You can use the net use command to connect to a shared resource, such as network printers, mapped drive, etc., in your local area network. If you are not familiar with this command, this guide will be handy for you to learn more about the net use command, which is quite useful for managing networked devices.

Before getting started with the workflow, you must know the availability of this command. For your information, you can use this command on almost any version of Windows, including Windows 11, Windows 10, and earlier versions. As it is a command-line tool, you must use the Command Prompt. However, you can also use the Command Prompt instance in Windows Terminal to get the same thing done.
The net use command helps you connect to, configure, manage, and remove any device from the shared resources. The two most common shared devices are mapped drive and printer. That said, you can configure or remove any mapped drive and network printer with the help of the net use command on your Windows computer.
Net Use command parameters
There are mainly thirteen parameters you can use with the net use command. They are:
- devicename: You can use this parameter to specify a device. Whether it is a mapped driver or network printer, you can select it using this parameter. That being said, it is probably the most common parameter you need to use. For your information, you need to specify the drive letter or shared printer name while using this command.
- /home: It lets you connect to the home directory.
- \\computername\sharename: It helps you select a specific folder of a shared computer or mapped drive.
- volume: It is handy when you use the NetWare server. If so, you can specify the volume using this parameter.
- password: When accessing a shared resource, you might need to enter a password to connect to the device. This parameter helps you enter the password.
- /user: By default, the net use command uses the current username to connect to a shared device. However, if you want to connect to a network drive or something else with other usernames, you can use this parameter.
- DomainName: It helps you select the domain name if you do not want to use the current domain.
- UserName: It lets you select the username you want to sign in to.
- DottedDomainName: In case you need to use the fully qualified domain name to connect to a network device, this parameter helps you do that.
- /savecred: The cred stands for Credentials. That said, it helps you save a credential to use in the future.
- /smartcard: If you have the smart card installed, you can specify it with the help of this command.
- /delete: It helps you cancel all the network connections at once.
- /persistent: {yes | no}: If you want to save a persistent connection, you need to use the yes command and vice versa. For your information, deviceless connections are nonpersistent.
How to use Net Use command in Windows 11/10
To use Net Use command in Windows 11/10, follow these steps:
- Press Win+X to open the WinX menu.
- Select Windows Terminal from the list.
- Enter the net use /? Command to find all the parameters.
- Enter other commands as you need.
To learn more about these steps, continue reading.
At first, you need to open the Command Prompt or the Command Prompt instance in Windows Terminal. For this example, we are about to use the Windows Terminal. Therefore, press Win+X, and select Windows Terminal from the list.
Once it is opened, enter net use /? command to find all the parameters you can use.
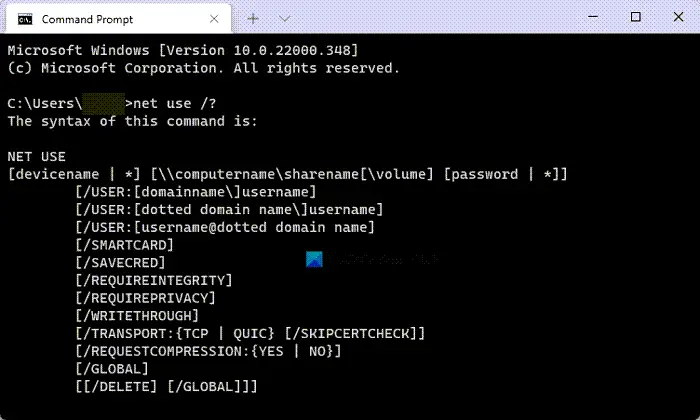
Following that, you can enter a command like this:
net use d: \\blog\documents
You need to follow the aforementioned parameters or the parameters shown after entering the net use /? command.
How do I map a network drive using net use command?
To map a network drive using net use command in Windows 11/10, you need to use the following command:
net use d: \\blog\documents\User
Before entering the above-mentioned command, don’t forget to replace the D with the network drive, path of the directory, and username.
That’s all! Hope this guide helped you use the net use command without any problem.
Read: How to use Net User command for administrators in Windows
Leave a Reply