Some Windows users reported that the DNS server could not create zone %1 from registry data. If you open the Event Viewer, you may see Event ID 504 – DNS server could not create zone. In this post, we will discuss this issue and see how it can be resolved.
What is a DNS server zone?
A DNS Server zone is a special space for the Domain Name Space namespace. This area is managed by one or more specific servers and helps keep track of information about names and their addresses, i.e., DNS records for a specific domain or set of domains. There are various types of zones with distinctive features, starting with the Primary zone, Secondary zone, Stub zone, Forward-lookup zone and many more.
Fix Event ID 504, DNS server could not create zone
If the DNS server is not able to create a new DNS Zone, and you see Event ID 504 in the Event Viewer of your Windows computer, execute the solutions mentioned below:
- Recreate the zone
- Check the DNS configuration settings
- Make sure that the DNS client computer can resolve names
Let’s get started with the first solution.
1] Recreate the zone
Often, information for the zone stored in the registry value gets corrupted or is missing some components. This can affect the DNS server and its ability to create DNS Zones. Therefore, we recommend deleting the corrupted ones and replacing them with functional ones. Let us first see how to create a zone using the Server Manager.
- Open the Server Manager by clicking on Start > Administrative Tools > Server Manager on the DNS server.
- Go to the console tree, double-click on Roles, and then on DNS Server.
- Now, double-click on DNS. Expand the DNS server as well as the folder in it.
- Right-click on the zone, and then hit the Delete button. Similarly, right-click the folder and this time select the New Zone option.
Follow all the instructions mentioned on the screen to recreate the zone. If you cannot delete the zone using this method, do the same using the Registry Editor.
It is necessary to carefully make amendments to the Registry entry, as any minor mishap can have a greater impact on the system. Therefore, tread this process with utmost care while doing it, and don’t forget to create a backup of the registry.
- Go to the DNS server, click Start, and go to the Start Search.
- There, type Regedit, hit the Enter button, and navigate to the Console tree.
- There, expand the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\DNS Server\Zones
- Now, right-click on the key for the zone, and then select the Delete option.
Once done, check if the issue persists.
2] Check the DNS Configuration settings
In this solution, we will ensure that the DNS configuration settings are not the reason behind this error. Various instances are recorded where improper configuration causes DNS servers to function incorrectly. To verify the DNS configuration, follow the solutions prescribed below:
- Start Server Manager by clicking Start, then Administrative Tools, and lastly, Server Manager on the DNS server.
- In the console tree, double-click on Roles > DNS Server > DNS.
- Right-click on the DNS server, select Properties, and check the settings on each tab to ensure they have all the intended values.
- Once done, expand the DNS server, and then the Zone folder, and select Properties.
- Again, check all the values and settings on all the tabs.
Repeat the process for each zone and see.
Read: How to enable the DNS Client Service if greyed out in Windows
3] Make sure that the DNS client computer is able to resolve names
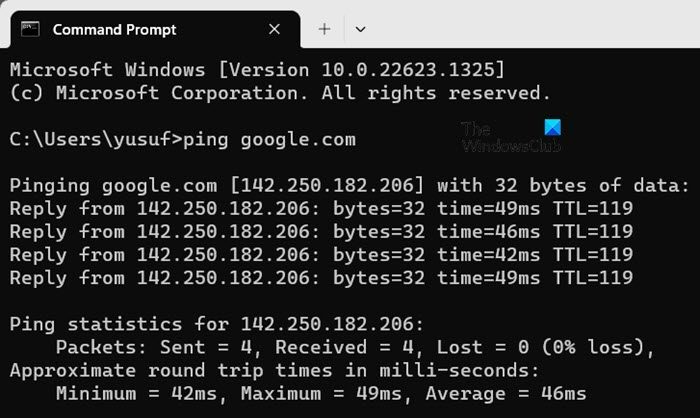
In this solution, we are going to make sure that the client’s computer is able to resolve names, i.e., it can resolve Domain names to IP addresses. Otherwise, this not only leads to issues such as DNS not being able to create a new zone, but other underlying issues such as misconfigured DNS settings, network connection issues, and so on.
Here’s how to make sure that the DNS Client computer can resolve names:
- Click Win + R to open the Run dialogue box, type cmd, and then hit the OK button on the DNS Client computer.
- Now, type ping hostname (for example, ping www.google.com) and hit the Enter button.
- If the client is able to resolve the ping, you will see the following message:
Pinging hostname [ip_adress]
- If not, the following message will appear on the screen:
Ping request could not find the hostname
If the client cannot resolve names, then ensure that the Internet, firewall, security software, and corrupted cache are not the reason behind this complication. Once verified, try resolving names on the DNS client computer.
Read: How to change DNS server with Command Line?
How many zones can we create in DNS?
The simple answer to this question is that there is no strict limit to the number of DNS zones. However, it is necessary to consider various factors that this depends on. This includes the current DNS server software, available resources on the server, and the specific requirements of the network environment. Commercial DNS servers and enterprise-grade solutions are known to accumulate more zones than simpler implementations.
Leave a Reply