FFmpeg is a popular software for processing, converting, or manipulating video and audio files. The program is used for endless things like rotating videos, scaling videos, extracting information about videos, and many others. It is an open-source program that is simply awesome for video scaling, format transcoding, decoding, encoding, demuxing, streaming, filtering, converting audio files, recording live audio/video, handling video and other multimedia files. This multimedia framework is designed for command-line-based processing of multimedia files, and you can make basic edits with single-line commands.
While the program is simple to use, accessing FFmpeg to execute commands is a little confusing. Installing and using FFmpeg can take a lot of time as you need to manually open the FFmpeg folder within the command prompt or Power Shell terminal to access the FFmpeg executive file to execute relevant commands for basic editing. If you are stuck with installing and using FFmpeg on your machine, you are in the right place.
To make things simple, all you have to do is install FFmpeg and add the FFmpeg program to the Windows path using Environment variables. This way you can directly access FFmpeg from a Command prompt or Power Shell in any directory. In this article, we explain how to install FFmpeg on Windows in order to access FFmpeg directly from Command Prompt or PowerShell
Install & use FFmpeg on Windows 11/10
Get the latest FFmpeg build from the official website here. You can either download the 32-bit version or the 64-bit version that suits your system. Click the Download Build button to start downloading.
The program doesn’t work directly on Windows 11/10. You need to add a program to the system path using Environment Variables.
So navigate to the downloaded folder where the FFmpeg zip file is a store. Right-click on the Zip folder and click extract from the drop-down menu.
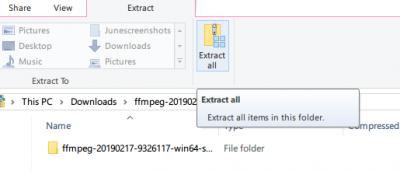
Select the folder or drive where you want to extract.
Next, rename the extracted folder. To rename the folder, right-click on a folder and click Rename from the drop-down menu with title FFmpeg-20180424-d9706f7-win64-static to FFmpeg.
Copy the FFmpeg folder and navigate to C drive. Paste the folder to the root of C drive.
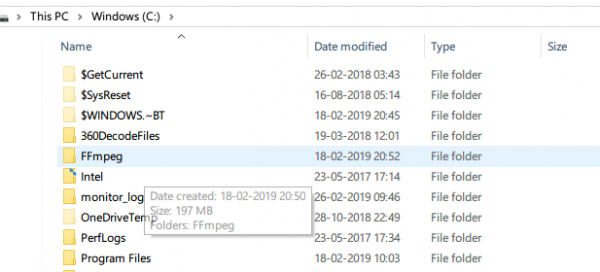
Once done, the next step is to enable FFmpeg using Command Prompt.
Add FFmpeg to Windows path using Environment variables
To use FFmpeg in Command Prompt, you need first to add the bin folder containing the FFmpeg executable file to your Windows path
In the Windows search menu, type Edit the system environment variables and click Enter. This will open the system properties window.
Navigate to Advanced button and click Environment Variables at the bottom of the window.
In the Environment Variables window, Select the variable Path and click Edit to change the Path variable.
Click New and type the path of FFmpeg folder “C:\ffmpeg\bin\” and click OK.
Type the path directory according to the drive or folder where you have placed FFmpeg folder.
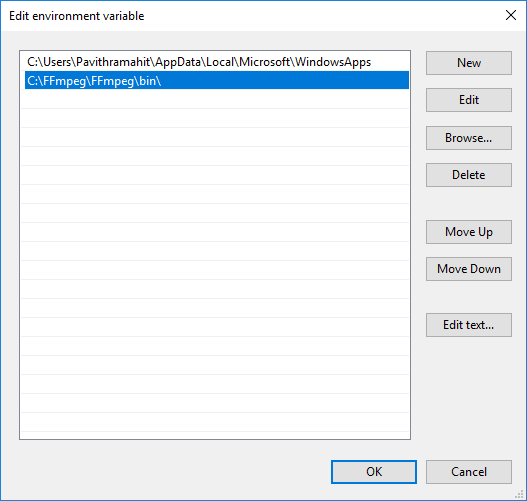
Once done, the path gets added to the Environment variables. Click OK to apply changes.
Verify FFmpeg path in Command Prompt
Launch Command Prompt and type the command FFmpeg in the command prompt terminal and hit Enter.
If the FFmpeg is added properly to Windows Path, the command prompt will display the details about FFmpeg like its version number, configuration, etc.
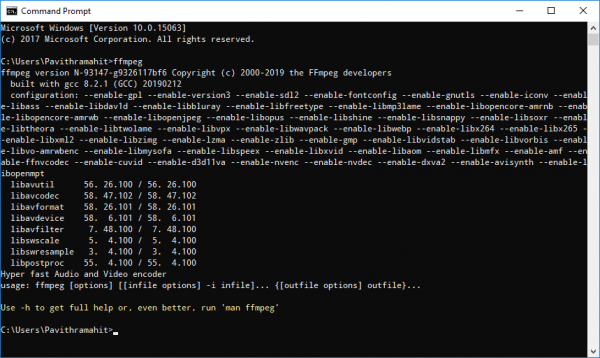
If you weren’t successful, it only means that your command prompt did not recognize the commands. Cross-check to see if you have added the FFmpeg folder to the system path properly.
Read: Fix Audacity FFmpeg error on Windows PC.
That’s all!
Leave a Reply