Windows Registry is a hierarchical database. It holds information related to settings, options, and other values for software and hardware on your system. Windows allows users to make changes in the Registry using a REG file. If the user follows a standard format, one can run Registry (.REG) File as administrator and make the changes.
Best Practices and Precautions before running a REG File
Before you go ahead and run a registry file, here are some practices and precautions to keep in mind:
Back up the Registry
As mentioned earlier, Windows Registry is a hierarchical database with configuration details for many Windows application settings. So whenever you change the Windows registry, any wrong configuration can lead to several issues.
For instance, you may encounter the Blue Death of Screen error; some applications might not work correctly, and so on. So in case things go out of your control, you will be able to restore the backup.
To take a Windows Registry backup, here is what you have to do:
- Press Windows Key + R to launch RUN.
- Type regedit and press Enter key.
- Go to File> Export.
- Choose a file location, name your backup file, and save it.
- To restore the backup, select the Import option under the File menu.
Review the contents of the Registry file
Before you run any Windows registry file, make sure to prevent the contents and ensure that there is nothing wrong.
Reviewing a registry file isn’t complicated; you can right-click the reg file and open it using Notepad.
Just run a quick look over the File and see what it says. If you find anything suspicious, a quick search will help you out.
Run Antivirus scan
Thirdly, you must run a quick antivirus for potential security threats, especially if you downloaded any registry settings online. While registry files cannot install malware, they can be quarantined if malware or viruses pose as REG files.
Related: Windows Registry Editor Tutorial, Tips and Features
When will you need to run .REG files as Administrator?
- When modifying system settings through the registry changes
- Resolving permission issues.
- Modifying security settings or configuring permissions
- Import complex or extensive registry modifications across multiple computers.
- Apply Group Policy-related registry changes.
How to run Registry (.REG) file as administrator
Running a registry or the REG file as an administrator on Windows 11/10 isn’t complicated. And there are four quick methods to do so, these are:
- Windows Context Menu or Double-Click
- Using Command Prompt or Windows Terminal or PowerShell
- Using Task Manager
- Nirsoft’s AdvancedRun
Make sure you have a backup or a system restore in place.
1] Windows Context Menu or Double-Click
It is the easiest way to run a REG file. You must double-click on the REG file for your permission to see a UAC prompt. Click on the Yes button to run the REG file.
Alternatively, you can also right-click on the REG file and select Open to launch it, and you will see a prompt screen asking for your permission.
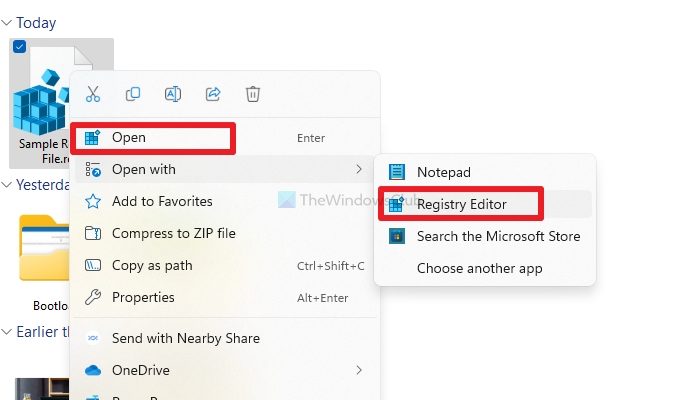
Another option that you can use is the Registry editor, for this follow the below steps:
- Go to Windows search, type registry editor and right-click on it and select Run as administrator.
- From Registry Editor, go to File> Import.
- Select your REG file and import it.
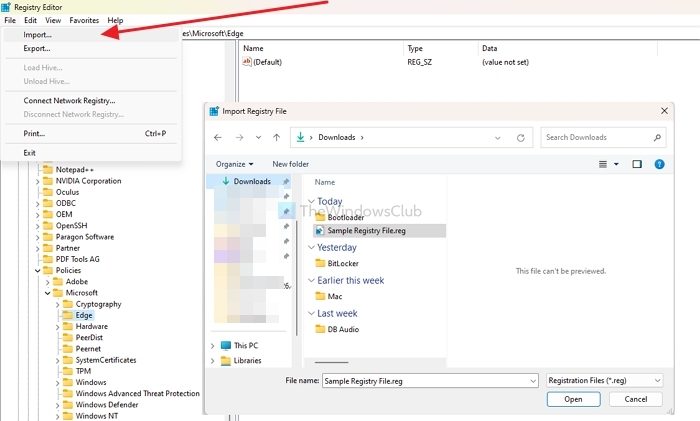
2] Using Command Prompt or Windows Terminal or PowerShell
The next option is to run a REG file using any Terminal programs on your Windows. You can use any application like Command Prompt, Windows Termina,l, or PowerShell. To get started, follow these steps:
- Press Windows Key + X to access the Quick menu.
- Select Windows Terminal (Admin) to launch the program as administrator.
- Next, navigate to the folder where your REG file is located.
- Now run the following command to install your REG file:
regedit /s YourFile.reg
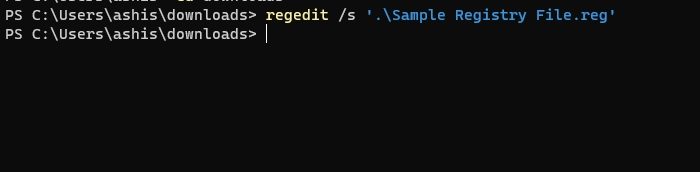
- Make sure to replace YourFile.reg file with your file name, and you are done.
Also, note that the terminal won’t show any confirmation message. Instead, when the REG file is imported, your PC screen will get refreshed, confirming the successful process.
3] Using Task Manager
Task manager allows you to run new tasks with admin privileges, including the Registry file. Follow the steps to do it:
- Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc on your keyboard to open the Task Manager
- On the Task Manager, click the File menu, and select Run new task. It will open the Create new task dialog box.
- In the Create new task dialog box, check the box that says Create this task with administrative privileges. This ensures that the REG file is executed with elevated permissions.
- Click the Browse button in the Create new task dialog box and navigate to where the REG file is saved. Select the file and click Open.
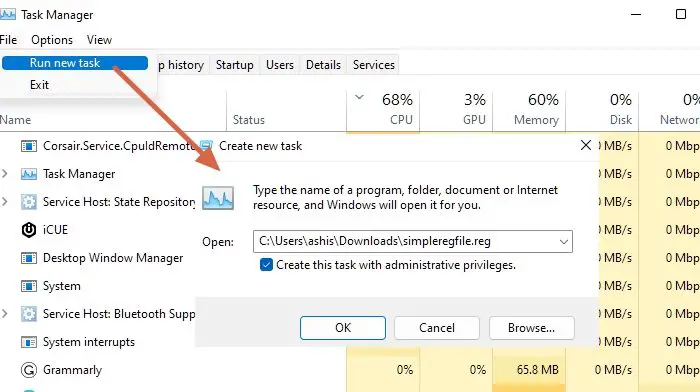
- After selecting the REG file, click the OK button in the Create new task dialog box.
The REG file will be executed with administrator privileges, and the registry changes will be applied.
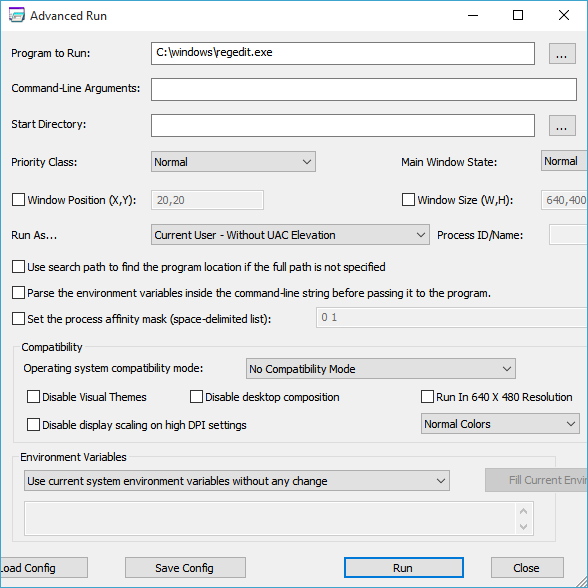
4] Nirsoft’s AdvancedRun
If you are more comfortable using software to run programs with admin permission, then the popular software website Nirsoft offers AdvancedRun. Once you download the software, set up the program or register file, and ensure to choose run as admin. Check out our detailed guide on how to use it.
Conclusion
So that was all for how to run Registry (.REG) file as administrator. Running a registry file is super easy. Just double-click on it, and you are good to go. However, do make sure to take a backup of your registry settings, and when adding a new registry file imported from other computers or downloaded from the internet, run an antivirus check to be on the safer side.
How do I run a .reg file from a batch file?
It is similar to running it from the Windows Terminal. You must write a step-wise command in the BAT file and then execute it. Here is an example of importing a REG file using a batch file.
@echo off echo Importing Registry files... reg import "C:\path\to\examplefile1.reg" reg import "C:\path\to\examplefile2.reg" echo Registry files imported successfully.
Save the file as BAT and change the registry file name as required.
How do I create a .reg file?
The format of a REG file is relatively straightforward. It consists of a set of registry keys and corresponding values identified by a path. Here’s an example of a REG file:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Example] "Setting1"="Value1" "Setting2"=dword:00000008 "Setting3"=hex:12,29,35,46
The file begins with a header line specifying the version of the registry editor. The most common version is “Version 5.00”.
In the example above, [HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Example] specifies an ” Example ” key under the “Software” key of the current user’s hive.