LDAP signing is an authentication method in Windows Server that can improve the security of a directory server. Once enabled, it will reject any request that doesn’t ask for signing or if the request is using non-SSL/TLS-encrypted. In this post, we will share how you can enable LDAP signing in Windows Server and client machines. LDAP stands for Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP).
How to enable LDAP signing in Windows computers
Enabling LDAP signing on the server and client machines is essential to ensuring that the attacker doesn’t use a forged LDAP client to change server configuration and data.
- Set the server LDAP signing requirement
- Set the client LDAP signing requirement by using Local computer policy
- Set the client LDAP signing requirement by using the Domain Group Policy Object
- Set the client LDAP signing requirement by using Registry keys
- How to verify configuration changes
- How to find clients that do not use the “Require signing” option
The last section helps you to figure out clients that do not have Require signing enabled on the computer. It is a useful tool for IT admins to isolate those computers, and enable the security settings on the computers.
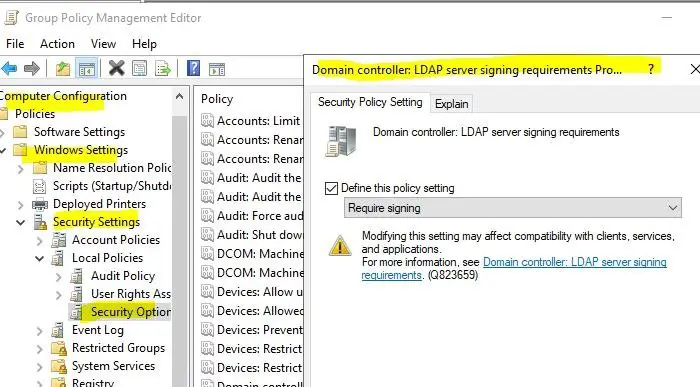
1] Set the server LDAP signing requirement
- Open Microsoft Management Console (mmc.exe)
- Select File > Add/Remove Snap-in > select Group Policy Object Editor, and then select Add.
- It will open the Group Policy Wizard. Click on the Browse button, and select Default Domain Policy instead of Local Computer
- Click on the OK button, and then on the Finish button, and close it.
- Select Default Domain Policy > Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies, and then select Security Options.
- Right-click Domain controller: LDAP server signing requirements, and then select Properties.
- In the Domain controller: LDAP server signing requirements Properties dialog box, enable Define this policy setting, select Require signing in the Define this policy setting list, and then select OK.
- Recheck the settings and apply them.
2] Set the client LDAP signing requirement by using local computer policy
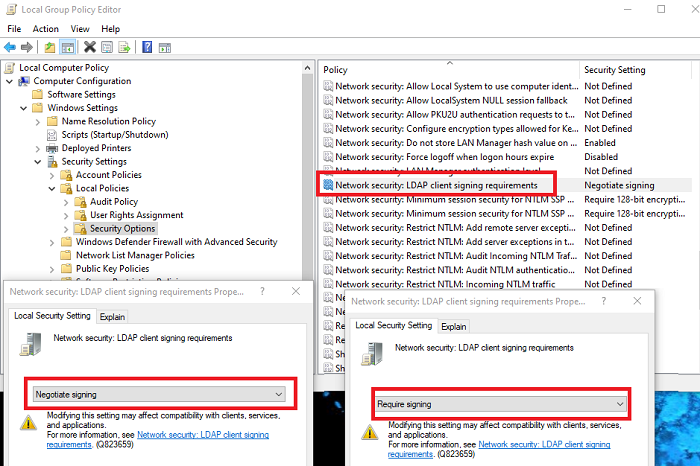
- Open Run prompt, and type gpedit.msc, and press the Enter key.
- In the group policy editor, navigate to Local Computer Policy > Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies, and then select Security Options.
- Right-click on Network security: LDAP client signing requirements, and then select Properties.
- In the Network security: LDAP client signing requirements Properties dialog box, select Require signing in the list and then choose OK.
- Confirm changes and apply them.
3] Set the client LDAP signing requirement by using a domain Group Policy Object
- Open Microsoft Management Console (mmc.exe)
- Select File > Add/Remove Snap-in > select Group Policy Object Editor, and then select Add.
- It will open the Group Policy Wizard. Click on the Browse button, and select Default Domain Policy instead of Local Computer
- Click on the OK button, and then on the Finish button, and close it.
- Select Default Domain Policy > Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies, and then select Security Options.
- In the Network security: LDAP client signing requirements Properties dialog box, select Require signing in the list and then choose OK.
- Confirm changes and apply the settings.
4] Set the client LDAP signing requirement by using registry keys
The first and foremost thing to do is take a backup of your registry
- Open Registry Editor
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \ SYSTEM \ CurrentControlSet \ Services \ <InstanceName> \Parameters
- Right-click on the right pane, and create a new DWORD with name LDAPServerIntegrity
- Leave it to its default value.
<InstanceName>: Name of the AD LDS instance that you want to change.
5] How to verify if configuration changes now require sign-in
To make sure the security policy is working here is how to check its integrity.
- Sign in to a computer that has the AD DS Admin Tools installed.
- Open Run prompt, and type ldp.exe, and press the Enter key. It is a UI used for navigating through the Active Directory namespace
- Select Connection > Connect.
- In Server and Port, type the server name and the non-SSL/TLS port of your directory server, and then select OK.
- After a connection is established, select Connection > Bind.
- Under Bind type, select Simple bind.
- Type the user name and password, and then select OK.
If you receive an error message saying Ldap_simple_bind_s() failed: Strong Authentication Required, then you have successfully configured your directory server.
6] How to find clients that do not use the “Require signing” option
Every time a client machine connects to the server using an insecure connection protocol, it generates Event ID 2889. The log entry will also contain the clients’ IP addresses. You will need to enable this by setting the 16 LDAP Interface Events diagnostic setting to 2 (Basic). Learn how to configure AD and LDS diagnostic event logging here at Microsoft.
LDAP Signing is crucial, and I hope this article helped you clearly understand how to enable it in Windows Server and on client machines.
Leave a Reply