Windows Server Backup is a built-in backup solution that allows administrators to schedule periodic, customized, and on-demand backups. It is a free utility that provides a set of wizards and tools to perform basic backup and recovery functions that can help optimize the system’s performance.
However, multiple backup copies, especially older ones, tend to occupy considerable disk space, affecting the system’s performance. This article explores the various ways of deleting older and unnecessary backup copies.

Overview of Windows Server Backups
The Windows Server Backup utility can back up specific system states, files, folders, drives, and the entire server data, OS, and installed applications. The backups taken by WSB are stored as snapshots or volume shadow copies using the Volume Shadow Copy Service, or VSS, in Windows. Once the data is copied, a shadow copy is automatically generated using the VSS, which preserves the system’s current state as the backup version.
There are two distinct methods of shadow copy creation:
- Full Copy: Creates a complete copy or clone
- Differential Copy: Copies only the changes made since the last backup.
The copy types create two separate data images: the original volume and the shadow copy volume. Though the original volume has read and write capabilities, the shadow copy volume is read-only. The read-only status ensures that the shadow copy volume records the changes made until the administrator changes it.
Read: Windows Server Backup utility UI missing
How to delete Windows Server Backup Copies
The Windows Server automatically deletes the copies of WSB at regular intervals. However, in case of exceptions, the same can be done manually from the Terminal Prompt using specific commands. WSB deletion process can be classified into three broad categories as detailed below:
- Automatic Disk Usage Management
- Deletion of System State Backups for Windows Server
- Deletion of Windows Server Full Backup
1] Automatic Disk Usage Management
WSB effectively manages the storage space for backup copies by automatically adjusting the disk space. It dynamically shrinks the space allocated for the old backup copies or snapshots to accommodate the new ones. The space extracted from the old snapshots to accommodate the newer ones is also termed the diff area.
However, WSB tends to avoid reducing the diff area to less than 1/8th of the target volume size so that old backups are not erased while making space for the newer ones.
Read: How to Start, Stop, Restart Windows Server Backup Service
2] Deletion of System State Backups for Windows Server
As the name suggests, a system state backup captures the snapshot of the current system state by backing up OS files and components necessary for running the system. It can help in system recovery when the device boots up, but the OS cannot be loaded as the system files or registry are damaged.
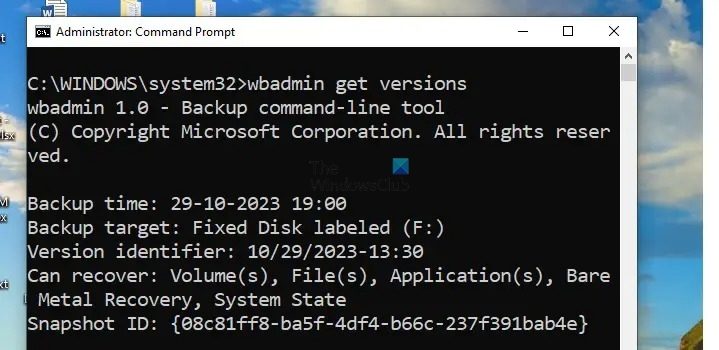
The wbadmin command and the relevant option or parameters are generally used for checking and deleting Windows Backup Server copies. To execute the command, we must log in to the Terminal Prompt as an Administrator. However, before starting the deletion process, we must verify the available backup copies and their types (system state or full) to execute the command correctly. For example, to check the available backups, we can open the Terminal prompt as an Admin and type:
wbadmin get versions
To delete System State backups, the wbadmin delete systemstatebackup command can be used with the relevant parameters as mentioned below:
Delete Oldest System Backup
For deleting the oldest backup on the system, the -deleteOldest parameter can be used along with the wbadmin delete systemstatebackup command. For example, to delete the oldest system state backup stored on the D drive (D:), type:
wbadmin delete systemstatebackup –backupTarget: d: -deleteOldest
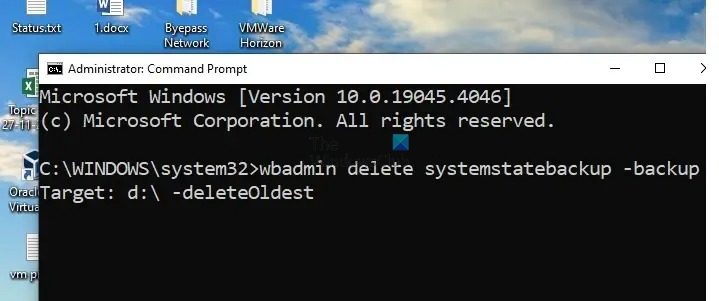
Note: If the backup is stored on the system drive or C:\, the target drive need not be mentioned in the command.
Delete all System Backups except the five most recent ones
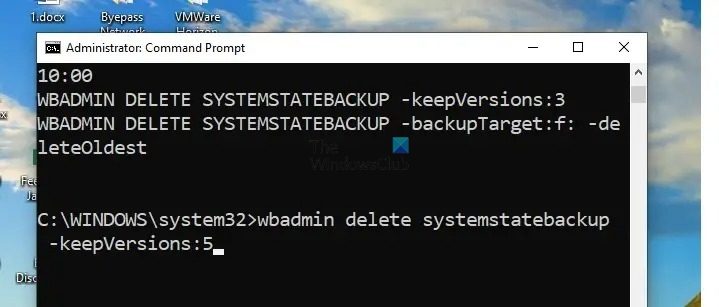
The deletion process can be customized for deleting particular backup copies as well. For example, if we are looking to delete all the system state backups except five most recent ones, we can use the wbadmin command with the –keepVersions parameter as shown below:
wbadmin delete systemstatebackup -keepVersions:5
Delete a Particular System State Backup
Using the wbadmin command, we can also delete specific backup copies. For example, to delete a system state backup taken on the 31st of March, 2023 at 10.00, the below command can be entered in the Terminal prompt.
wbadmin delete systemstatebackup -version:03/31/2023-10:00
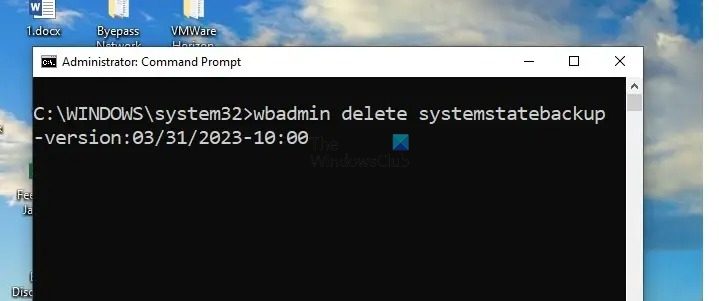
Note: The details of the backup copy concerning its date and time need to be checked from the version identifier line while viewing the list of available backups.
Read: Shadow Copies are lost during backup in Windows
2] Deletion of Windows Server Full Backup
To delete full backups, the wbadmin command can be used along with the delete backup option instead of the delete systemstatebackup as mentioned below:
Delete oldest full backup
wbadmin delete backup -deleteOldest
Delete all backups except the last 5
wbadmin delete backup -keepVersions:5
Delete a particular system state backup
wbadmin delete backup -version:02/02/2024-06:43
Does WSB take registry user hive backups?
No, the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS), also known as Windows Server Backup (WSB), does not directly back up the Windows registry user hives. Since VSS focuses on file-level backups, the Windows registry is not a traditional file but a hierarchical database stored in memory and on disk.
Read: How to Install, Uninstall, Reset Windows Server Backup
What is the storage limit for Windows Server Backups for the latest Windows Server?
WSB in the latest Windows Server doesn’t have a specific storage limit, thanks to VHDX files. However, there are some limitations, such as the Underlying storage system being limited to 16TB, and the VSS may not support volumes exceeding 64 TB.
Leave a Reply