Windows PowerShell ISE is a GUI-based application that is used to run and debug commands and scripts. If you compare it with Windows PowerShell, you will find that PowerShell ISE offers many advanced features which are not available in Windows PowerShell. The graphical user interface of PowerShell ISE makes it more user-friendly for beginners. In this beginner’s guide, we will explain how to install, uninstall, and use Windows PowerShell ISE.
How to install and uninstall Windows PowerShell ISE
We will explain the following methods to install and uninstall Windows PowerShell ISE:
- Installing PowerShell ISE via Windows Optional Features.
- Uninstalling PowerShell via Windows Optional features.
- Installing PowerShell ISE via Command Prompt.
- Uninstalling PowerShell ISE via Command Prompt.
1] Install PowerShell ISE via Windows Optional Features
By default, Windows 10 comes with a pre-installed PowerShell ISE app. But if you do not find it on your computer, you can install it through Windows Optional Features.
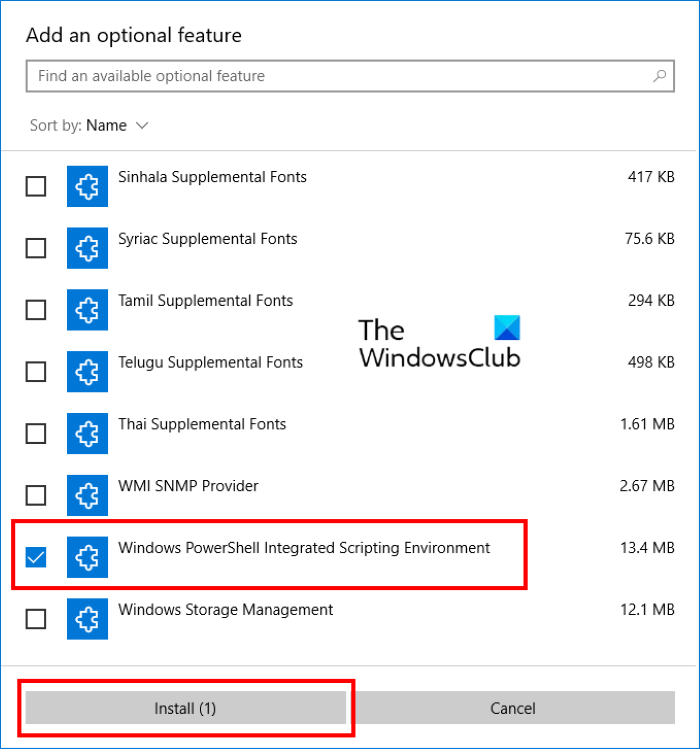
The following steps will help you install and uninstall Windows PowerShell ISE:
- Launch the Settings app and click Apps.
- Click Apps & features on the left pane.
- You will see a link named Optional features on the right pane. Click on it.
- Now, click on the Add a feature button. This will open the Add an optional feature window.
- Scroll down the list and select Windows PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment, and click on the Install button.
After the installation gets completed, you can access PowerShell ISE from the Start menu.
2] Uninstall PowerShell ISE via Windows Optional Features
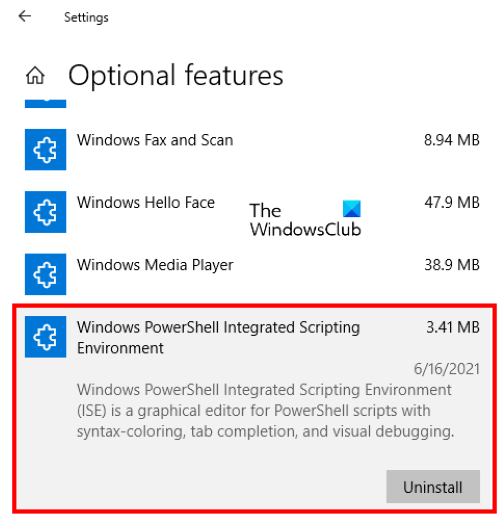
The following steps will help you uninstall PowerShell ISE using Windows Optional Features:
- Go to “Settings > Apps > Apps & features > Optional features.”
- Scroll down the list and click on the Windows PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment.
- Click Uninstall.
You have to wait till the uninstallation process gets completed.
3] Install PowerShell ISE via Command Prompt
To install Windows PowerShell ISE using Command Prompt, first, launch the Command Prompt as an administrator, then copy and paste the following command into it. When you are done, hit Enter.
DISM /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:Microsoft.Windows.PowerShell.ISE~~~~0.0.1.0
Please do not close the Command Prompt till the installation process gets completed.
4] Uninstall PowerShell ISE via Command Prompt
Launch the command prompt as an administrator, copy the following command and paste it there. After that, press Enter.
DISM /Online /Remove-Capability /CapabilityName:Microsoft.Windows.PowerShell.ISE~~~~0.0.1.0
Do not interrupt the uninstallation process or close the Command Prompt before uninstallation gets finished.
Read: Windows PowerShell ISE vs Windows PowerShell – What is the difference?
How to use Windows PowerShell ISE
To launch the app, click on the Windows Search box, type PowerShell ISE, and click Windows PowerShell ISE. If you want to launch it with administrative rights, right-click on it and select Run as Administrator.
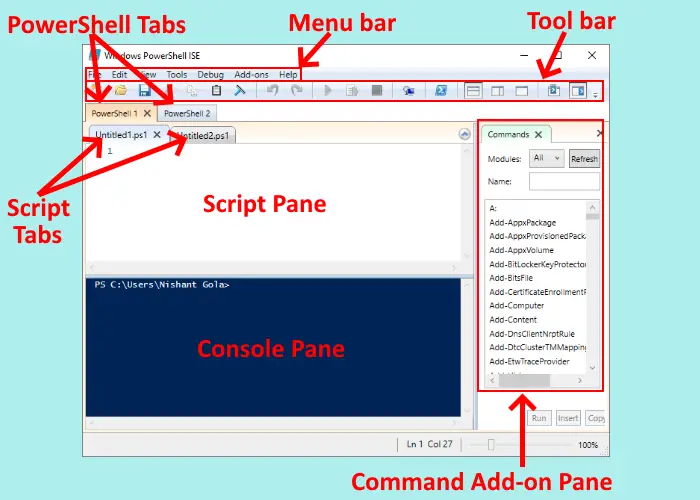
The PowerShell ISE comes with the following elements:
- Menu bar
- Toolbar
- PowerShell tabs
- Script tabs
- Console pane
- Script pane
- Status bar
- Text-size slider
These elements make it easy for a user to run, edit, and execute the commands and scripts. Let’s see the function of each of these elements:
1] Menu bar
As the name implies, the menu bar of PowerShell ISE consists of different menus including File, Edit, Tools, View, Debug, Add-ons, and Help. Using these menu buttons, you can perform different tasks, customize the ISE interface, debug commands or scripts, etc.
2] Toolbar
Like other software and apps, Windows PowerShell ISE also features a toolbar that consists of different tools. Some of these tools include:
- New Script button
- Open Script button
- Save Script button
- Clear Console Pane button
- Start PowerShell in a separate window button, and more.
3] PowerShell tabs
You can create multiple tabs in Windows PowerShell ISE. This feature lets you run multiple scripts and commands at a time. To open a new tab, go to “File > New PowerShell Tab.” Alternatively, you can also press the Ctrl + T keys on your keyboard.
To close a particular PowerShell tab, select it and click on the small cross icon, or simply press Ctrl + W keys.
4] Script tab
You can create multiple Script tabs in each PowerShell tab. This lets you run and edit more than one script at a time. To open a new Script tab, go to “File > New” or press Ctrl + N keys on your keyboard.
To close a specific Script tab, select it and click on the small cross icon. There is no keyboard shortcut to close the Script tabs.
5] Console Pane
It shows the results of the scripts and commands you run. Apart from that, you can also use Console Pane to run PowerShell commands.
6] Script Pane
This is the space where you can write and run PowerShell scripts.
7] Status bar
As the name implies, here, you can view the status of the commands and scripts that you have executed. It tells you whether the commands or scripts are completed or not.
8] Text-size Slider
It lets you increase and decrease the text size on the screen. You will find it at the bottom right corner of the PowerShell ISE.
That’s it.
Related posts: