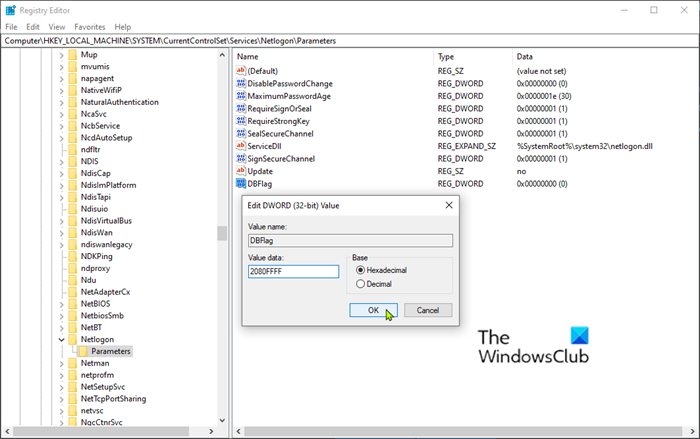
- Launch Registry Editor (press the Windows key and type regedit, then hit Enter).
- Navigate to the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Netlogon\Parameters\DBFlag
If DBFlag exists, delete the Reg_SZ value of the registry entry, create a REG_DWORD value with the same name, and then add the 2080FFFF hexadecimal value.
- Exit the registry editor.
To disable it, do the following:
- Launch Registry Editor.
- Navigate to the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Netlogon\Parameters\DBFlag
- Change the DBFlag data value to 0x0.
- Exit registry editor.
In both cases, it’s typically not necessary to stop and restart the Netlogon service in later recent versions of the operating system to disable Netlogon logging. Netlogon-related activity is logged to:
%windir%\debug\netlogon.log
Verify that no new information is being written to this log in order to determine whether a restart of the Netlogon service is necessary. If you have to restart the service, then open an administrative Command Prompt window and then run the following commands:
net stop netlogon
net start netlogon
That’s it, folks!
I hope you find this post useful.
Leave a Reply