Event ID 5137 is one of the security errors on Windows. An event log entry in Windows indicates audit failure related to a directory service object in Active Directory. The error could appear for various reasons, such as routine administrative activities like creating new user accounts, groups, or organizational units.
However, fixing Event ID 5137: A directory service object was created error is not as complicated as it may seem. And below, you will find a handful of ways to eliminate the error. But first, let’s learn what the error is all about:
What is the Event ID 5137 error?
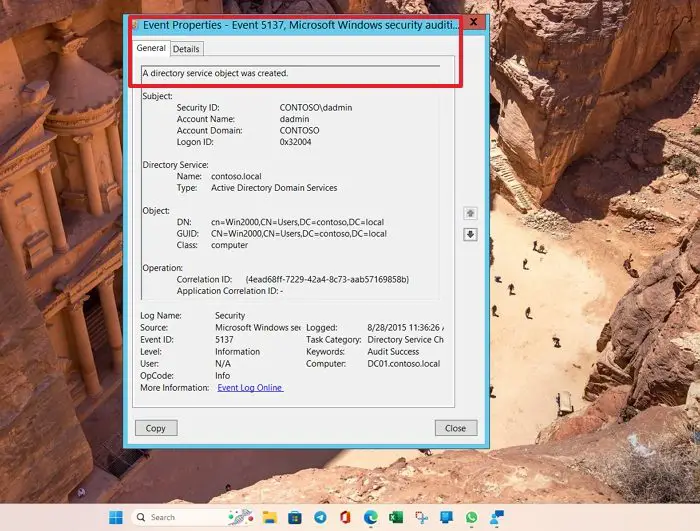
Event ID 5137 is a common error code in the Windows Security event log. It is related to security audit failures in the Active directory, specifically to a directory service object.
Whenever an object gets created in the Active directory, such as a user account, group, or organization unit, the event gets logged with this event.
It provides information like when the object was created, the name, unique identifier or GUID, and location within the directory structure.
The event also provides helpful information, which comes in handy while troubleshooting or identifying the cause of the failure.
The error could appear because of several reasons, such as:
- Legitimate Object creation: It may occur during day-to-day administrative activities like creating a user account, group, or organizational units.
- Misconfiguration: The error may occur if improper configuration errors exist in the Active Directory settings.
- Unauthorized object creation: Event ID 5137 may appear whenever an unauthorized or suspicious object is created.
Fix Event ID 5137: A directory service object was created
Fixing the issue is pretty straightforward. All you have to do is identify the changes and take necessary actions based on them. For this, you can follow these methods:
- Identify the affected directory service object
- Verify object permissions
You will need an administrator account to execute these suggestions.
1] Identify the affected Directory Service Object
The first step in fixing the error is to identify the subjected directory service object, as it will have all the information related to the cause of the error. So whenever you see the error, make sure to take note of the object’s name or distinguished name.
When you have the name noted, follow the below steps:
- Go to Windows search, type Event viewer, and launch it.
- Click on Windows Logs and then Security, and you should see all the logged events.
- Next, use the noted name to identify the event log and click on it.
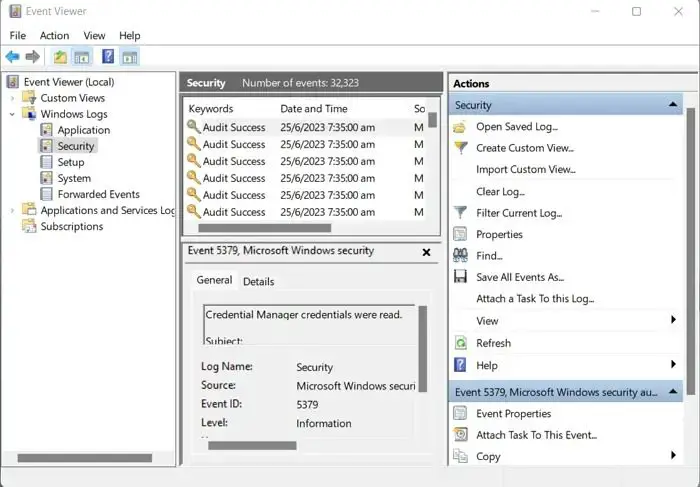
- Finally, in the below pane, you will see the error details in General.
If you believe the changes were legit, then there is no need to take further action. However, if you believe anything suspicious, move to the below fixes.
Read: What is Audit Success or Audit Failure in Event Viewer
2] Verify object permissions
Next, ensure that all the object’s permissions are configured as they should be. To verify this, follow the below steps:
- Press the Windows key + R to launch Run.
- Type gpedit.msc and press Enter.
- Now navigate to the following path:
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Audit Policy.
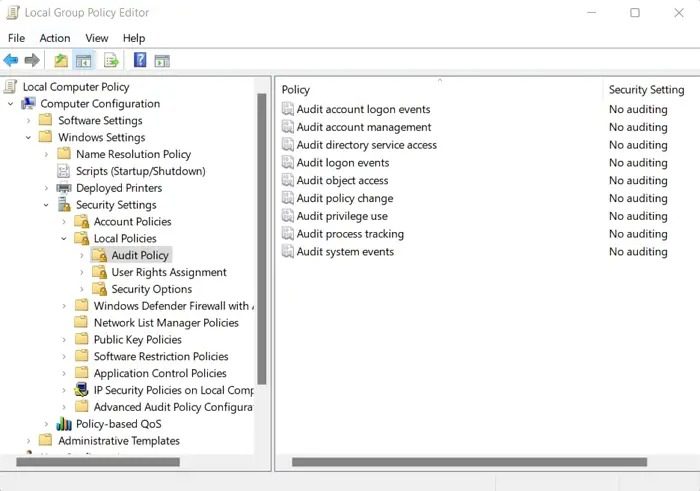
- Over here, ensure that all the policies listed on the right pane are appropriate.
Conclusion
So that was all about how to fix Event ID 5137: A directory service object was created for the error. If the above steps didn’t work out for you, consider using a Windows utility tool capable of repairing your PC and see if that works for you. Also, if you have any other questions, please comment below.
Read: How To create Custom Views in Event Viewer on Windows
What is a directory service object?
In Windows, a directory service object pertains to an individual entity within the directory service. It helps manage and control different network parts, such as user accounts, security rules, who can access what, and how the system is set up.
What is an example of a directory service?
A domain name system (DNS) server is an example of a directory service. The DNS server links computer hostnames with IP addresses, resulting in all computing resources (hosts) functioning as clients of the DNS server.
Leave a Reply