Every time your Windows 11/10 computer crashes, it creates a Memory Dump File. These minidump files are memory images of that point in time when your Windows computer had crashed.
This dump file type includes the following information:
- The Stop message and its parameters and other data
- A list of loaded drivers
- The processor context (PRCB) for the processor that stopped
- The process information and kernel context (EPROCESS) for the process that stopped
- The process information and kernel context (ETHREAD) for the thread that stopped
- The Kernel-mode call stack for the thread that stopped.
There are different kinds of memory dump files possible: Kernel Memory Dump, Small Memory Dump & Complete Memory Dump. Windows 8 adds a new option called Automatic Memory Dump.
Change number of Memory Dump Files Windows creates
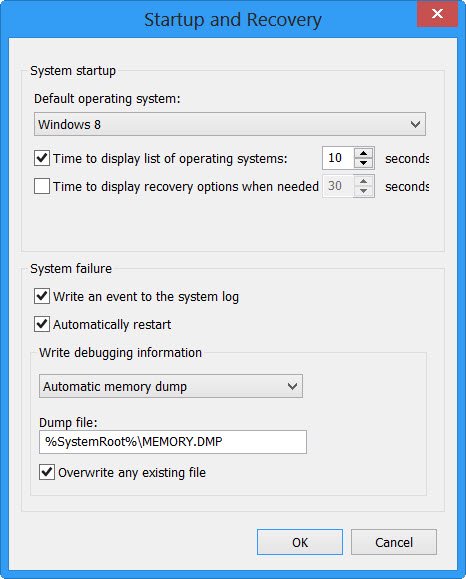
You can change Dump settings from Control Panel > All Control Panel Items > System > Advanced system settings > Advanced tab > Startup & Recovery > Settings.
Windows, by default, creates and stores 50 minidump files. These minidump files are located in the %SystemRoot%\Minidump directory.
If you are a geek who needs to use these dump files to troubleshoot computer crashes, then having the last 50 dump files may be useful to you.
Read: How to manually create a Crash Dump file in Windows.
If not, they will simply end up eating disk space.
You can, if you wish, reduce the number of dump files that your Windows creates.
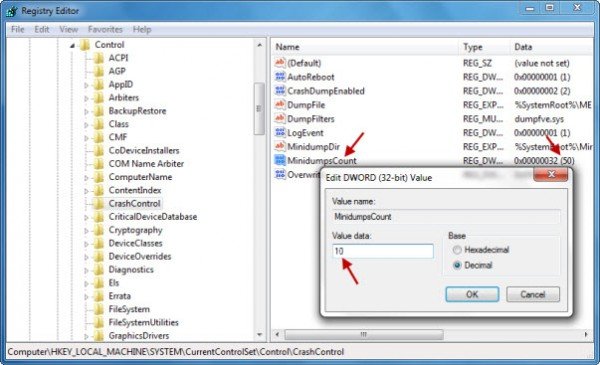
To do so open regedit and navigate to the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl
Double-click MiniDumpsCount and change its value data.
The default in Windows is 32 Hexadecimal or 50 Decimal. Reduce its Decimal value to 10, if you only want the last 10 minidump files to be saved.
I hope this helps.
Related read: Windows Memory Dump Settings on Windows 11.
How do I stop Windows from deleting memory dump files?
To prevent Windows from deleting memory dump files, navigate to System Properties > Advanced > Startup and Recovery Settings. Under “System Failure,” uncheck “Automatically delete memory dump files when disk space is low.” Ensure sufficient disk space is available to retain these files. This adjustment helps maintain memory dump files for troubleshooting purposes.
What is the difference between Automatic memory dump and Complete memory dump?
An Automatic memory dump is a smaller, default type created when Windows crashes, using a portion of available memory, whereas a Complete memory dump captures all system memory content. Automatic dumps aid in diagnosing issues without consuming much space, while complete dumps provide exhaustive information but require more storage.
“If you are a geek who needs to use these dump files to troubleshoot your computer crashes, then having the last 50 dump files may be of use to you!”
sooo funny :)