If you want to find the number of CPU cores and threads in Windows 11 or Windows 10 PC, here is how you can do that. There are multiple ways to find the number of CPU cores and threads on Windows 11/10, and this article explains most methods. You can follow any one of them to get the job done.

How to find CPU cores and threads in Windows 11/10
To find CPU cores and threads in Windows 11/10, follow these methods:
- Using System Information panel
- Using Task Manager
- Using Windows PowerShell
- Using Command Prompt
- Using Device Manager
To learn more about these steps, continue reading.
Note: For your information, the threads are also known as Logical Processor(s).
1] Using System Information panel
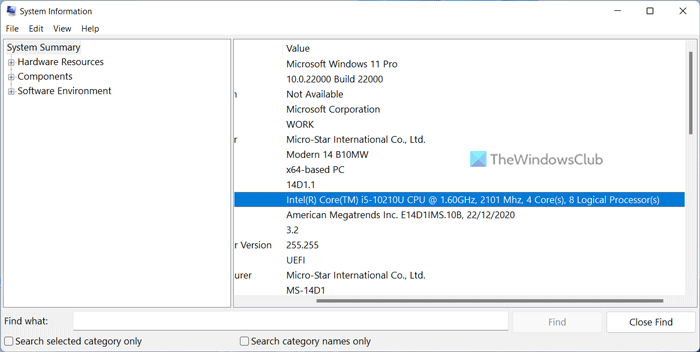
It is probably the easiest method to find the CPU cores and threads on Windows 11 or Windows 10 PC. As the name denotes, the System Information panel displays all the information about your system hardware, including the processor. Therefore, follow these steps to find CPU cores and threads in Windows 11/10 using the System Information panel:
- Press Win+R to open the Run prompt.
- Type msinfo32 in the empty box.
- Head to the Processor section.
- Read the entire line to learn about the cores and threads.
However, if you do not want to use the System Information panel, you can follow other methods as well.
2] Using Task Manager
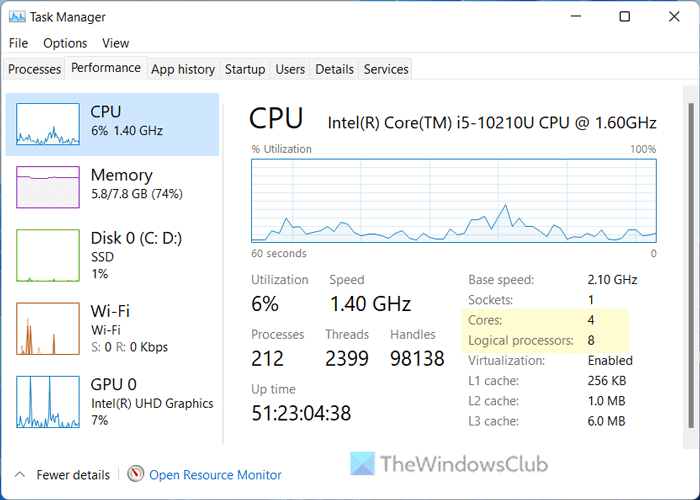
Task Manager displays so many things about your computer. Whether it is about the hardware or software, you may find handy information from Task Manager. To find CPU cores and threads using Task Manager, follow these steps:
- Press Win+X to open the WinX menu.
- Select the Task Manager from the menu.
- Switch to the Performance tab.
- Make sure that the CPU is selected.
- Find the Cores and Logical processors information.
3] Using Windows PowerShell
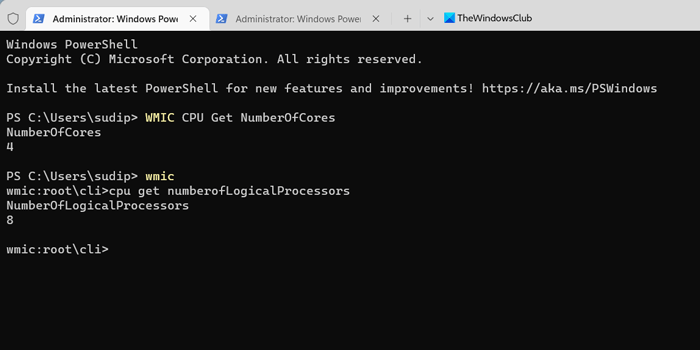
You can find the same information using Windows PowerShell as well. For that, do the following:
- Search for windows powershell in the Taskbar search box.
- Click on the Run as administrator option.
- Click the Yes button.
- Enter this command to find the CPU cores: WMIC CPU Get NumberOfCores
- Enter this command to find the threads: WMIC cpu get numberofLogicalProcessors
You can find the information immediately on the Windows PowerShell screen.
4] Using Command Prompt
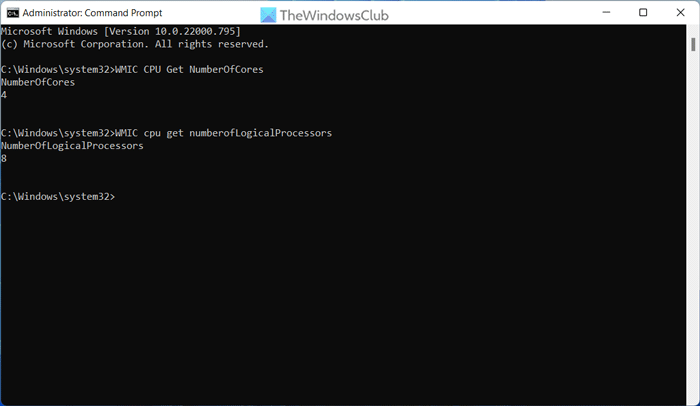
You can use the same WMIC parameter to find the same information using the Command Prompt. For that, follow these steps:
- Search for cmd in the Taskbar search box.
- Click on the Run as administrator option.
- Click on the Yes button in the UAC prompt.
- Enter this command to find the CPU cores: WMIC CPU Get NumberOfCores
- Enter this command to find the threads: WMIC cpu get numberofLogicalProcessors
As usual, you can find the information about the CPU cores and threads on the Command Prompt screen immediately.
Note: You can also use Windows Terminal to use the WMIC command. In that case, you need to press Win+X, select the Windows Terminal (Admin) option, and click on the Yes button in the UAC prompt.
5] Using Device Manager
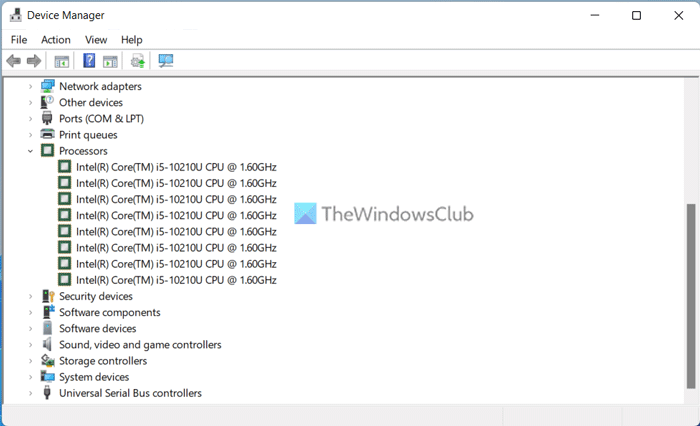
Although Device Manager displays so much information about the hardware, it doesn’t show anything about the number of cores. However, you can find the number of threads using the Device Manager. To use the Device Manager to find the CPU threads, follow these steps:
- Right-click on the Start Menu to open the WinX menu.
- Select Device Manager from the list.
- Expand the Processors section.
- Count the number mentioned under the Processors menu.
Read: How to check Intel processor generation in Windows
How do I check my CPU and cores on Windows?
There are multiple ways to check your CPU and cores on Windows. Whether you use Windows 11, Windows 10, or any other version, you can go through the aforementioned methods to get the job done. For example, you can check the System Information panel or the Task Manager. In the Task Manager, go to the Performance tab and click on the CPU option. Then, head to the Cores and Logical processors section.
Read: Do more CPU cores mean better performance?
How many cores and threads does my CPU have?
To find how many cores and threads your CPU has, you can follow the above-mentioned guides. As said earlier, there are many ways to extract this information without opening your CPU case. You can use the System Information panel, Task Manager, Windows PowerShell, Command Prompt, Device Manager, etc.
Read: Quick CPU lets you optimize CPU performance & Power consumption.
Leave a Reply