This post will cover ways to enable and fix the missing Local Security Policy in Windows 11/10. Many Windows Home Edition users have reported that the Local Security Policy Manager (secpol.msc) is missing from their systems running Windows 11 or Windows 10. If you are trying to open the Local Security Policy Manager using the Run dialog box, you get the error message:
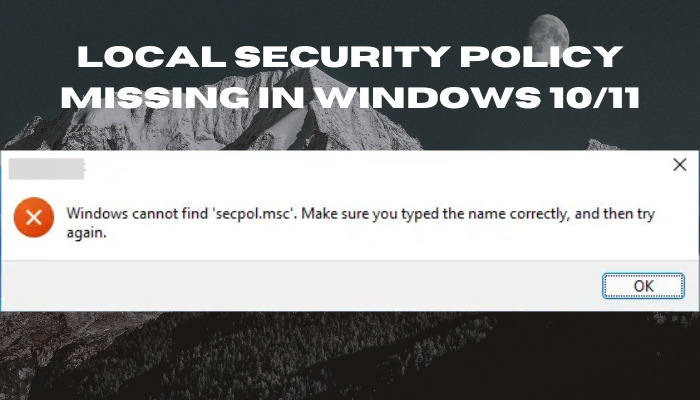
Windows cannot find ‘secpol.msc’. Make sure you typed the name correctly and then try again.
This means that your Windows OS is missing secpol.msc or that it’s not enabled.
Windows 11/10 comes with Microsoft Management Consoles that help users manage their operating systems. However, some consoles, like Local Security Policy Management and Group Policy Editor, are only available to Enterprise and Professional operating system users. We will assist you in resolving this issue because secpol.msc is missing in Windows Home editions. There is no need to buy another OS in order to get the consoles, you can install, find, or enable them with your current OS. Keep it here for more insights on this topic.
What is secpol.msc and why is it missing on Windows 10/11?
Local Security Policy (secpol.msc) is a management console that is used by an administrator to set and configure security settings on the host computer. For instance, an administrator can set password requirements, like the number of characters, length, and type.
The security policies also have User Account Control (UAC), which is used to prevent and control changes in the systems that are not confirmed or authorized. Secpol also grants permissions and privileges based on how a user is interacting with a computer and what they can access. If a user account has administrative permissions, they can access and edit the Local Security Policy Manager.
The Local Security Policy Manager, or secpol, is missing on your PC because you are using a Windows Home edition operating system. You will get an error indicating that Windows can’t find secpol.msc. These settings are under Group Policy Editor, which is an advanced Windows feature only found in Windows 10/11 Pro, Education, and Enterprise editions. Another reason why secpol.msc is missing is that it’s not enabled on your PC. So, you will need to manually enable it using different methods, like PowerShell commands.
Fix Local Security Policy missing in Windows 11/10
To fix the Local Security Policy missing error on your Windows, you need to install or enable secpol.msc using the command prompt or downloading a gpedit.msc script. It’s good to note that the Local Security Policy Management is a collection of settings under the Local Group Policy console. This means that when you enable gpedit.msc, you activate the Group Policy and consequently enable Local Security Policy.
You have the following options:
- Install Local Security Policy using Command Prompt
- Download and run GPEDIT Enabler
- Upgrade from Windows Home to Pro, Professional, or Education
Before you begin, check which version of Windows 11/0 you have installed. If it is Windows 11/10 Enterprise, Pro or Education and you still do not see secpol.msc, then run the System File Checker, DISM or Reset This PC to repair potentially corrupted system files. If you are using Windows 11/10 Home, then read on.
Windows cannot find ‘secpol.msc’
1] Install Local Security Policy using Command Prompt
Here, you will need to run some commands using DISM on Windows Home OS. It is a straightforward method that needs no robot to perform.
If the Local Security Policy (secpol.msc) is missing on your Windows 11/10 computer, type cmd on the search box and select Run as administrator to open Command Prompt.
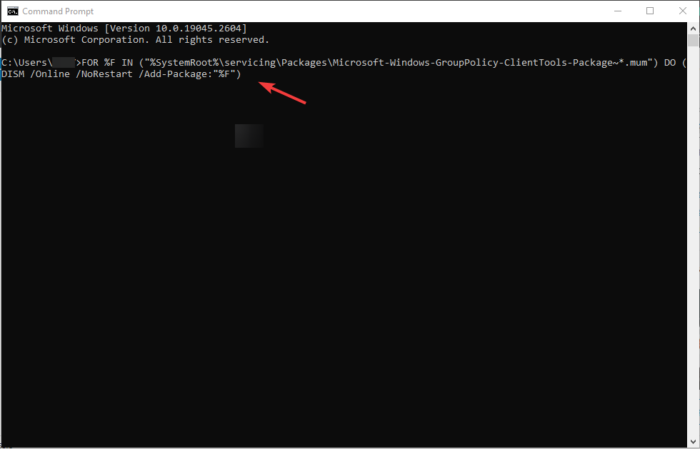
Put the following commands in the Command Prompt windows and press the Enter button after each.
FOR %F IN ("%SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\Microsoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientTools-Package~*.mum") DO (DISM /Online /NoRestart /Add-Package:"%F")
FOR %F IN ("%SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\Microsoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientExtensions-Package~*.mum") DO (DISM /Online /NoRestart /Add-Package:"%F")
Wait for the commands to run up to 100%.
Once done, restart your PC.
After that, open the Run dialog box by pressing the Windows key + R.
Type gpedit.msc and then click OK or press Enter. The error should not appear. That’s it.
The steps above will enable the Group Policy Editor and hence activate the Local Security Policy. Your OS will now have all necessary and functional policies available on Windows Enterprise, Pro, or Education versions.
2] Download and run GPEDIT Enabler BAT file
This step involves using a third-party installer. We have looked at many GPEDIT enablers and we believe many of them are safe to download. In our case, we will use a Mediafire .zip file.
To download and install gpedit.msc, create a system restore point first and then follow the steps below:
- First, download gpedit enabler BAT file from our servers
- Locate the zip file in your Downloads folder and right-click on it, then choose Extract here.
- After extracting, you should see a GPEDIT-Enabler.bat in the folder. Right-click on the file and click Run as administrator.
- A Command Prompt window will appear and start to install gpedit.msc automatically.
- Give your PC to finish the process, it will indicate the progress in percentage.
- You will see the message Press any key to continue on the same window, go ahead and hit any key on the keyboard. This will exit the Command Prompt.
- Restart your computer and test gpedit.msc in the Run dialog box. It should open.
3] Upgrade from Windows Home to Pro, Professional, or Education
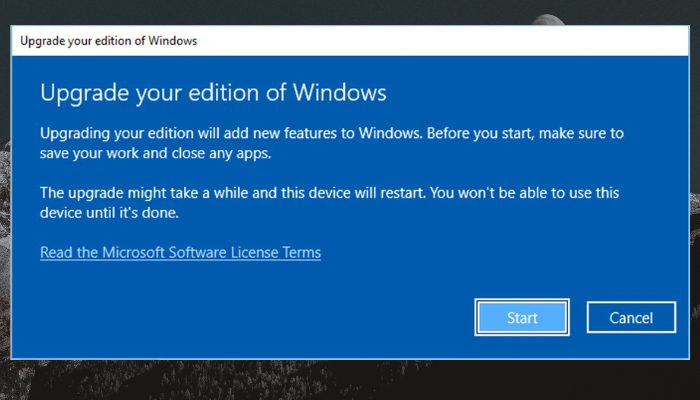
If you wish and can upgrade your Windows Home edition, you can do so. Upgrading your OS will not require any other steps because Group Policy Editor comes natively with Windows Pro, Education, and Professional versions. Here is how to upgrade your Windows Home edition:
- Go to your PC Settings by pressing the Windows key + I.
- Go to Update & Security, and then to Activation.
- Click on the Go to the Store option.
- Go ahead to buy the Pro edition of Windows 111/10
- Test gpedit.msc as we did in the methods above. It should work now.
We hope one of the methods above works for you.
How do I refresh the Local Security Policy?
To refresh the Local Security Policy manually, type gpupdate in PowerShell and press Enter. When the policy is refreshed, the local host is auto-enrolled by the certification authority (CA). Group policy is usually refreshed automatically when a user signs in to the domain user’s computer or when you restart the domain user’s computer. There is also periodic refreshment, which is performed after every 1 hour and 30 minutes.
Related: Windows cannot find GPEDIT.MSC on Windows 11
How do I import Local Security Policy?
To import Local Security Policy, open the Local Security Policy Editor and, on the left pane, right-click on the Security Settings. Click on the Import Policy option. Navigate and locate where you saved the security settings file, and then see the INF file. Click on the Open button, and then reboot your PC to save and apply the local security policy you imported. That’s all.
Leave a Reply