Mozilla has shipped the support for Windows Group Policy Support. Mozilla Firefox uses autoconfig files that support an automatic configuration system for Firefox installations and hence this makes it compatible with the supported desktop platform. This is all supported by a new Policy Engine in Firefox that reads data directly from the Registry. Group Policy Objects create this Registry and applies the policies if they are found to be absolutely valid.
Integrate Firefox with Group Policy in Windows 11/10
In order to check all the policies, you need to view the policies using the Group Policy Editor.
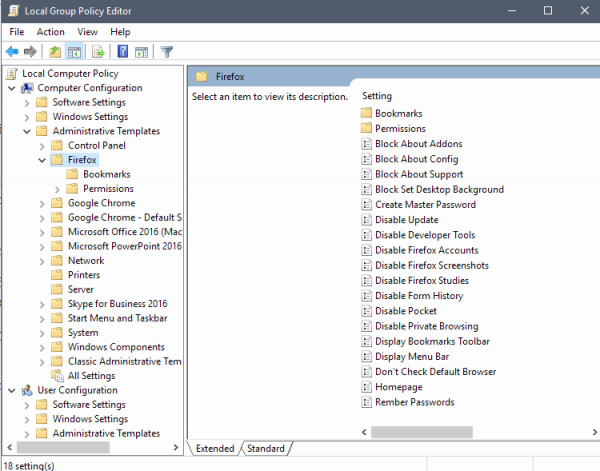
To view these policies, open Group Policy Editor.
To do this, open Run and type in gpedit.msc and hit Enter.
Or just search for Edit Group Policy in Search box and select the Entry to open the Group Policy Editor.
Then navigate to this location:
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Firefox and User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Firefox
Then the following policy template files are added to the directories on Windows:
- Block About Addons – prevents access to about://addons to manage addons.
- Block About Config – prevents access to about://config.
- Block About Support – prevents access to the troubleshooting page about://support.
- Block Set Desktop Background – users cannot set the wallpaper of the desktop using Firefox.
- Create Master Password – prevent the creation of a master password.
- Disable Update – block Firefox from updating.
- Disable Developer Tools – turn off the Developer Tools in the browser.
- Disable Firefox Accounts – prevent sign-in to accounts and syncing.
- Disable Firefox Screenshots – turn the Screenshots tool off.
- Disable Firefox Studies – turn participation in Firefox studies off.
- Disable Form History – prevent Firefox from remembering the form history.
- Disable Pocket – turn off Pocket in Firefox.
- Disable Private Browsing – block Private Browsing functionality.
- Display Bookmarks Toolbar – show the Bookmarks Toolbar by default.
- Display Menu Bar – show the Menu Bar by default.
- Don’t Check Default Browser – block checks for default browser.
- Homepage – set a homepage (or multiple), and optionally disallow the changing of those.
- Remember Passwords – allow or disallow the saving of passwords.
- Bookmarks – Set default bookmarks.
- Permissions: Addons – Allow addon installation on specified URLs.
- Permissions: Cookies – Set URLs to allow or block cookies on.
- Permissions: Flash – Set URLs to allow or block Flash on.
- Permissions: Popups – Allow popups on selected sites.
The Enterprise Policy Generator addon is available here. You can learn more about this new feature of Firefox here.
This post will show you how to configure Google Chrome using Group Policy.
How do I make Firefox my default browser in Group Policy?
To make Firefox your default browser in Group Policy, open the Group Policy Management Editor and navigate to Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Set Program Associations. Configure the default associations using an XML file that specifies Firefox as the default. Ensure the XML file path is accessible for the policy to apply.
How do I configure Firefox to use Windows Certificate Store via GPO?
To configure Firefox to use the Windows Certificate Store via Group Policy, first download the Firefox policy templates. Then, use the Group Policy Editor to import these templates. Navigate to the Firefox settings and enable the “Use Windows Certificate Store” option under Certificate settings. Apply the policy to the desired organizational units.
Read next: How to disable add-on installation in Firefox using Group Policy.