Windows 11/10 users can use the inbuilt Windows Boot Performance Diagnostics to detect Windows Boot Performance problems and attempt to determine their root causes.

Many users face the problem of a slow Windows start-up. Disabling startup entries using the MSConfig utility is one easy way to make Windows start faster. Then again, some suggestions may make Windows start, run, and shut down faster. But how do you optimize performance during startup? Your Windows might start properly but may take a long time to boot. Such problems can be difficult to troubleshoot because there’s no straightforward way to monitor processes while Windows is starting. Microsoft has come up with a solution for this. To help administrators identify the source of startup performance problems and to automatically fix some problems, they have introduced Windows Boot Performance Diagnostics.
Read: Beginner’s tips to optimize Windows for better performance.
Windows Boot Performance Diagnostics
Windows 11/10 ships with the Windows Boot Performance Diagnostics tool to detect Windows Boot Performance problems and attempt to determine their root causes.
You will first have to activate it from the Group Policy Editor. To do so, type gpedit.msc in start search to open the Group Policy Editor. The gpedit.msc feature is only present in select Windows editions, by the way. You won’t see it in the Home editions.
Now navigate to Computer configuration > Administrative Template > Systems > Troubleshooting and Diagnostics > Windows Boot Performance Diagnostics.
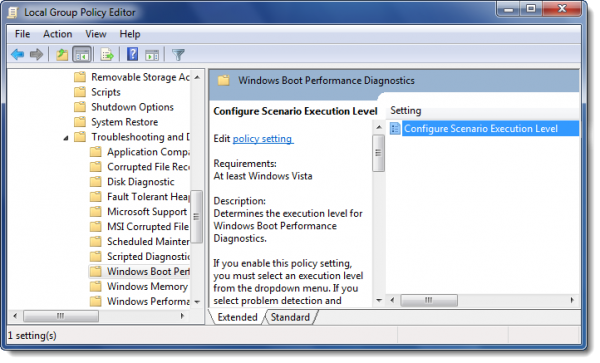
In the right panel, double-click Configure Scenario Execution level.
You may see it set to “Not configured”. Select “Enabled”.
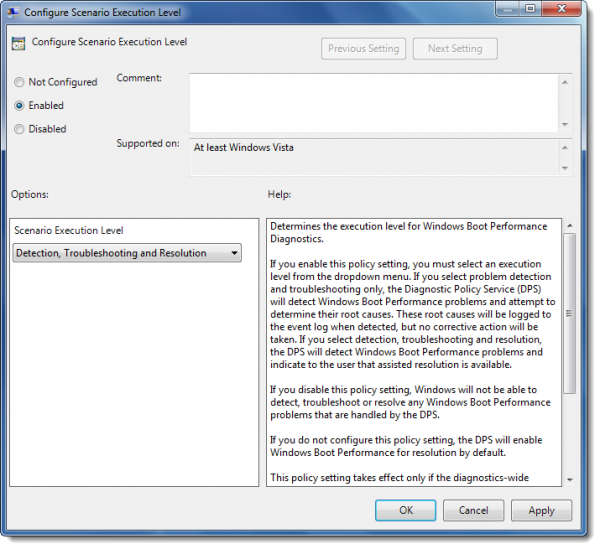
Now select Scenario Execution Level. From the drop-down menu select “Detection and Troubleshooting Only” or “Detection, Troubleshooting and Resolution”.
- If you select “Detection and Troubleshooting only” then the Diagnostic Policy Service (DPS) will detect Windows Boot Performance problems and attempt to determine their root causes. These root causes will be logged to the event log when detected, but no corrective action will be taken.
- If you select “Detection, Troubleshooting and Resolution”, the DPS will detect Windows Boot Performance problems and indicate to the user that assisted resolution is available.
Also note:
- If you disable this policy setting, Windows will not be able to detect, troubleshoot or resolve any Windows Boot Performance problems that are handled by the DPS.
- If you do not configure this policy setting, the DPS will enable Windows Boot Performance for resolution by default.
During shutdown or restart, you may see a Shutdown Tracker window.
![]()
Do note that this policy setting will only take effect when the Diagnostic Policy Service is in the running state. When the service is stopped or disabled, diagnostic scenarios will not be executed.
Read: Make Windows ignore external USB HDD during boot for faster startup
As mentioned, the Group Policy Editor or gpedit.msc is not included with Windows Home editions. It’s only available in Pro, Education, Business, Ultimate and Enterprise editions.
How do I run diagnostics on Windows boot?
To perform a diagnostic startup on Windows, use the System Configuration tool. Press “Windows Key + R”, type “msconfig” in the Run box, and press Enter. In the System Configuration window, select the “General” tab, then choose “Diagnostic Startup”. Apply the changes and restart your computer to run the diagnostics at boot.
How do I check boot performance on Windows PC?
To check boot performance on a Windows computer, use the Event Viewer. Navigate to the ‘Windows Logs’ section, then ‘System’. Filter the current log for ‘Event ID 100’, which indicates the boot duration time. Boot performance can also be analyzed using the Task Manager under the ‘Startup’ tab to see impact scores of startup applications.
This post will show you how to troubleshoot performance issues in Windows.
Many thanks for this precious post, AndyK! ^_^
Windows is forever increasing in size – and feature count. This isn’t necessarily a bad thing…
IF Microsoft would only integrate them in a way that doesn’t force us users to dig into the OS ‘ bowels like this, to make it work correctly. :-s
Best regards,
Valentin
Very Nice!
Does this work on Windows 8.1 64 bit?
Its working in 8.1 64 bit. But how do I check the logs or diagnostics?