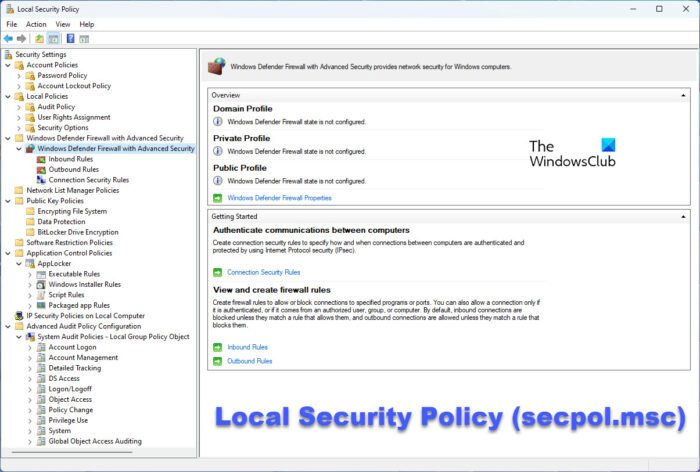
In this post, we will show you how to open the Local Security Policy on Windows 11/10. Secpol.msc or Local Security Policy editor is a Windows administration tool that allows you to configure and manage security-related policies on a local computer. It shows a subset of policies (registry entries) available in the Group Policy Editor, such as password and account lockout policies, software restriction policies, application control policies, network-related policies, etc. If you don’t know how to access the Local Security Policy (secpol.msc) on Windows 11/10, we show you eight ways to do that.
Notes:
- The Local Security Policy module (or the entire Group Policy module) is only available in Windows 11/10 Enterprise, Pro, and Education editions. If you have the Home edition of Windows 11/10, you will have to add it separately.
- You should have admin rights to access the Local Security Policy.
How to open Local Security Policy (secpol.msc) on Windows 11/10
In this section, we will see how to open Local Security Policy (secpol.msc) on Windows 11/10 PC using the following methods:
- Using Windows Search.
- Using Run prompt.
- Using Control Panel.
- Using Windows File Explorer.
- Using Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell.
- Using Windows Task Manager.
- Using Local Group Policy editor.
- Using Desktop Shortcut.
Let us have a look at these methods in detail.
1] Using Windows Search
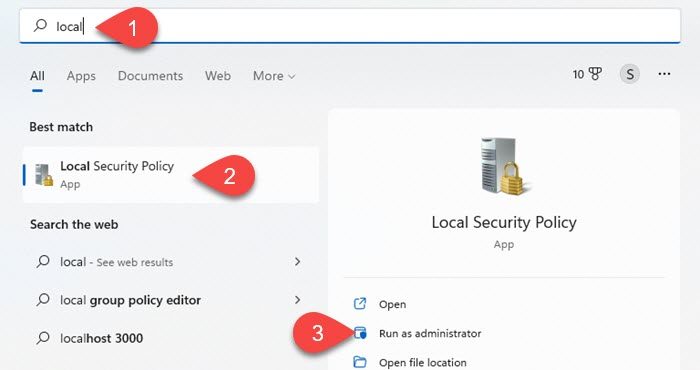
- Click on the Windows Search icon in your taskbar area.
- Type ‘local security policy’. Local Security Policy app will show up on top of the search results.
- Click on the Run as administrator option on the right panel.
2] Using Run prompt
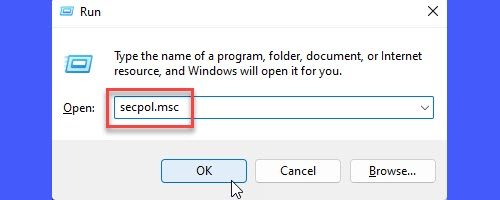
- Press the Win + R key combination.
- In the Run dialogue box that appears, type secpol.msc.
- Press the Enter key.
3] Using Control Panel
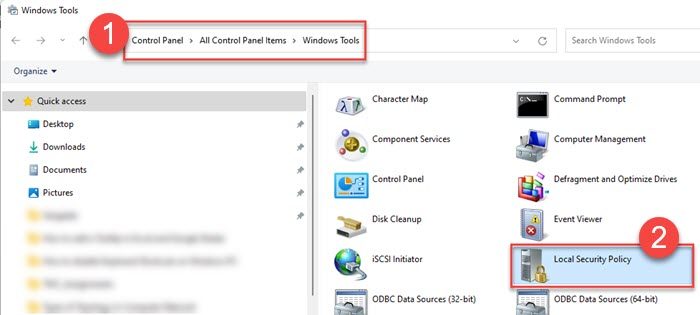
- Click on the Windows Search icon.
- Type ‘control panel’.
- Click on Open on the right panel to open Control Panel.
- Switch to the Small Icons view in the Control Panel.
- Click on Windows Tools.
- Then click on Local Security Policy.
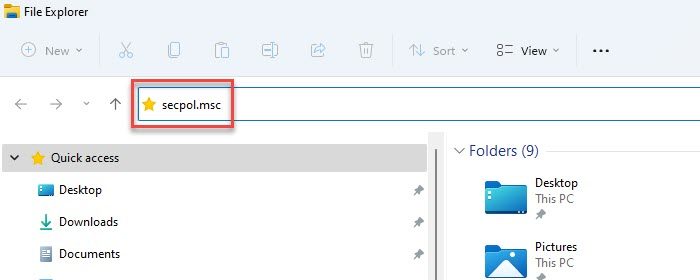
4] Using Windows File Explorer
- Click on the Windows Search icon.
- Type ‘file explorer’.
- Click on Open on the right panel to open File Explorer.
- Type secpol.msc in the address bar.
- Press the Enter key.
Also Read: Best Windows 11 File Explorer Tips and Tricks.
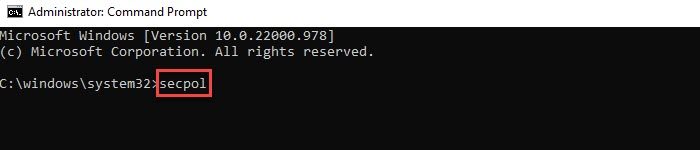
5] Using Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell
Command Prompt and PowerShell are Windows Command-line tools. You can use either of them to open Local Security Policy (secpol.msc) on Windows 11/10. Here’s how to do that:
- Click on the Windows Search icon.
- Type ‘command prompt’ to open Command Prompt or ‘powershell’ to open Windows PowerShell. Make sure to run the app as administrator.
- Click on Yes in the User Account Control prompt.
- In the Command Prompt/ PowerShell window, type secpol.
- Press the Enter key.
Read: What is AuditPol and how to enable and use it?
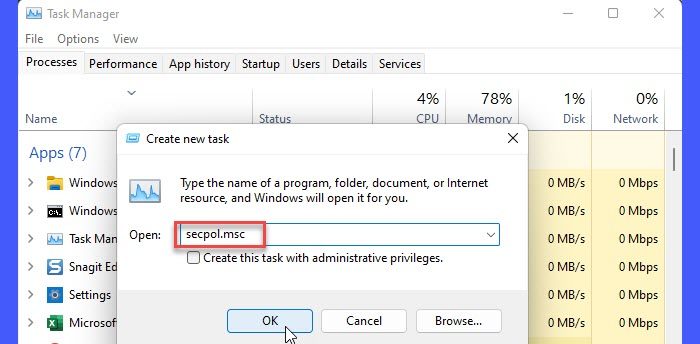
6] Using Windows Task Manager
- Right-click on the Start menu icon.
- Select Task Manager.
- Click on the File menu.
- Select Run new task.
- In the Create new task window, type secpol.msc.
- Press the Enter key.
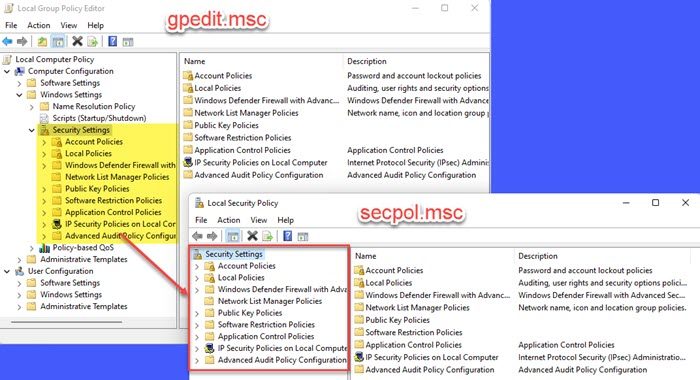
7] Using Local Group Policy editor
- Press the Win + R key combination.
- In the Run dialogue box, type gpedit.msc.
- Press the Enter key.
- In the Local Group Policy Editor window, navigate to the following path: Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings.
As you can see from the above picture, the policies available in the Local Security Policy module are essentially a subset of the policies available in the Group Policy Editor. So you can access these policy settings from the Group Policy Editor on your Windows 11/10 PC.
8] Using Desktop Shortcut
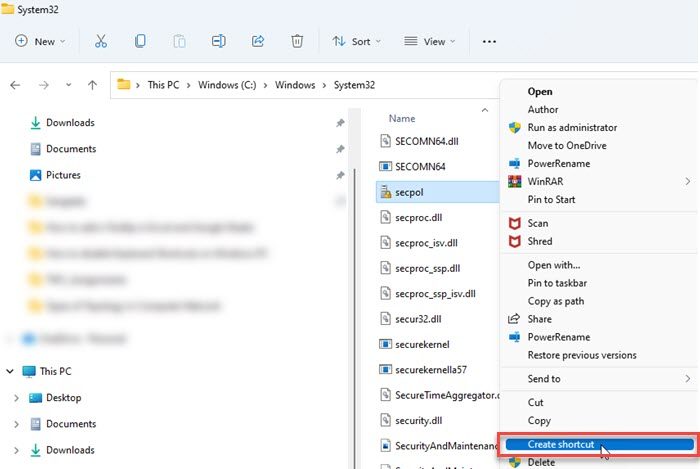
You can also create a desktop shortcut to quickly launch the Local Security Policy editor. Here’s how to do this:
- Open File Explorer.
- Navigate to the following path: C:\Windows\System32.
- Search for secpol.
- Right-click on it and select Create shortcut.
- The shortcut will appear on the desktop. Double-click on it to launch the Local Security Policy editor.
How to Enable SecPol.msc in Windows 11/10 Home?
To enable secpol.msc, you need to run a script on your Windows 11/10 Home PC. Here’s how you can do it:
- Open Notepad.
- Copy the following script into a new Notepad file:
@echo off pushd "%~dp0" dir /b %SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\Microsoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientExtensions-Package~3*.mum >List.txt dir /b %SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\Microsoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientTools-Package~3*.mum >>List.txt for /f %%i in ('findstr /i . List.txt 2^>nul') do dism /online /norestart /add-package:"%SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\%%i" pause - Click on File > Save as.
- In the Save as dialogue box, select a location to save the file.
- Enter gpedit-enabler-file.bat in the File name field.
- Select ‘All files’ in the Save as type field.
- Click on the Save button.
- Go to the location where you’ve saved the file.
- Right-click on the file and select Run as administrator.
- The script will start running in the Command Prompt.
- Wait for the script to finish.
Now you have both the Group Policy Editor and the Local Security Policy enabled on your Windows 11/10 Home PC.
Read: Local Security Policy missing
How to Reset All Local Security Policy Settings to Default?
- Open the elevated command prompt.
- Enter the following script in the Command Prompt window:
secedit /configure /cfg %windir%\inf\defltbase.inf /db defltbase.sdb /verbose
- Press the Enter key.
- Reboot your PC.
Please note that when you reset the Local Security Policy using the above script, any local user accounts you have created under Family & other users will be removed from the Local Users and Groups section on your Windows PC. So you will not see those accounts when you log in to Windows. You have to add those users back to the Local Users and Groups section to allow them to access your computer.
Where is Local Group Policy Editor in Windows 11?
Local Group Policy Editor is an in-built utility that is available in Windows 11 and most of the other older versions of Windows. You can open the Local Group Policy Editor using Taskbar search box, Run prompt, etc. To use open it using the Run prompt, type Win+R, type gpedit.msc, and hit the Enter button.
Read Next: How to repair a corrupt Group Policy in Windows 11/10.