The portion of a computer’s RAM that is used by a hardware device such as a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), sound card, network adapter, and other hardware components is known as Hardware Reserved. These hardware components should work properly; that’s why this memory is set aside. When some users open the Task Manager to find out the reason for the slow running of the computer, they notice a large amount of hardware reserved memory on their computer. In this article, we are going to talk about why Hardware Reserved Memory is too high in Windows and how we can reduce it.
What is Hardware Reserved Memory?
Hardware Reserved Memory is part of a computer’s physical memory or Random Access Memory (RAM), which is set aside for system hardware like the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) and other allied low-level system resources. Reserved Memory aids in the seamless functioning of the computer system by enabling various other hardware components.
Possible causes for Hardware reserved memory too high in Windows
- Memory allocation for Integrated Graphics in BIOS/UEFI: Integrated Graphics is a GPU built into the processor that shares the system memory used by the CPU. The memory allocated for the GPU can vary based on computer settings, and more allocation can increase Hardware Reserved Memory. Outdated BIOS or firmware versions may not handle the allocation efficiently, contributing to higher allocation.
- Faulty or Incompatible RAM: Memory modules that are damaged or incompatible can also contribute to problems with efficient memory allocation, including the Hardware Reserved Memory.
- Higher Memory Allocation During Boot Process: If the amount of physical memory allocated during the boot process is too high, it can lead to higher Hardware Reserved Memory in Windows.
How to reduce Hardware Reserved Memory in Windows
If the Hardware Reserved Memory is too high, here are some steps you can take to reduce the Hardware Reserved Memory on your Windows 11/10 computer:
- Change Maximum Memory from the Boot options
- Optimize the Virtual Memory
- Update drivers
- Update BIOS
- Restore BIOS/UEFI to the Default Settings
Before you begin, create a system restore point first.
1] Change Maximum Memory from the Boot options
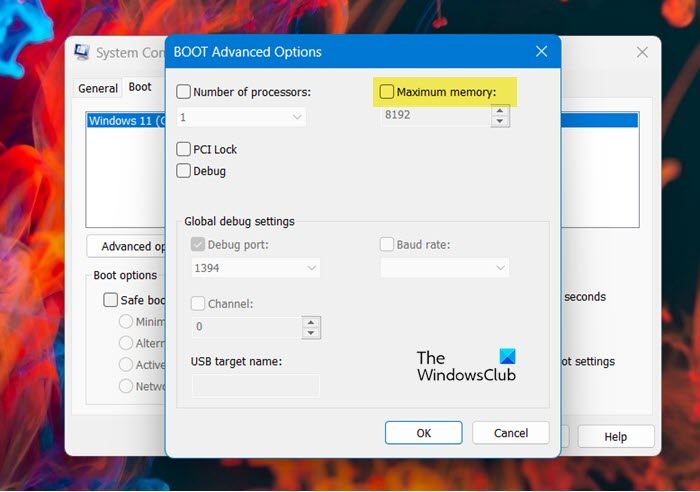
In Windows, you have a Maximum memory option available in the boot procedure
which is used to reserve RAM. If you have set the maximum memory here, then you
can see a large amount of Hardware Reserved RAM. In that case, we can stop the system from having a lot of reserved memory by altering the system configuration. Following are the steps to do the same.
- Press Windows + R key to open the Run dialog box.
- Type msconfig and then hit the Enter button.
- In the System Configuration window, go to the Boot tab.
- Now click on the Advanced option and then uncheck the Maximum memory box.
- Here, click OK to save the changes.
- In the System Configuration window, click on Apply and OK button.
Once you restart the computer, the issue will be resolved.
2] Optimize the Virtual Memory
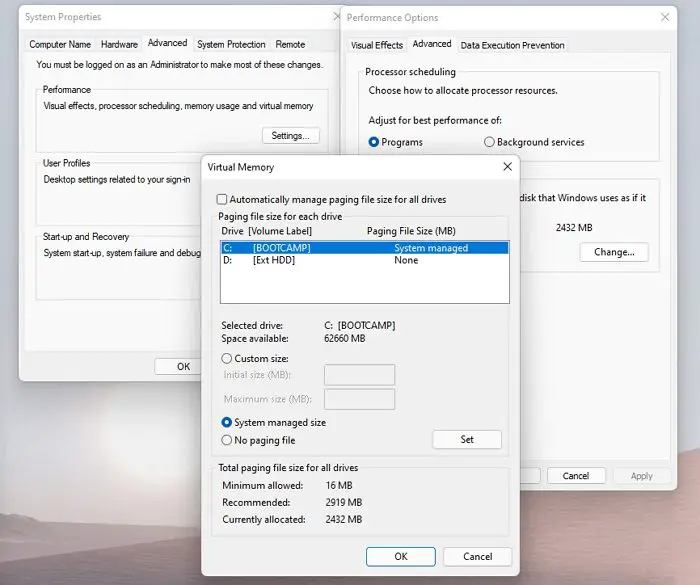
Virtual Memory is a technique that allows the system to allocate more memory to the system on top of its physical memory. In case, the settings are configured wrongfully, it is very likely that we will face memory-related issues. Here, we are going to optimize
- To open File Explorer, press the Windows + E key.
- Right-click on This PC and select Properties.
- On the right side of the window, click on Advanced system settings.
- This will launch the System Properties window, you have to click on the Settings tab under the Performance section.
- Now in the Advanced tab and click on the Change button in the Virtual memory box.
- Uncheck Automatically manage paging file size for all drives.
- Here, select the C drive and then select Custom size and enter the size depending on the reserved memory you see in the Task Manager.
- Click on the OK button to apply the change.
Reboot the computer and check if the hardware reserved RAM Windows 11 is resolved.
3] Update drivers
Update your device drivers and see if that helps in any way.
4] Update the BIOS
BIOS is a firmware that controls the input/output of your system. If it has bugs or compatibility issues, it fails to communicate the operating system and other components, such as RAM. In that case, we must update the BIOS to make things compatible. So, go ahead and update the BIOS to get rid of this error. You should also check for Windows Updates and download them if available.
5] Restore BIOS/UEFI to the Default Settings
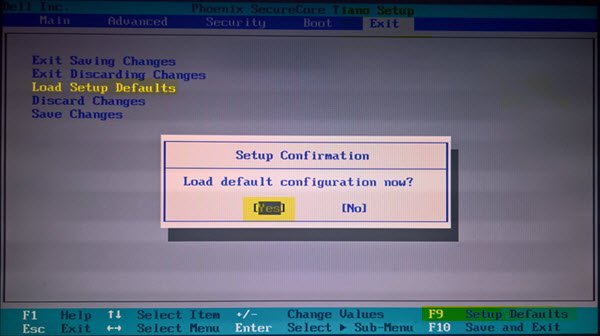
If updating does not help, you may have to reset the BIOS settings to their defaults. Follow the steps mentioned to do the same.
- Start the computer and press F2 or the Delete key or some other key, depending on your laptop’s OEM to enter into BIOS.
- Click on the Restore Settings or Load Defaults option.
- Now Exit from BIOS and restart the computer.
Hopefully, this issue will be resolved once the computer is started.
Reducing hardware reserved memory can improve system performance and efficiency. This article provides insight into factors contributing to the high allocation of hardware-reserved memory and steps to mitigate the issue. Caution is advised when accessing BIOS/UEFI and system settings to avoid unintended errors that could disrupt system stability.
How to check actual size of the installed RAM and memory allotted?
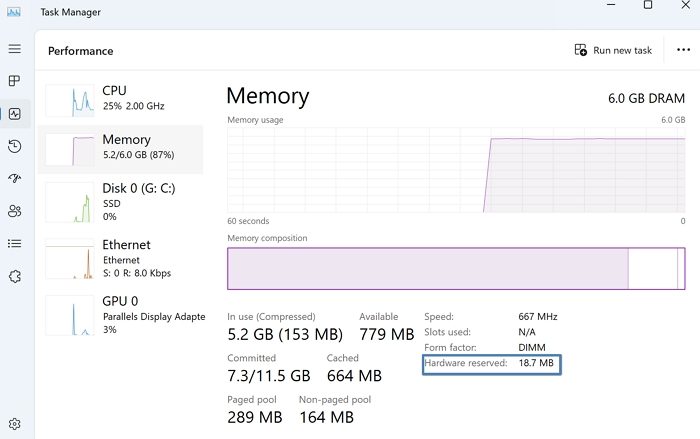
To check the actual size of the installed RAM, the memory allotted by the OS, and the preprocessor type (32-bit or 64-bit), go to System Information > System Type. A 32-bit system can only use up to 3.5 GB of RAM, regardless of the installed physical memory.
Why is my Hardware Reserved Memory too high?
Hardware Reserved Memory will be high if you have configured the settings to do the same. You may not have configured it manually, it may happen due to an update or a third-party app, but whatever it is, we can easily reconfigure the same. You may also face the same issue due to corrupted or outdated BIOS, corrupted/outdated Graphics Driver and we will talk about that as well.
How do I reduce Hardware Reserved RAM?
If Hardware Reserved on your computer is way too high, you need to disable Maximum Memory from Boot options as it forces the system to reserve RAM depending on the value set. If we don’t want the same, our best option is to disable the settings and you will be good to go.
Read: Fix 100% Disk, High CPU, Memory or Power usage in Windows.
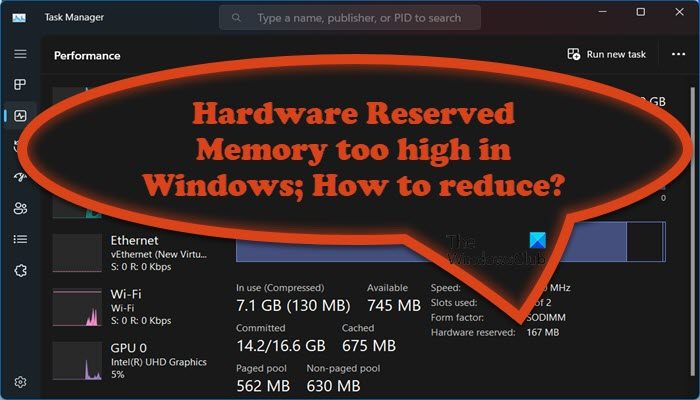
How do you check Hardware reserved memory in Windows?
Hardware reserved memory allocation can be checked by opening the Task Manager (pressing CTRL+SHIFT+ESC together), followed by selecting the Performance Tab and clicking on the Memory option.
What happens when reserved memory is too high?
If the amount of reserved memory is too high, it reduces the amount of physical memory available to other applications, which can significantly impact the overall performance of the computer.