A sudden blue screen on the computer screen starting with Your PC ran into a problem and needs to restart error message can be common on Windows computers. Also referred to as the Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) or Stop Errors, they are characterized by a sad face, and the screen displays an error code or message. These Blue Screens can occur randomly and are also known to occur when your system is idle. Effective troubleshooting of this error involves a detailed study of the error message and the potential causes.

What causes a Blue Screen when system is idle?
- Conflicts arising from Power Management: Almost all desktops and laptops have effective power management features that ante up when the system is idle. These features might be at variance with specific hardware or device drivers, causing the occurrence of the error.
- Hardware Malfunction: Defective hardware components of a computer system that are not attached correctly may also cause the error. The system, at times, might try to access them while idle, leading to impaired communication.
- Faulty or unstable Device Drivers: Flawed or unstable device drivers may not be empowered to handle idle states at times, so the operating system might crash, signaling the above-mentioned error.
- Erroneous software applications: Software applications installed on the computer might be in pursuit of accessing specific system resources while idle. Software conflicts may arise in such scenarios, subsequently leading to the error.
- Overheating of hardware components: Implausible as it may sound, faulty or restricted airflow attributed to the improper functioning of the processor or SMPS fans, can lead to overheating of the hardware components, leading to the error.
- Hard Disk Errors: In its plight to access a particular sector of the hard drive that might be damaged or corrupted while in an idle state, the system can also trigger the blue screen when idle.
Fix Windows 11 Blue Screen when idle
If a Blue Screen occurs frequently when your Windows 11/10 computer has been idle, here are some troubleshooting suggestions to help you. Some of them will need admin permission to change settings.
- Resolve Power Management issues
- Resolve Hardware issues
- Fix faulty device drivers
- Address Overheating issues
- Other troubleshooting suggestions
- Check the system logs and memory dumps
We have also recommended reseating the hardware. Ensure you have a clear idea of doing that.
1] Resolve Power Management issues
To address and subsequently resolve power management issues in pursuit of a solution for the blue screen error or BSOD, the below-mentioned steps can be followed:
Change the power settings
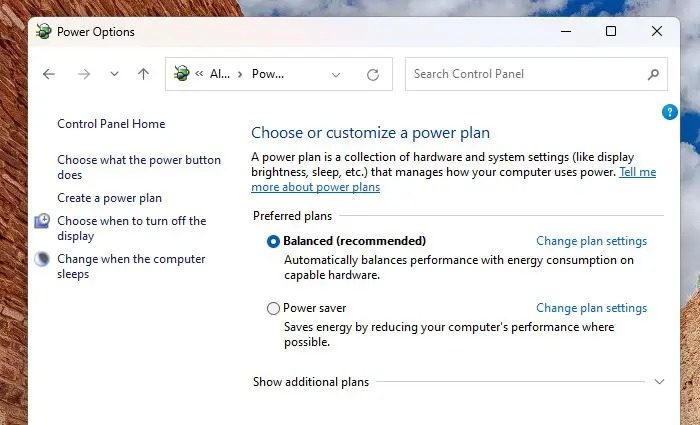
Reverting to the default power plan or choosing to balance the system performance and the energy consumption can be an effective resolution for the discussed error.
Change USB selective suspend settings
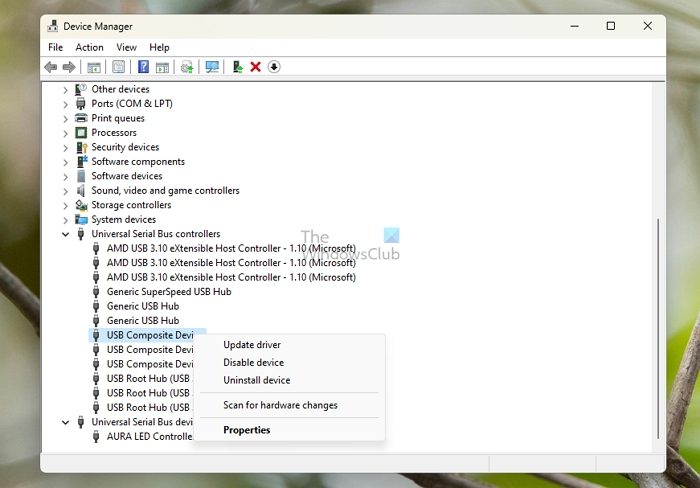
USB selective suspend refers to the temporary suspension of power connection for a particular USB port that has been inactive for a while, thereby saving power. However, on the flip side, this could occasionally lead to a device conflict, resulting in the blue screen error. To eliminate the possibility of the BSOD error, disable USB Selective Suspend and see.
Check the power settings from BIOS/UEFI
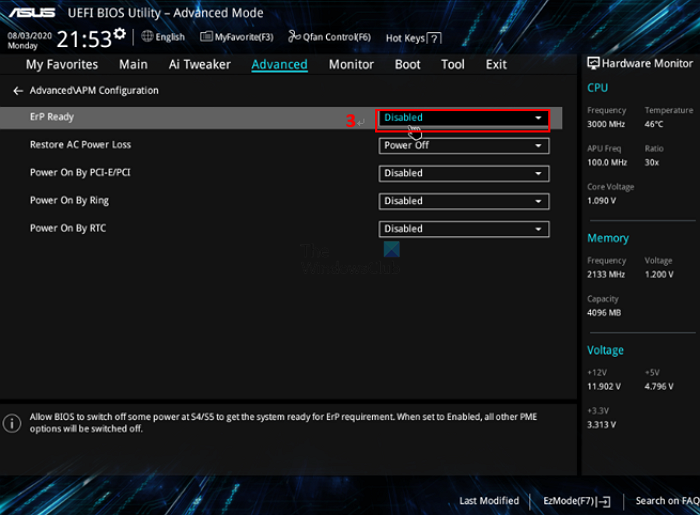
Checking the power settings recorded in the BIOS or UEFI can also be an effective troubleshooting measure for the BSOD issue.
Since the interface and the option names vary by manufacturer, referring to the relevant motherboard manual and following the same is advised. Restoring the default setting of the BIOS/UEFI can also serve as a remedial measure.
Read: Understand and Troubleshoot common Windows Blue Screen of Death
2] Resolve Hardware issues
Faulty or malfunctioning hardware can also contribute abundantly to the cause of the BSOD error, and hence, corrective measures need to be undertaken to resolve the same as detailed below:
Re-seat the hardware components
Dislodging of hardware components can be expected if the system is moved or transported. Hence, re-seating the hardware components, if necessary, can be opted for as a remedial measure.
Faulty Memory
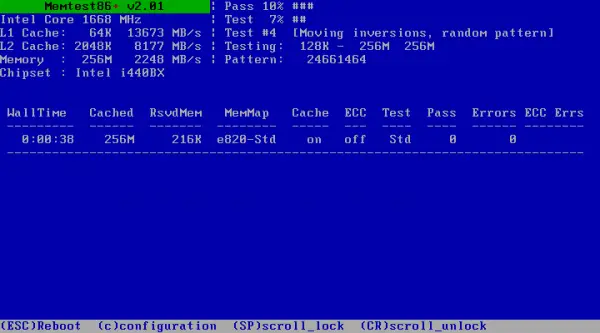
A faulty temporary memory or RAM can also cause the Blue screen error, and hence 3rd, third-party memory testing applications like MemTest86, available online, can be used to check the health of the concerned hardware.
TIP: If you want the error code, you may have to force Windows to display Stop Error details.
3] Fix faulty device drivers
Since the user is unaware of the exact device driver that might be causing the error, the below-mentioned steps can be adopted to nullify the effects of device driver malfunction.
Update device drivers
Update the drive and see if that helps fix the issue. This post will show you how to find which Driver is causing the Blue Screen.
Rollback the recently installed drivers
At times, the onset of the blue screen error might occur just after installing a specific device driver. In such cases, a rollback of the concerned device driver can help resolve the issue.
- Identify the recently update driver and then open Device Manager
- Locate the device in the Device Manager, right-click, and select the Properties menu.
- If the driver update was recent, Rollback Driver will be available. Use that.
- Check if the issue is resolved.
System Restore
If this doesn’t work, you can use System Restore to go back to a date on which everything was working fine, and it will also restore the old driver, resolving the issue.
4] Address Overheating issues
The below-mentioned checks can help if the error occurs due to improper airflow or ventilation.
Check the temperature of the hardware components
Using 3rd party software like HWMonitor, available online for free, the temperature of the hardware components can be tracked. High-temperature readings of 90 degrees for the CPU and nearing the threshold for the GPU would indicate overheating.
Physical cleaning of the system
Dust accumulated on the CPU or the hardware components inside can block airflow, causing heat retention. Hence, physical cleansing can help facilitate seamless airflow.
Disable CPU overclocking
Changing the voltage settings of the hardware components to their default ones and disabling the CPU and GPU overclocking can also help lower the overall heat emanating from the hardware components, thereby contributing to the resolution. However, the steps should ideally be performed under the supervision of an expert.
4] Other troubleshooting suggestions
- Troubleshoot in Clean Boot State: Since application software can also be responsible for conflicts in the system, resulting in errors, the below-mentioned remedies can be tried out for a possible resolution. It can be done in a Clean Boot State where the OS will run with minimal drivers, helping narrow down potential software or background processes causing the conflict.
- Update Windows OS: To update Windows OS, type Windows Update in the Search Bar on the Desktop and click on the Check for updates option in the search result.
- Uninstall or disable dubious software: Go to Settings > Apps > Installed Apps. Search the app, and use the menu to uninstall programs.
- Disable unfamiliar background processes: Open the Task Manager and check for any dubious process. If found, right-click on the same and select the End Task Option.
- Run virus and malware scans: Malicious software can also contribute to the error. Hence, scanning the system can help ascertain and resolve the problem.
5] Check the system logs and memory dumps
On every instance of the error occurrence, Windows records the details of the activities performed along with corresponding results and stores them as system dumps. Analyzing these log files can provide helpful and direct insight into the cause of the errors.
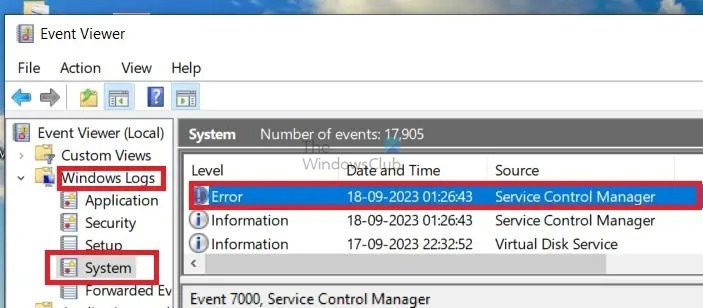
Check the Event Viewer
- Type eventvwr.msc in the Run Dialog Box to open the Event Viewer
- In the Event Viewer window, select Windows Logs and then System and check for any error around the same time as the Blue Screen Error occurrence.
TIP: Analyze Windows Memory Dump .dmp files with WhoCrashed
Set the log file or minidump
- To set up the minidump file, right-click on This PC, then click on Properties, then the Advanced System Settings.
- In the Startup and Recovery section, click on Settings.
- Select the Small Memory Dump option under the Write debugging information dropdown list and note the dump file’s default location.
Read: How to open and read Small Memory Dump (DMP) files
Analyze the minidump using 3rd party software
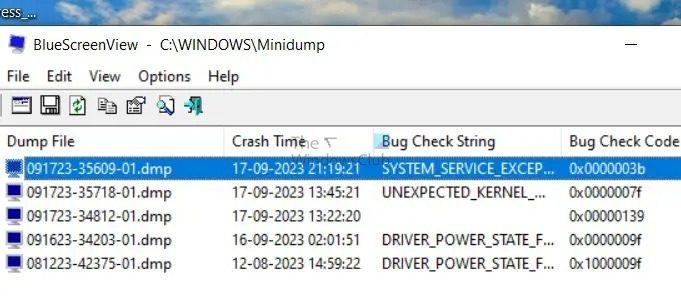
You can use free Crash Dump Analyzer software like BlueScreenView on your computer. This free utility helps you give all the information regarding the BSOD, including the driver’s name responsible for the error. It can be used to analyze the minidump to identify the exact cause of the issue.
The scope of the Blue Screen Error, or BSOD, in its entirety, extends across the hardware and software realm. However, methodical evaluation and troubleshooting, as mentioned above, can help identify the problem’s exact cause and its eventual resolution.
I hope the post was easy and helps you resolve the issue.
TIP: Windows 11 offers a new Blue Screen Troubleshooter that can be run in the Get Help app. This new built-in Blue Screen Troubleshooter is easy to run and helps you fix BSODs.
Can unstable RAM cause a blue screen?
Yes, unstable RAM can also cause a blue screen. It’s important to ensure that your computer’s RAM functions properly to avoid any issues.
Can corrupt Windows cause a Blue screen?
A blue screen can be caused by various issues, such as malfunctioning components, faulty device drivers, or corrupted system files.