Commonly called MitB, the Man In The Browser attack is one of the most dangerous types of attacks a cybercriminal can use. This method employs the usage of a Trojan Horse or similar malware to gain important information from users of websites, especially banking and credit card information. It is a piece of a code that alters and adds different input fields to a webpage you are visiting. Since the URL is not changed, you believe that the site needs that information, you simply fill it in.
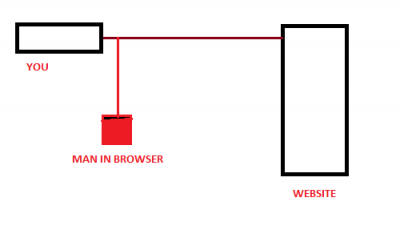
Man In The Browser attack explained
Unlike Man In The Middle Attack, where a third party is situated between two endpoints listening to packets for useful information, the MitB attack is about altering and adding input fields to the website you are visiting. A malware like a Trojan Horse is situated between your computer and the site server. Using that malware, different input fields are added to the website, asking you for your confidential information.
In some cases, it is not just a page but the entire sequence of webpages arranged so that you are sure it is genuine. Since it is based on the malware reading the IP addresses, it looks okay to webmasters. When in doubt, take a screenshot and send it to the webmasters for confirmation. You may get doubts when suddenly your bank website starts asking verification by means of a credit card.
For example, most bank websites simply require your ID and a PIN (OTP) to log in. Some may use passwords in addition. But anything more than that, like asking you your credit card number, PIN, CSV code, etc, should ring an alarm inside your head. If that happens, stop immediately, take a screenshot and send it to the bank asking if they really want that data.
Note that this is different from normal phishing. When phishing, they send you emails trying to hook or social engineer you into providing them with the information you want. In Man in the Browser attack, the cybercriminal makes the input field look genuine. They look true as the URL is the same even after being compromised. Sometimes, they just say they want to up your security and hence you need to provide them with the required (additional, personal) information.
How is MitB Implemented
Man In The Browser attack relies on malware to know your destination on the Internet. Then it creates code for extra input fields and places them on the website page you visit. You may wonder if your computer is clean where the malware comes in! The answer lies in browser extensions, patches (fake), and DOM objects. That is to say, the browser is compromised using some method or the other and is not caught by the anti-virus you are using. This is what makes it complex to detect MitB attacks.
Protection against Man In The Browser attack
Apart from using an up-to-date OS and good updated security software, the protection at the moment of writing this article is just common sense. You have to be careful on the Internet. You do not provide credit card or social security information to anyone easily in real life so why should you do that in an online world? Keep looking for what all information asks while logging you or at registration. If something does not add up, quit, and inform webmasters. You can also close the browser and start a new session to see if the same fields appear again.
Other than the above, to prevent Man In The Browser attack, you also need to keep extensions, etc, in check. Use only reputed extensions and try to use a minimum of them. If you still find anything fishy, contact the webmasters of the said website.
Now read: What are Browser in the Browser Attacks?
Leave a Reply