Computer memory plays a vital role in having quick access to applications and programs. The computer memory or RAM is used by the system processor to store the data. It is a volatile memory on a motherboard that stores the system’s operating system and programs for quick access. Your system processor continuously loads the data from the hard disk to the RAM before execution. But sometimes, you may need to buffer a high-quality video, video editors, 3D structures, and new games on your Windows PC.
What is dedicated VRAM?
Graphics-intensive applications and programs use a large space of system memory for rendering graphical data with high quality, color, clarity, and definition to the display. In these cases, your system may fall into a shortage of RAM and struggle to buffer high intensive graphics programs, as your graphics card shares the system memory. Unless you need to buffer high-end video applications, your PC normally works with the RAM. Otherwise, to buffer the high-quality visual display to your system monitor, you will require a special type of memory called Video RAM (VRAM).
Video RAM is dedicated to processing high-intensity video faster than system RAM. Graphics cards or GPUs use Video RAM (VRAM) built on them to store images and video data. VRAM is also called virtual RAM and is used as GPU memory for easily processing graphical applications, games, complex textures, and 3D graphics.
However, some applications like the latest games and videos may require you to play videos at 1080p or 4k resolution that needs plenty of VRAM. Moreover, the VRAM processes more pixels for higher resolution images to display them better. That being said, modern games require increased detailing and the exact system requirements to launch them on your system monitor and, having an insufficient VRAM will lead to a heavy overload of GPU.
Why do you need VRAM?
If you have an insufficient VRAM, you won’t be able to run modern games. In such a case, you will require a graphics card having plenty of VRAM. To easily load complex textures with high resolutions images, you may need to increase the amount of dedicated video RAM on your graphics card.
Increase dedicated Video RAM in Windows 11/10
We next explain how to change the amount of video RAM on your Windows 11/10 system. You can reallocate the system RAM as the dedicated video RAM on the Windows PC either through BIOS settings or through registry settings.
Check the amount of VRAM on your graphics card
Before trying out the methods to increase the VRAM, you need to check how much dedicated video memory your graphics card has in Windows 11 and 10.
In Windows 11:
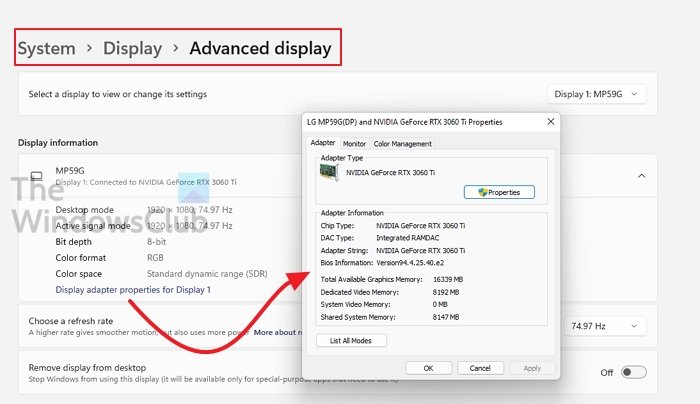
- Open Settings using Win + I keys
- Navigate to System > Display > Advanced Display
- Select the monitor and then click on Display Adapter properties for Display
- It will open the properties window where you can change Adapter, Monitor, and Color Management options.
- Note the amount of Video RAM or Video Memory.
In Windows 10:
Go to the Start menu and click Settings. Navigate to System and click Display on the left sidebar of the System Settings.
Scroll down the Display menu and click on the option Display adapter properties at the bottom of the box.
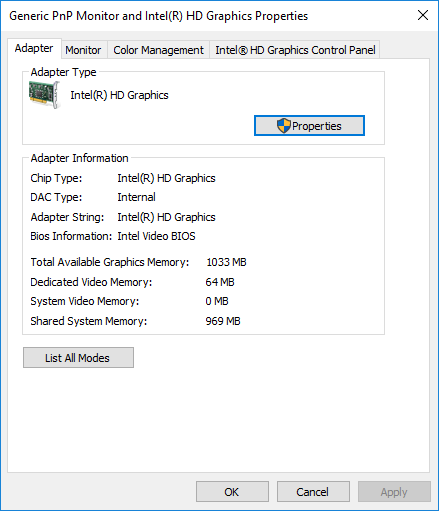
In a new pop-up window, you will see the adapter type used on your system and other graphics information in the Adapter tab. Check the total amount of allocated space for the dedicated video RAM under Adapter information.
Increase the dedicated video memory on your graphics card from BIOS
This is the recommended method to reallocate the memory of VRAM allocation. However, this doesn’t work for all the motherboards, and you may not be allowed to reallocate memory on your PC all by yourself. Still, you can try to change the BIOS settings and check if you have enough privilege to change the amount of dedicated video RAM on your PC.
Restart your PC and press the BIOS key – F2, F5, F8, or Del key repeatedly during the bootup.
In the BIOS menu, go to Advanced Features or similar options.
Now click on video/ Graphics settings or VGA Share Memory Size. If you don’t find these options, look for a category with a similar option.
Adjust the option that best suits your task. The default memory allocated to the GPU is usually 128MB. You can scale up the preallocated VRAM to 256MB or 512 MB.
Save the changes and restart your system.
Increase the dedicated video memory on your graphics card using Registry Editor
Depending on the applications you run, the system automatically adjusts the amount of video RAM it needs. And thus, the adapted information showing the amount of VRAM used on your graphics card is not always genuine. However, to run some applications, you will need more VRAM. In such a case, you can simply replica the amount of VRAM to substitute for the amount of VRAM your system needs to run the application. You are not increasing the value for real, but you scale up the amount of VRAM to a value to serve as a substitute for the memory requirements to start the game or an application.
Follow the below steps to reallocate RAM as VRAM for integrated Intel graphics cards.
Open Run and type regedit. Navigate to the following path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Intel
Right-click on the Intel folder. Choose New and click on Key. Name the key as GMM.
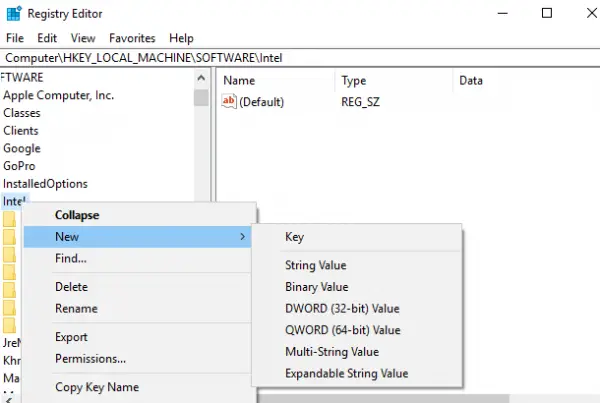
Select the new GMM folder on the left sidebar.
Right-click on the right side of the Window and click on New from the drop-down menu.
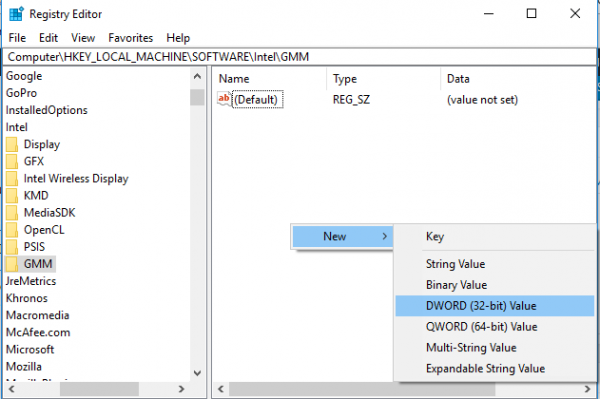
Choose the Dword (32-bit ) and name it as DedicatedSegmentSize.
Double-click on the DedicatedSegmentSize and click on the radio button with the option Decimal to set the base to Decimal.
Enter the number of megabytes of RAM you want to allocate as VRAM in value data. Make sure you type a number within the range from 0 to 512.
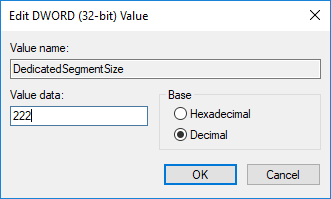
Save to apply the changes and Restart the system.
Can you allocate RAM to VRAM?
If you mean increasing the amount of VRAM by allocating some from your Physical RAM, this may happen automatically. However, the impact may not be huge, considering VRAM is much faster compared to the physical RAM. So you cannot do it, but let the system work for you.
How much RAM do integrated graphics use?
It will vary. Since integrated graphics cards don’t have their own memory banks, they draw them from physical memory. This depends on the usage. Rendering a video will take up more memory, but it will be a lot less when playing a video.
How much RAM should I allocate to Integrated Graphics?
If given an option, you can set up part of the RAM dedicated to the integrated graphics. However, make sure you don’t dedicate a lot of them. As per the current scenario, you need at least 8 GB of RAM. If you have 8 GB, set up 1 GB of dedicated RAM; if you have 16GB, you can set up 4GB of RAM.
Prove me wrong, but isn’t dedicating system RAM to the graphics card kind of useless. I mean if you have a dedicated GPU with hopefully GDDR5 VRAM then that should be good enough. Even if your VRAM does run out it automatically starts using the system memory. The only place I would see this being somewhat useful is with GPUs that don’t have their own VRAM like (I think) the integrated graphics shown here. And it could actually make things worse by making part of the system memory unusable by the actual system. For example if you had 8GB of RAM and dedicate 2GB of that you would lose them for use in non-graphics intensive tasks. But of course it’s your computer and your RAM to do with as you will. This is just my opinion on the subject.
Damian, since RAM is not same as VRAM the latter becomes a deciding factor in some cases. On the other hand GPU’s with higher VRAM are expensive and increasing the dedicated VRAM is an affordable workaround. As you said dedicating more video RAM depends on ones preferences and the trade off is decreased RAM for other non graphic intensive task.
I need more then 512 Mb, i need at least 1Gb. How do i do this?