In this post, we will show you how to exclude individual users or computers from a Group Policy Object. Usually, when group policy is applied, it is applied for all the computers or user groups or all the users. There are no exceptions. However, if you want to exclude individual Users or Computers from a Group Policy Object (GPO), then there is a method. It will allow you to exclude a single user or computer. Before we start, this works on a Windows 11/10 computer that is part of the domain. It means you cannot apply this to computers you are using at home.
Exclude Individual Users or Computers from Group Policy Object
Excluding individual users or computers from a Group Policy Object is relatively simple. It doesn’t necessarily require creating separate Organization Units (OUs) to link different policies to different OUs or block inheritance for a domain or organizational unit. Rather, you can use security filtering to decide whether or not the GPO settings will apply to a specific computer and/or user object(s).
Use security filtering to exclude individual users or computers from GPO
Please note that while this approach is easy to follow, it should only be used in certain situations and done using group membership to avoid the administrative overhead of constantly updating security filtering on GPOs.
Here are the steps you need to follow:
Select the Group Policy Object in the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) to which you want to apply the exception.
GPO settings will be listed in the right panel. Switch to the Delegation tab and then click the Advanced button in the bottom-right corner.
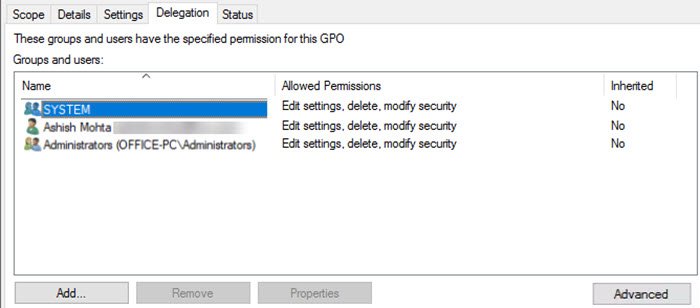
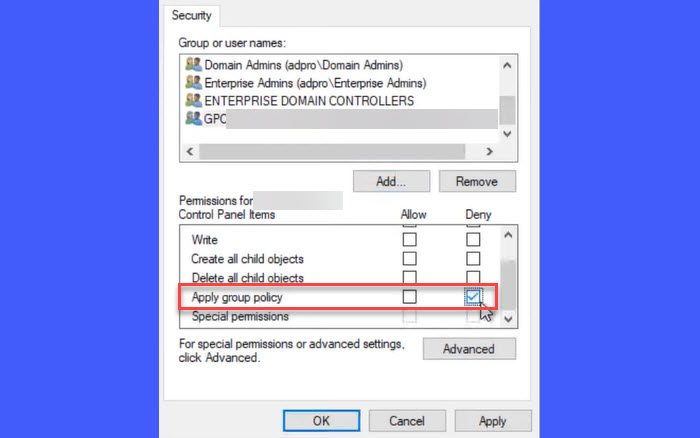
Security settings window for the selected GPO will appear. Click the Add button and list the user or computer whom you want to exclude from group policy enforcement.
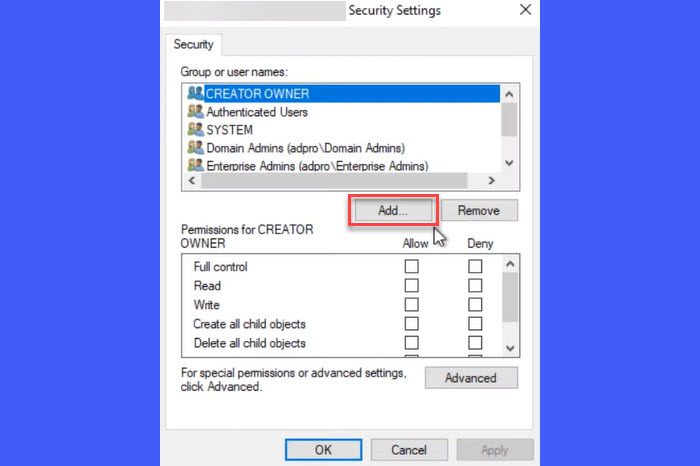
Note:
- When searching, the ‘user’ is the default search mode.
- Switch to all searches to list computers as well.
- You can also add a user group if you want to block a bunch of users.
Select the user or user group or the computer you’ve added.
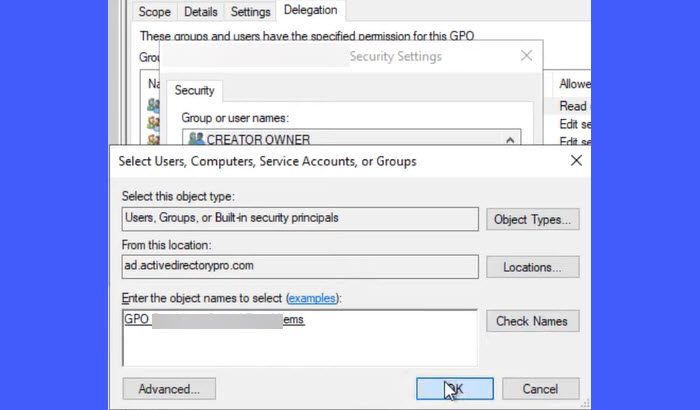
Locate Apply group policy under Permissions and select Deny next to the option. Click Apply and then OK. Click Yes to confirm your action if a confirmation message appears.
Link the group policy to a container or OU (If you haven’t done it already).
Next, open the Command Prompt by typing ‘cmd’ in the Run prompt (Win+R) and launch it using Ctrl+Shift+Enter. This will open the command prompt with admin permission.
Next, type the following command and press the Enter key to execute the command:
gpupdate
It will force an immediate update of Group Policy and instantly apply the change across the computer with the exception made.
That’s about it.
I hope the post was easy to follow, and you were able to exclude individual Users Or Computers from a Group Policy Object.
Make sure you group people whenever possible else, it will be difficult to remember and manage them.
Read: How to apply Group Policy to Non-administrators only
How to apply GPO to only certain users?
To apply a Group Policy Object (GPO) to only specific users, you can organize targeted users into a separate OU within your Active Directory structure and link the desired GPO to this OU within the Group Policy Management Console. Once you do this, only users within that OU will receive the policies defined in the GPO.
How do I block a specific Group Policy from inheritance on an OU?
Open the Group Policy Management Console and navigate to the Organizational Unit (OU) where you want to block inheritance. Right-click on it and select Block Inheritance from the context menu. If you want to block only specific GPOs rather than all inherited policies, right-click on the GPO you want to enforce and select Enforced. This will ensure it is applied even if inheritance is blocked.
Read Next: How to reset all Local Group Policy settings to default in Windows.