In this tutorial, we will show you how to dismount a volume in Windows 11/10 and mount it back. When a logical drive or volume is mounted, we can access its files and folders and other data on Windows OS. By default, Windows automatically mounts a new drive or volume by assigning a drive letter. A unique volume GUID (a 36-character hexadecimal number) is also assigned to easily identify the volume even if the drive letter is unassigned. Those who don’t want Windows to mount new drives automatically can unmount a volume with some simple steps.
What happens if you dismount a volume?
Once you dismount a volume (a hard disk volume, USB drive volume, etc.), Windows removes the volume mount point for that volume. The drive becomes inaccessible as the file system of volume is not available for reading and writing. The drive letter is also unassigned which can be used by another volume. However, your data remains safe. You can manually mount a volume when needed and you will have access to all the data again.
How to dismount a volume in Windows 11 and mount it back?
There are two native options to dismount or unmount a volume in Windows 11 and mount it back when needed. These are:
- Dismount a volume in Windows 11 using the Disk Management utility
- Unmount a volume in Windows 11 using Windows Terminal.
Let’s check both options.
1] Dismount a volume in Windows 11 using the Disk Management utility
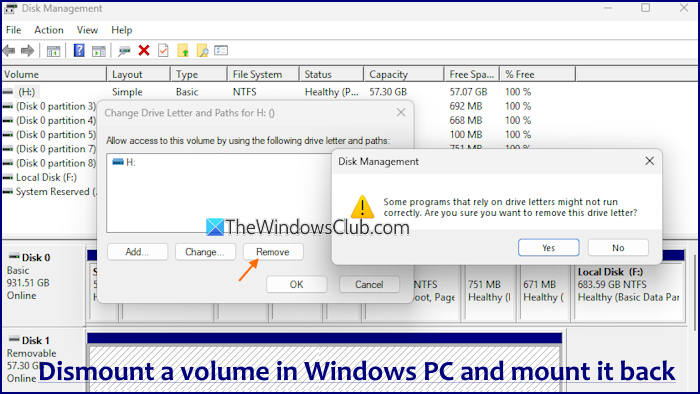
Disk Management is a system utility for creating partitions, mounting and unmounting a drive, converting an MBR disk to GPT, and more. The steps to dismount a volume using the Disk Management tool are as follows:
- Open the Disk Management tool and you will see a list of volumes on its interface
- Right-click on a disk or volume
- Click on the Change Drive Letter and Paths option. A small box will pop up
- Click on the Remove button
- A Disk Management confirmation box will open
- Press the Yes button to confirm that you want to dismount the volume.
Now you won’t see that volume in the This PC section, navigation pane of File Explorer, etc.
Mount a dismounted volume using the Disk Management utility
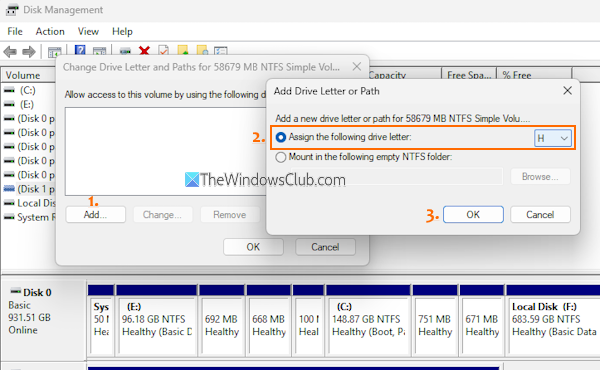
Here are the steps:
- Connect the dismounted volume
- Launch the Disk Management utility
- Right-click on the dismounted volume
- Select the Change Drive Letter and Paths option
- Press the Add button in the box that appears
- An Add Drive Letter or Path box will open
- Select the Assign the following drive letter option and use the drop-down menu to select a letter. If the last assigned letter is available, you can select it. Otherwise, choose a different drive letter. Here, you also have the option to mount the drive as a Folder. But, for mounting the volume with a drive letter, you have to use the first option
- Press the OK button.
Related: How to take a Drive Offline or bring a Disk Online in Windows 11
2] Unmount a volume in Windows 11 using Windows Terminal
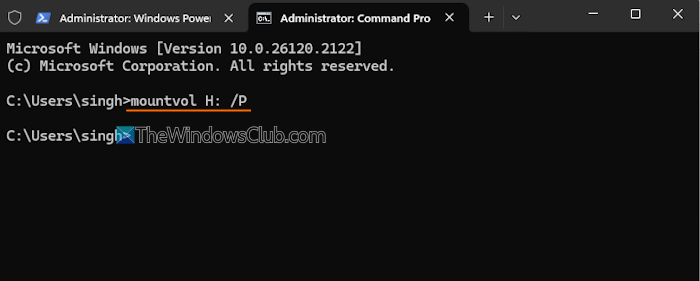
Use the following steps to unmount a volume in Windows 11 using Windows Terminal:
- Connect the volume or drive
- Open Windows Terminal as administrator. Right-click on the Start button and select the Terminal (Admin) option
- Launch a Command Prompt profile in a new tab
- Now, we will execute a command that will include:
- mountvol command: that creates, lists, or deletes volume mount point
- The Drive letter of the drive or volume that we need to dismount, and
- /P parameter that removes the volume mount point from the specified directory, takes the basic disk offline and makes it unmountable. So, let’s say you want to unmount an H drive. The command is:
mountvol H: /P
Remember to replace H: with the actual drive letter. The drive will be dismounted successfully.
Mount a volume in Windows 11 using Windows Terminal
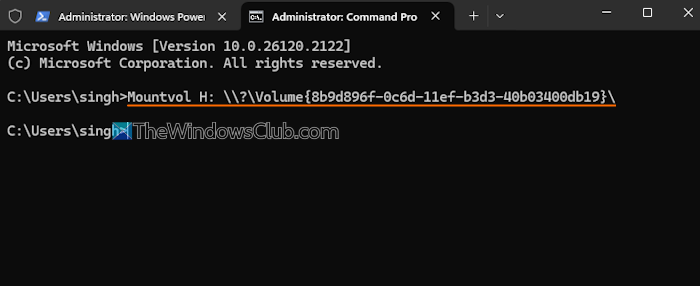
As we mentioned in the beginning, a volume GUID (or unique volume name) is assigned to each mounted volume. Even if a volume is dismounted, the volume GUID helps to mount the drive back. So, we will use the volume GUID and mountvol command in Windows Terminal to mount the drive along with a drive letter. Here are the steps:
- Connect the unmounted volume
- Launch an elevated Windows Terminal
- Open a Command Prompt profile
- Execute the mountvol command. This will list volume GUIDs per disk along with volume letter
- Look for a volume with *** NO MOUNT POINTS *** or *** NOT MOUNTABLE UNTIL A VOLUME MOUNT POINT IS CREATED *** text. This is your dismounted volume. Copy the GUID for this volume. Now here is a catch. Multiple volumes (such as Recovery Partition, EFI System Partition, etc.) could have the same text. In that case, it’s difficult to identify the exact volume you need to mount back. To avoid this situation, you need to act proactively and copy the GUID of the drive before the dismount process using the mountvol command
- Now, to mount back the drive, execute the command with mountvol, a drive letter (say H), and volume GUID. The command would be:
Mountvol H: \\?\Volume{8b9d896f-0c6d-11ef-b3d3-40b03400db19}\
That’s all!
Would you like to force a dismount on this volume?
When you use the CHKDSK command with the /f or /r parameter for a volume and the volume is in use, then you may receive this message:
Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another process. Chkdsk may run if this volume is dismounted first. ALL OPENED HANDLES TO THIS VOLUME WOULD THEN BE INVALID. Would you like to force a dismount on this volume? (Y/N)
Pressing Y will help you proceed further. It will first dismount the volume (making it inaccessible), examine the basic file system structure, etc., and complete the file system scanning.
Once the process is complete, the volume will be ready to use again.
You may also receive a similar message when you try to format a USB drive using the Format command in Command Prompt.
Read next: How to Mount & Unmount ISO file in Windows PC.
Leave a Reply