With Windows 11/10, Microsoft allows users to run multiple Linux distros based on WSL or Windows Subsystem for Linux. But when reinstalling or resetting Windows, all the configuration stored with these WSL distros gets deleted. To back up and restore this configuration, it becomes challenging for the user to do so. But Microsoft has got it covered. Users can import and export these WSL or Windows Subsystem for Linux distros. In this article, we will check out how to do it using the export or import arguments.
Import & export WSL distros on Windows 11/10
We will look at three aspects that deal with the import and export of WSL distros on Windows 11/10. They are as follows:
- Import WSL distro.
- Export WSL distro.
- Uninstall imported WSL distros.
You need to have all your installed distros to be up to date via the Microsoft Store.
1] Import WSL distro
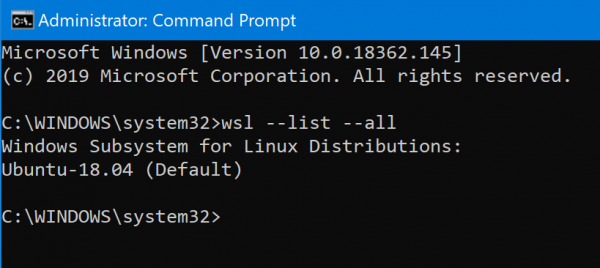
Open the Command Prompt with Admin level rights. Execute the following command in Command Prompt:
wsl --list --all
It will list all the install WSL Distros on your computer.
To import a WSL distro, execute the following command in Command Prompt:
wsl --import <Name of the distro> <Fill path to save the backup .tar file>
![]()
For example:
wsl --import Ubuntu-18.04 C:\Users\Ayush\Desktop\Ubuntu1804Backup.tar
The command will restore the backup to the given WSL Distro.
2] Export WSL distro

Open Windows Command Prompt with Administrator permissions. Execute the following command in CMD:
wsl --list --all
It will list all the installed WSL Distros on your computer.
To export a WSL distro, execute the following command in Command Prompt:
wsl --export <Name of the distro> <Fill path to save the backup .tar file>
For example:
wsl --export Ubuntu-18.04 C:\Users\Ayush\Desktop\Ubuntu1804Backup.tar
After that, your imported backup will be found in the location you entered in the command.
3] Uninstall imported WSL distros

Open CMD with Administrator permissions. Execute the following command:
wsl --list --all
Next, execute the following command to uninstall the imported WSL distros:
wsl --unregister <Name of the distro>
Once the process completes, close the Command Prompt.
I hope this guide is useful.
Read next: How to set default user, switch user, and remove a user for WSL.