Every time you run an application on your PC, a Prefetch file that contains information about the files loaded by the application is created by the Windows operating system. The information in the Prefetch file is used for optimizing the loading time of the application the next time that you run it. In this post we will show you how to open Prefetch Folder and view Prefetch Files in Windows 11/10.

What is Prefetch Folder in Windows
Windows uses this directory to speed up launching applications. It analyzes the files you use during startup and the applications you launch, and it creates an index to where those files and applications are located on your hard disk. Using this index, Windows can launch files and applications faster.
How to view Prefetch Files in Windows
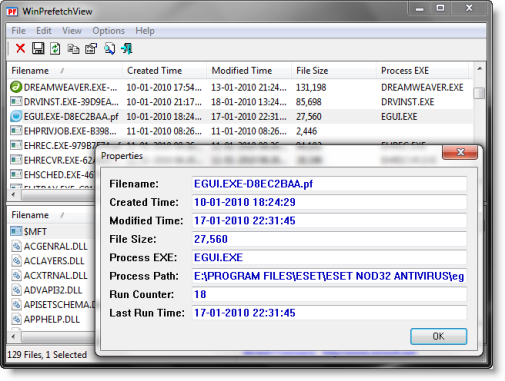
WinPrefetchView is a small portable freeware utility that reads the Prefetch (.pf) files stored in your system and displays the information stored in them. It is available here.
By looking in these files, you can learn which files every application is using, and which files are loaded on Windows boot.
This utility works on any version of Windows, from Windows XP to Windows 11. Earlier versions of Windows are irrelevant for this utility because they don’t use Prefetch files.
If, when you run the app you cannot see any files in your prefetcher, you may have to take ownership of your C:\Windows\Prefetch folder. You may use UWT to do so easily via the right-click context menu.
Tweak Prefetch Files
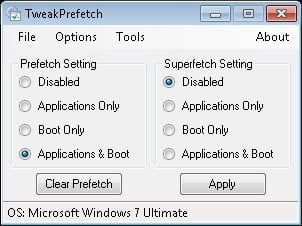
TweakPrefetch is an easy-to-use application that is designed to manage your system’s fetching. It allows the user to set separate parameters for Prefetch and Superfetch. It is available here.
If you notice that Windows won’t rebuild the “Layout.ini” file after you have cleaned the Prefetch folder, or maybe you just want to update it to your latest startup configuration, you can force the process using the “Rebuild Layout.ini” function in the “Options” menu.
TweakPrefetch will also detect the wrong parameters for Prefetch and Superfetch and will let the user fix them with a single click. Version 3.0, implements a fetching configuration wizard, which will help less experienced users to find the optimal Prefetch and Superfetch settings for their system and needs.
For the regular Windows user, however, the Prefetcher is best left alone!
Some utilities have the option to clear the prefetcher. Should you choose to use this option of ‘clearing prefetcher‘, be ready to run an ‘un-optimized’ windows for a little while. As mentioned earlier, the Prefetcher is best left alone! In any case, Windows cleans it at 128 entries down to the 32 most used application’s prefetch files.
That’s it. I hope this helps.
Where are Prefetch files stored on Windows 11/10?
The prefetch files are located inside the Prefetch folder in the C drive. The complete path of the Prefetch files is:
C:\Windows\Prefetch
Copy the above path and paste it into the address bar of File Explorer. After that, hit Enter. Alternatively, you can also paste the above-mentioned path in the Run command box and click OK. To open the Prefetch folder, you need administrative rights. Therefore, you have to sign in to Windows with your Administrator account.
Why can’t I access my Prefetch folder?
Permission issues are one of the most common causes for not being able to access the Prefetch folder. Therefore, make sure that you are signed with your Administrator account. If despite signing in to your Administrator account, you cannot access the Prefetch folder, take full control of it. But you can only do this if you are signed in with your Administrator account. Take these steps to open the Prefetch folder:
- Open Explorer and go to C:/Windows.
- Right-click on the Prefetch folder and select Properties.
- Click on Security tab from the top and under Group or user names click on Edit.
- Now click on Add and type Everyone.
- Next, click on Check names and click OK.
- Select everyone and under Allow select Full control.
- Click on Apply and OK.
Now see if you can open the Prefetch folder.
Read next: What is the ProgramData folder in Windows?