Photoshop has features and tools that allow you to do very practical and useful things. Knowing how to blur image backgrounds without affecting the image in Photoshop can be a very practical and useful feature. This feature can be used to enhance the image. When the background is blurred, the image will be more focused. The background may be distracting because of the many colors or objects. When the background is blurred it can give the image the illusion of movement and speed. This is so because in movement, the camera would focus on the image and the background would look blurred.
How to Blur Image Background in Photoshop without affecting the image

Blurring the image background without affecting the image is very easy to follow and duplicate. Learning this skill will prove useful for jobs or personal use. There may be cases where you need to highlight an image and blur the background for emphasis. A client may want to give a still image the illusion of speed and blurring the background can achieve that. This article will show you how to blur an image background using Photoshop.
- Place the image in Photoshop
- Select the Image
- Copy the selection
- Remove the original image
- Blur the background
- Save
1] Place the Image in Photoshop

This is the original image
Before the process of blurring the background, you need to get the image into Photoshop. One method of getting the image into Photoshop is to find the image then right-click on it and choose Open with Photoshop <version>. The image will open as a background. You can also go into Photoshop then go to File then Open then search for the file, select it and click Open. The image will be placed in the layers panel on the right and will be a background.
Read: How to remove or blur Background with Photos App in Windows 11
2] Select the image
There are several ways to select the image in Photoshop. You can use the Pen tool, Lasso tool, Magnetic lasso tool, Magic wand tool, or the Quick selection tool. For versions of Photoshop that are later than 2020 you can go to Select then Select subject. This is a much easier way to select the foreground image, Adobe uses AI to figure out the subject and make a selection around it. The tool that you will use to select the image will depend on the image. Images with lots of colors will need a tool that can cut around the foreground image as accurately as possible. Note that there may be multiple images in a photo but you may just want to keep one than blur the background. This can be achieved with this method.
For this image, the Quick Selection tool will be used. The Quick Selection tool will do well because it will select the image easily. The Quick Selection tool will also work in this case because there is a high contrast between the background and the image that you want to select.
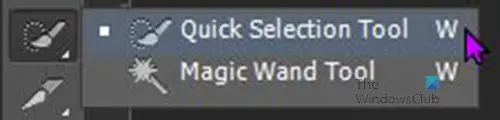
To access the Quick Selection tool, go to the left tools panel and click the Quick Selection tool. To select multiple places without breaking the selection, hold Shift while you select. You can hold down the left mouse button + Shift while dragging around the image. To make corrections to the selection, use Alt or Ctrl. Alt will bring the selection closer while Ctrl will bring it out from the image.
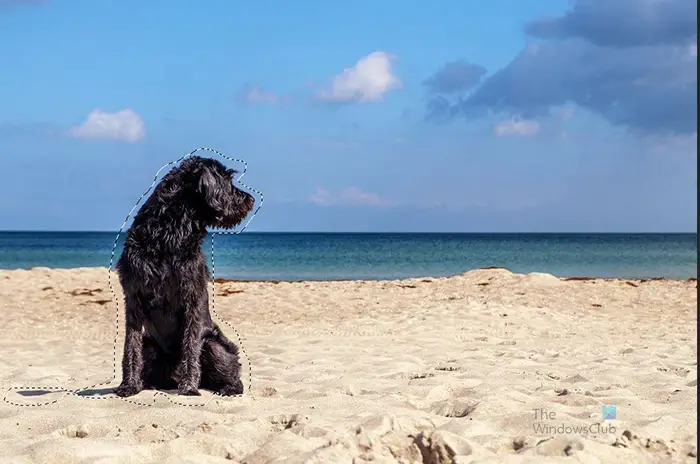

This is the image with the selection around it.
3] Copy the Selection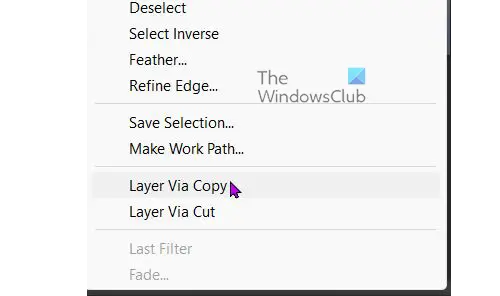
When the full image has been selected, (including shadow if you want it) right-click on the image and choose Layer via copy. This will create a new layer using the selected areas. Ensure that the selection is well done or the copy will have missing pieces, the missing pieces will not be obvious until the original image is gone. To see if the copy has all the parts turn off the original by clicking the eye icon on its layer. The copy layer will be left and you will be able to see if there are any missing pieces. If there are missing pieces, turn on the original layer and go to the History panel and go back to the last Quick Selection tool action. Make sure that the Quick Selection tool is selected. To make corrections to the selection, use Alt or Ctrl. Alt will bring the selection closer while Ctrl will bring it out from the image, you may have to zoom in to see properly.
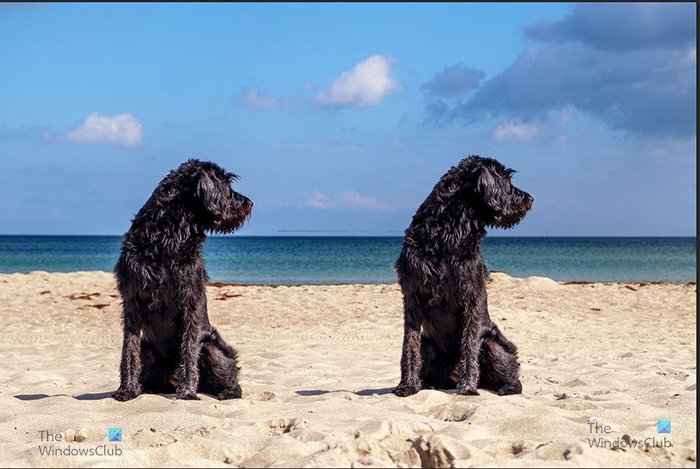

When you have verified that all the image has been selected and copied as a new layer, you can select the new layer and move it. You should see two of the images. You could use this method if you wanted to add extra images to a photo. You can also use it to move an image to a different location in a photo.
In the case of this image, the dog is sitting on the sand and the sky and sea are the backgrounds, you can use the Quick selection tool and select the sky and sea as one and then right-click and copy them as a separate layer. You would then blur the sky and sea layer and the dog and the sand would remain the same. Depending on the image you chose, the background may not have this variation so you would skip this step. Also if you want to blur everything except the foreground (dog) then you would skip this step.
In this article, the sky and sea are copied as a separate layer and will be blurred, as how the dog is a separate layer. The dog and the sand will remain unchanged. You could have also copied the sand and dog as a separate layer and the sky and sea as a separate layer.
4] Remove the original image
The next step is to remove the original image from its background and keep the background. Removing the original image from its background will give the freedom of blurring the background without affecting the copied image. Removing the original image will be achieved with the use of the Clone stamp or the Content-aware feature. The Content-aware feature will be used in this article.

To use the content-aware feature you will have to select the part that you want to cover. Make sure that you select the layer below the image that was copied. You then go to the left Tool panel and click the Lasso tool. Hold the left mouse button and then drag around the image that you want to remove, make the line as close as possible without cutting the image. The outline does not have to be neat. Notice the image with the outline, that is the original image, it will be filled over. You do not have to remove the copied image from the space where the original image is. When you select the image below in the layers panel, it will be the only one affected by the removal when you use the content-aware.
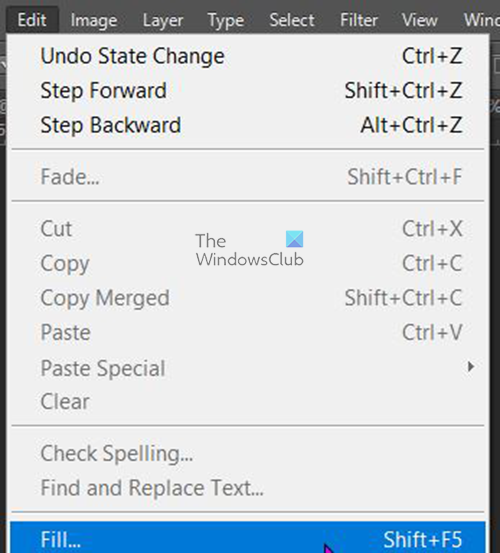
When the outline is finished, go to the top menu bar and select Edit then Fill or click Shift + F5 or Shift + Backspace.
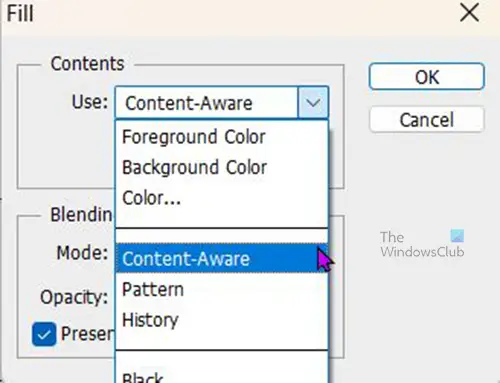
The Fill option box will appear. under Content click the drop-down arrow and choose Content-aware. When you have chosen Content-aware click OK to confirm or Cancel to stop the procedure.
When you have clicked Ok you will not notice that the object that was selected is gone and the background is there with the copy of the object. To see that the image is gone, you can move the copied layer. You will see that the Content-aware filled the spot with the background color. To get rid of the outline just click inside it with the selection tool. If you look in the layers panel you will see the image is missing from the background.
You will notice that the background and the image are separate, you can move the image without affecting the background, you can also make changes to the image and the background will not be affected. You can also make changes to the background and the image will remain the same. In this article the dog in the image will be moved to the center instead of being at the left edge as it was in the original image.
5] Blur the background
Now we are almost at the end, this is the final step before saving the final result. It is time to blur the background. The background layer would be the layer under the image that was selected and copied. The blur you choose would depend on what you want to do with the image. You can choose to try different blend options until you find a suitable look.
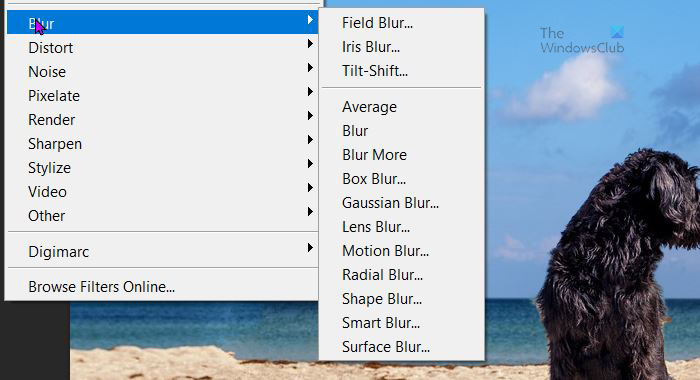
To get to the blur options select the background then go to Filter then Blend and choose one of the options from the drop-down menu.
Gaussian Blur
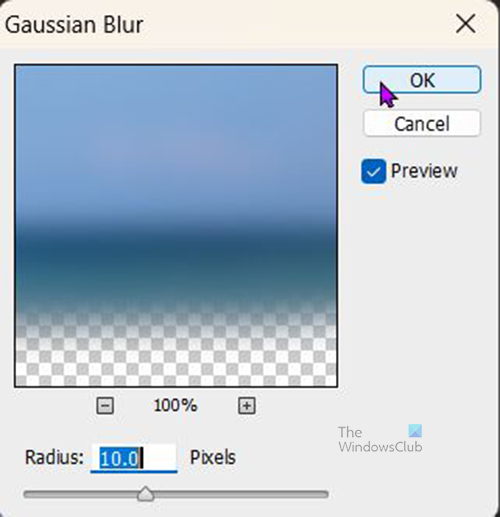
To get to the Gaussian blur go to Filter then Blur then Gaussian blur.
You can try the Gaussian blur to use on the background, this will blur the background so that you are unable to see it. However, you can change the radius to a lower value so that the background is still visible but blurred. Experiment with the Radius value to get a satisfactory blur.
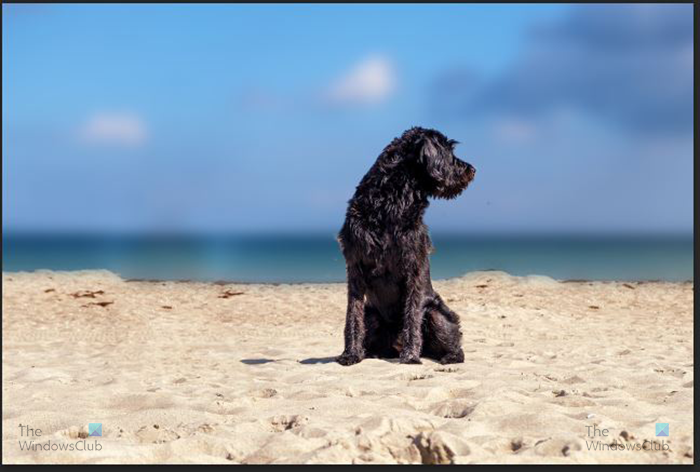

Image with Gaussian blur background.
Motion Blur
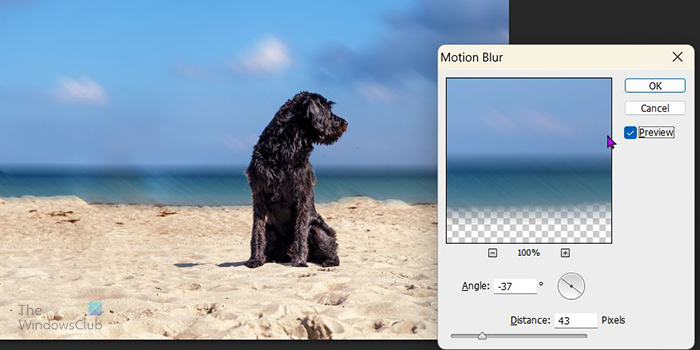
You can try the motion blur. The motion blur is best for images where you want to give the illusion of motion or speed. You can change the angle of the blur and also the distance. This image has a radius blur angle of -37 degrees and a distance of 33 pixels. Experiment with different values until you are satisfied with the result.
Radial Blur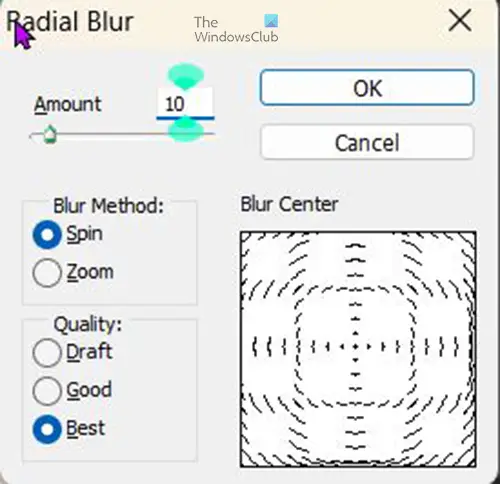
Another blur that you can try is the Radial blur, this gives the background a circular blur look. You can experiment with the different options to get the look you are satisfied with.
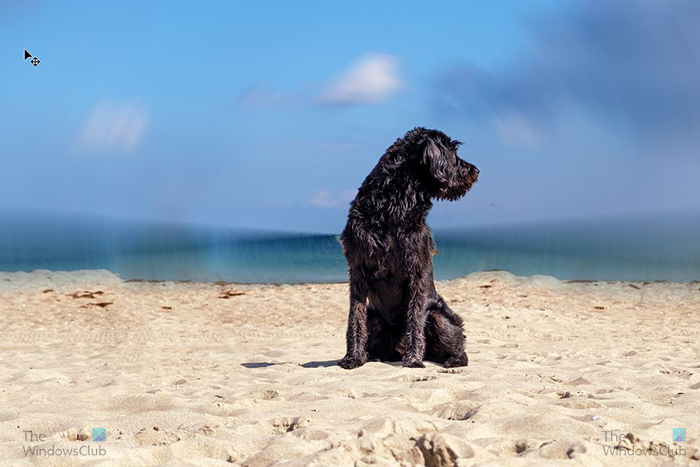

This is the image with the radial blur background.
6] Save
After all that hard work, it is now time to save. While you were working you should have been saving the file just in case something happened, it would not be lost. That means the first save would be as an editable Photoshop PSD file, when everything is finished it can be saved as a JPEG for use online or for sending online via email or social media. A copy can also be saved as a PNG file without a background.
Read: How to recolor objects in Photoshop
How do I blur the background of a picture I already taken?
There are a few ways to blur parts of an image in Photoshop. You can use one of the Marquee selection tools then select part of the image. Make sure that the image I selected then go to Filter then Blur then select the blur that you want and apply it then, adjust options then press OK.
Read: How to Blur or Pixelate an Image on Windows 11/10 using various other software.
How do you slightly blur a photo in Photoshop?
To slightly blur a photo in Photoshop when working with the Blur, Sharpen or Smudge tool, create a new blank layer, or use an Adjustment layer for the different adjustments. This will ensure that all changes are made on the new layer or the Adjustment layer. You should also duplicate the original image and make all changes to the duplicate.
Leave a Reply