You can use WMIC command line to find & check running processes by name on your Windows 11/10 computer. We show you how. A simple WMIC command can help you get a list of all processes running on your computer. Instead of using Task Manager, you can give this WMIC command a try to get the job done.
What does the WMIC display about the process?
Although Task Manager is a great source of information, you can use the WMIC command to get the same thing done. The advantage of using WMIC is that you can find more detailed information than Task Manager. For your information, it displays the following things:
- ExecutablePath
- KernelModeTime
- PageFileUsage
- Priority
- PageFaults
- ReadTransferCount
- SessionID
- TerminationDate
- WorkingSetSize
- WriteOperationCount
- VirtualSize
- WindowsVersion
- WriteTransferCount
- PeakPageFileusage
Before you proceed, you should know that the WMIC tool is being deprecated now and has been superseded by Windows PowerShell for WMI.
How to find all running processes using WMIC in Windows 11/10
To find all processes using WMIC in Windows 11/10, follow these steps:
- Press Win+X to open the WinX menu.
- Select the Windows Terminal option.
- Enter this command: wmic process list
- Find the details on the Windows Terminal window.
It is possible to use Command Prompt and the Command Prompt instance in Windows Terminal. Either way, you will get the same result. However, here we have used the Windows Terminal to show you the example.
First, you need to open the WinX menu by pressing the Win+X buttons. Then, select the Windows Terminal option in the WinX menu.
As mentioned earlier, if you want to use the Command Prompt, you need to search for cmd in the Taskbar search box and click on the individual search result.
Once the Windows Terminal is opened, you need to enter this command:
wmic process list
Then, you can see all the information required to diagnose your PC or something else.
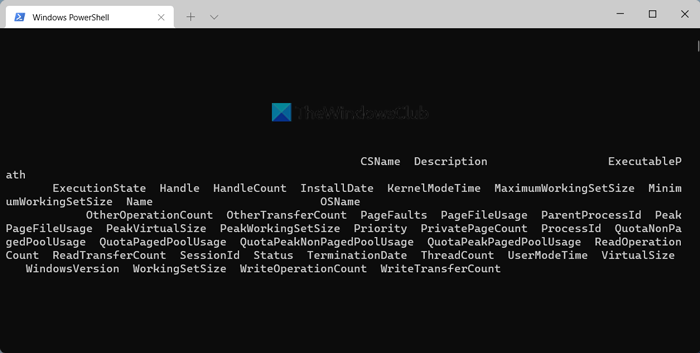
As we said before, you can find the ExecutablePath, Description, InstallDate, etc.
Disadvantage of using WMIC over Task Manager
The main disadvantage or drawback of using WMIC over Task Manager is the user interface. Although it displays more details than Task Manager, the user interface makes it difficult to read the data. No matter, which monitors you try it on, you can find the same issue across all the displays.
When the Task Manager shows columns, task names, etc., separately, WMIC prompt displays them together. The only way to read the data is by exporting it to a text editing app, such as Notepad, Notepad++, etc.
Whether you execute the aforementioned command in the Windows Terminal or the standalone Command Prompt window, the data displays in a similar way. However, if you can overcome this problem in any way, you will find this method of knowing about all running processes pretty handy.
Read: How to check Battery level using WMIC in Windows
How can I see all the running processes?
There are multiple ways to see all running processes on Windows. However, the easiest way to find them is by using the Tasklist command for Task Manager. The Task Manager has a dedicated Processes tab, where you can find all the running processes. Apart from that, you can switch to the Services tab, where it displays all the running services your computer has. Last but not least is the Details section, where you can find all the processes according to the user. This post will show you how to generate and print the list of running Processes in Windows Task Manager.
How do I list all processes in Windows?
As described earlier, you can list all processes in Windows 11/10 with the help of the Task Manager. However, if you do not want to export anything, you can always try the WMIC method. A simple command in the Command Prompt or Windows Terminal can help you find all the running processes within moments.
Leave a Reply