LocalServiceNoNetworkFirewall is a service used by Windows Defender Firewall and is a part of Windows security. In general scenarios, it doesn’t consume much memory space and resources. However, some users have complained that the LocalServiceNoNetworkFirewall service is consuming too much CPU or Power in the Task Manager of Windows 11/10. Some users reported that it consumes over 50% CPU on their PCs. For many users, it has made their system sluggish and slowed their PC making it almost difficult to use.
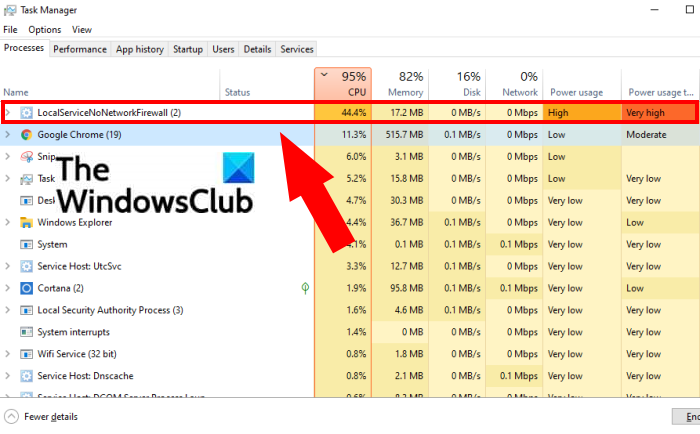
If you are dealing with the same problem, we are going to show you how you can get rid of this problem. In this post, we are going to discuss multiple working fixes that worked for users to resolve the problem. Let us check out.
Why does LocalServiceNoNetworkFirewall use so much CPU?
After analyzing several reports, here are the possible causes that may trigger this problem:
- If you are using a third-party firewall and it is conflicting with Windows Firewall, this issue can be caused.
- In case you have set up too many rules in Windows Firewall, it can result in excessive CPU usage of LocalserviceNoNetworkFirewall. You can try deleting custom firewall rules in that case.
- This issue can be caused if you are dealing with the corrupted installation of your third-party firewall program and it is conflicting with Windows Firewall. In that case, uninstalling and then reinstalling the third-party firewall might help you fix the issue.
- Another reason for this problem can be corrupted customizations or settings of the Windows Firewall. If the scenario is applicable, you can set the Windows Firewall to default configuration to resolve the problem.
Based on the scenario you think is best suited to you, you can try an appropriate fix from the guide to counter this problem.
Fix LocalServiceNoNetworkFirewall High CPU or Power Usage
Here are the methods to fix the high CPU usage of the ‘LocalServiceNoNetworkFirewall’ service on Windows 11/10:
- Restart Windows Firewall.
- Update Windows to the Latest Build.
- Disable, then Enable third-party Security Firewall and Windows Defender Firewall.
- Revert the Driver Update.
- Reset Windows Firewall to its Defaults.
- Delete the Firewall Rules.
- Reinstall the third-party security suite.
1] Restart Windows Firewall
It could be some temporary glitch of the Windows Firewall that might be causing high CPU usage of LocalServiceNoNetworkFirewall. In that case, you should be able to fix the problem by restarting Windows Firewall. To do that, you can follow the below steps:
- Firstly, open the Task Manager by using Ctrl + Shift + Esc hotkey.
- In Task Manager, go to the Services tab and locate the WinDefend (Microsoft Defender Antivirus Service) service.
- Now, right-click on the WinDefend service.
- Next, select the Restart option from the context menu.
- When the service is restarted, see if the problem is resolved now.
If the issue still persists, you will need to try some additional troubleshooting methods to fix it up. So, move on to the next potential fix.
Read: Fix error 0x8007042c for Windows Update or Firewall
2] Update Windows to the Latest Build
If you are using an outdated version of Windows OS, consider updating it to the latest build. Some incompatibility issues with OS and other system modules might be causing high CPU usage of the LocalServiceNoNetworkFirewall service. So, update your Windows and then see if the error is fixed now. Updating your Windows is recommended to improve the stability of your system and it also fixes some bugs.
To update Windows, open the Settings app and then go to the Windows Update section. Here, you can click on the Check for updates button and download and install all available updates. In case you are on the latest OS build and still encountering this problem, you can move on to the next fix.
See: Windows could not start the Windows Firewall on Local Computer
3] Disable, then Enable third-party Security Firewall and Windows Defender Firewall
Are you using more than one firewall security on your PC? If yes, the problem might be caused due to that. To counter the issue, you can try disabling both the firewalls and then enable them again.
First of all, close the third-party firewall you are using. To do that, right-click on your firewall from the system tray and click on the Exit button to close it. You can also open that Task manager and end processes related to your third-party firewall.
After that, open the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security as an administrator and then click on the Windows Defender Firewall Properties button. Now, set the Firewall State to Off for Domain Profile, Private Profile, and Public Profile. Then, click on the Apply > OK button to apply changes.
Next, you can open Windows Defender Firewall and enable/ set it to On. And then, launch your third-party firewall. See if this method fixes up the issue for you.
Related: Windows Firewall with Advanced Security snap-in failed to load
4] Revert the Driver Update
If you recently installed some driver update, there are chances that it might be conflicting with Windows Firewall. If the scenario is applicable, you can try rolling back recent driver updates and see if this resolves the issue for you.
5] Reset Windows Firewall to its Defaults
The high CPU usage of LocalServiceNoNetworkFirewall can be caused due to customizations of the firewall. For example, if you have added inbound or outbound rules or some more customizations to Firewall, it can overload your system. In that case, you can try resetting Windows Firewall to its default settings and see if the problem is fixed.
Firstly, open the Windows Security app from search and then go to the Firewall & Network Protection tab. Next, click on the Restore firewall settings to default button.
After that, go to the Virus & Threat Protection tab and then click the Manage Settings option. Then, press the Add or Remove Exclusions and tap on the Add an exclusion option, and then select Folder. Now, enter C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows Defender\ location and click on Select Folder.
Finally, close Windows Security and restart your PC to check whether the problem is resolved now.
Read: Windows Firewall can’t change some of your settings
6] Delete the Firewall Rules
If there are rules added to the Windows Firewall from a previous installation of a third-party firewall and there are conflicts with the Windows firewall’s own rules, it can cause this problem. So, you can delete the firewall rules to resolve the issue. Here are the main steps to do that:
- Open Windows Firewall with Advanced Security and from the right-side pane, click on the Export Policy to save existing policy just to be on the safe side.
- Go to the Inbound Rules tab and then delete the custom rules you want to remove. However, make sure don’t delete important rules.
- Do the same for outbound rules by going to the Outbound Rules tab. See if this fixes the issue and if not, go to step (4).
- Click on the Action menu and select the Restore Default Policy option and confirm the process.
- Close the window and then check whether the problem is resolved.
7] Reinstall the third-party security suite
If you have installed a third-party security suite and it is not installed correctly or there are some corrupted installation files associated with it, there are chances it might be conflicting with Windows Firewall and thus, causing the issue in hand. In this case, you can try reinstalling the third-party firewall or security suite that you have installed on your system. So, first, uninstall the security suite via the Settings app. Then, reboot your PC and see if the CPU usage of LocalServiceNoNetworkFirewall has slowed down.
You can later download the setup for your security suite from its official website and install it back on your PC.
Read: Windows Firewall services fail to start – Error 1079
How to reduce CPU usage by service host?
In order to reduce CPU usage by Service Host, you need to turn off the BITS service first. It is also suggested to turn off all the other unnecessary services from the Services panel. Finally, you can terminate the process from the Task Manager temporarily. For that, you can press Ctrl+Shift+Esc and find the Service Host process. Select it and click on the End task button.
Leave a Reply