The revelations that companies like Facebook, Google, etc. were using user data for advertisements and other purposes led to widespread public outrage and companies started justifying the act and promising users better privacy for the future. But even more, since users were mostly unaware of this fact, the news prompted them to check their Google, Facebook and Microsoft archives.
When I check my data that Google has stored, I was shocked to know that they knew everything from the locations I have been to and on what date to my call history. Obviously, privacy is important, and every user should be allowed to protect themselves from such data breaches.
Manage App permissions on Windows 11/10
Here’s how app permissions could be managed for Windows 11 and Windows 10.
Where are the App permissions located?
Windows 11

Press Win+I key together to open the settings. Alternatively, you can right-click the Windows button residing on the Task Bar and choose Setting from the list of options displayed.
Scroll down to Privacy & security heading in the side panel.
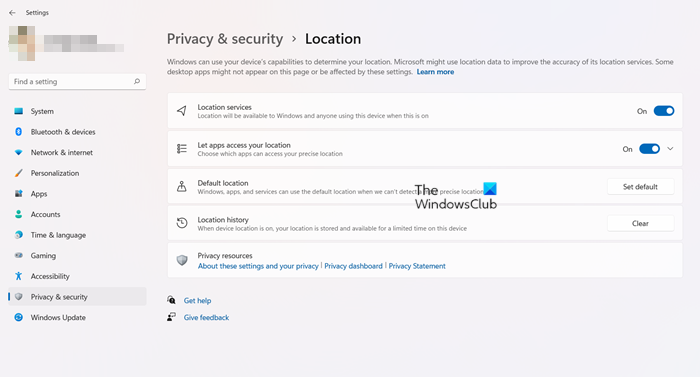
Switch to the right pane and go to the App permissions section.
Here, you’ll find settings related to each heading.
Windows 10
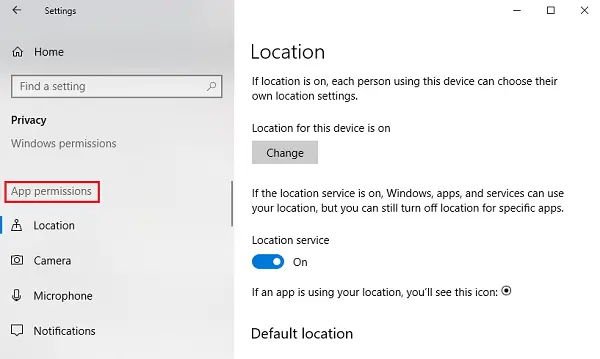
- Click on Start and then the gear-like symbol to open the Settings page.
- Select Privacy, and it shows a list of App permissions on the list on the left.
Now let us take a look at all the sections.
Location
Windows 11
Location: This setting allows each user logged on to the system to configure their preferences.
- Location service: Turning Off the Location service disallows all apps, services, and websites from accessing the user’s location. However, when turned On, only permitted apps can access the user’s location. By default, the Location service is set to On.
- Location history: Location history stores the location history of users for some time, so apps needing the same could use it. There is an option to clear the location history as well.
- Default location – It enables Windows apps and services to use the default location when it fails to locate your precise location. It replaces Geofencing setting, seen in Windows 10.
Windows 10
- Location: This setting allows each user logged on to the system to choose their own location settings.
- Location service: Turning Off the Location service disallows all apps, services, and websites from accessing the user’s location. However, when turned On, only permitted apps can access the user’s location. By default, the Location service is set to On.
- Location history: Location history stores the location history of users for some time, so apps needing the same could use it. There is an option to clear the location history as well.
- Geofencing: This service helps Windows find out when you change your geolocation and remind of places of interest.
The following settings remain the same for Windows 11 and Windows 10.
Camera
Allow access to the camera on this device: Camera is usually not activated by default for any app, and they prompt if the user wishes to use the camera or not. However, turning this setting Off will disallow all apps and services from accessing to a camera totally.
Allow apps to access your camera: This setting is a subset of the previous setting. If we turn this setting Off, it disallows all apps from accessing the camera, but not Windows itself. We can choose which apps have access and which don’t.
Microphone
The Allows access to the microphone on this device and Allow apps to access your microphone settings have the same functions as for similar options mentioned with the camera settings earlier.
Notifications
Let apps access my notifications: Turning this Off this setting restricts all apps from accessing the user’s notifications. When On, we can choose individual apps which could access the notifications.
Account info
Just like earlier settings, Allows access to the Account info on this device and Allow apps to access your Account info allow apps and Windows or just apps to access the user’s account information.
Contacts
Microsoft stores users’ contacts (name, phone number, email ID, etc.) and this setting help users choose whether they want Windows and/or apps to access their contacts.
Calendar
This setting refers to the Calendar schedule the user has set, which means allowing the system and apps to access it by making your calendar schedule available to them. Eg. If you have an important meeting scheduled for a specific date, the app (and administrator) would be able to access the same.
Call history
Most users will hate if anyone finds their call history is shared with anyone. Perhaps we live in the perception that only legal authorities have access to it, but that isn’t a fact. Any calls made from a device which you have logged on from your Microsoft account would save that information and make it available for apps and Windows. The Call history settings help to turn off this access.
Microsoft allows apps and settings to access the emails of its users. Yes, it literally means they can check your emails along with the date and time of sending/receiving. This setting helps deny them access to the same.
Tasks
Most advertisements are based on your tasks on the system or any system on which you have logged on with your Microsoft account. This setting could prevent apps and Windows from accessing the same.
Messaging
Here messaging refers to SMS and MMS on systems and phones where the user has logged on with his/her Microsoft account. Disabling it prevents apps and Windows from accessing the same.
Radios
Radios are options like Bluetooth which could be controlled by apps remotely. Eg. A music sharing app could automatically switch On your device’s Bluetooth and start sending files. We can select apps that have this access from this setting.
Background apps
At times (or mostly) apps run in the background while the user is working on the system, being invisible to the user. So, apps could be running on your system in the background without your being aware of it at all. Users can disable all or specific apps using this setting.
App diagnostics
Apps collect diagnostic data from your system, and this setting allows or disallows other apps to use that diagnostic data from the system.
Automatic file downloads
Online storage providers (e.g. OneDrive) have a facility to download files to the system automatically. While that setting is disabled from the provider’s website itself, we can allow the again from this setting.
Documents
This setting helps allow or disable Windows/apps from accessing documents stored either on the system or Microsoft storage accounts.
Pictures and Videos
Windows and apps have access to all your pictures and videos by default. To prevent them from accessing your personalized pictures and videos, we can turn Off this setting.
File system
This a cumulative of all pictures, videos, and documents on the system. We can modify this setting as per our preferences.
By now, you must have a precise understanding of what all information Microsoft can access, and rather does by default.
What are permissions for apps?
App permissions in Windows lets users grant apps control over their phone and access tools like camera, microphone, photos, etc. These requests are usually privacy-related and you can allow or deny them, depending on your preferences.
Does uninstalling an app remove permissions?
Yes! The permissions you give are only for the app. So, if the app is not residing on your device, it doesn’t have access to your tools like a microphone, camera and cannot use it in any way.
We hope this post helps you make your Microsoft experience private and secure.
Leave a Reply