If the Maximum Memory setting in MSConfig triggers a Blue Screen or Resets to 0, the solutions provided in this article will help you. MSConfig or System Configuration allows us to diagnose and troubleshoot issues on our Windows computers. We can use it to enter Safe Mode, Clean Boot state, etc. We can also use it to enable or disable bulk Services at a time.

MSConfig Maximum Memory triggers BSOD or Resets to 0
If setting the MSConfig Maximum Memory triggers BSOD or it resets to 0, you can try the solutions provided here. The advanced options in System Configuration set the number of processors and maximum memory or RAM. The Maximum Memory feature limits how much RAM your Windows computer can use.
These advanced features are for debugging purposes and are used by developers to troubleshoot issues. Therefore, it is suggested that you leave them in their default state. Modifying them without knowledge can negatively impact your system’s performance and cause serious errors in some cases.
- Sign in as administrator
- Revert the changes in the Windows Recovery Environment
- Repair your PC
- Perform System Restore or Reset your PC
- Reinstall Windows
Let’s see all these fixes in detail.
1] Sign in as administrator
If the maximum memory keeps resetting to 0 after restarting, make sure that you are signed into your system as an administrator. It is not recommended to make changes to these advanced features if you are using a school or work PC.
2] Revert the changes in the Windows Recovery Environment
If, after setting up the maximum memory in MSConfig, you encounter the BSOD error and cannot use your computer, you have to reset the advanced settings in MSConfig via Windows Recovery Environment.
Because you cannot use your system due to the BSOD error, you can enter the Windows Recovery Environment by interrupting the normal boot process. Follow the steps provided below:
- Turn on your computer.
- Press and hold the power button immediately when the Windows logo or the computer manufacturer’s logo appears on the screen until your computer shuts off.
Repeat the above two steps until you see the Preparing Automatic Repair screen. Your system has not entered the Windows Recovery Environment. Now, select Advanced options > Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Command Prompt.
Copy and paste the following commands in Command Prompt one by one and hit Enter after entering each command:
bcdedit /deletevalue {current} removememory
bcdedit /deletevalue {current} truncatememory
bcdedit /deletevalue {default} removememory
bcdedit /deletevalue {default} truncatememory
Now, close the Command Prompt and restart your computer. The BSOD error should be fixed and you should be able to use your computer this time.
3] Repair your PC
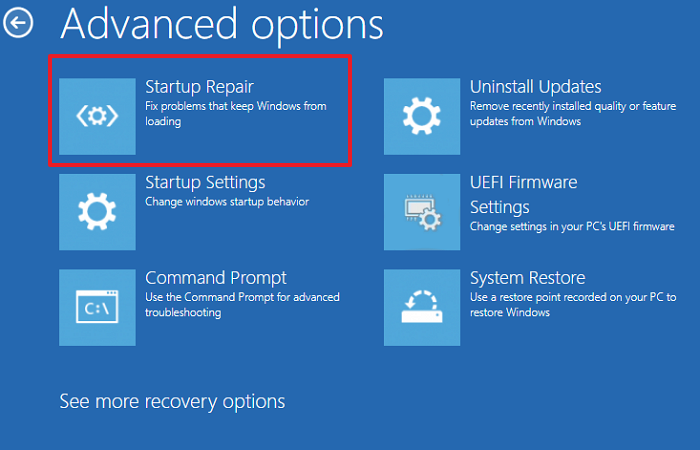
If the problem persists, you can repair your computer by using the built-in tool, Startup Repair. You can access this tool through the Windows Recovery Environment. Follow the steps above to enter Windows Recovery Environment and go to Advanced options > Troubleshoot> Advanced options> Startup Repair.
4] Perform System Restore or Reset your PC
Windows automatically creates System Restore Points whenever it notices any changes to your system. However, it is a good practice to create system restore points manually. If the restore points exist on your system, you can use them to restore your computer to the previous working state.
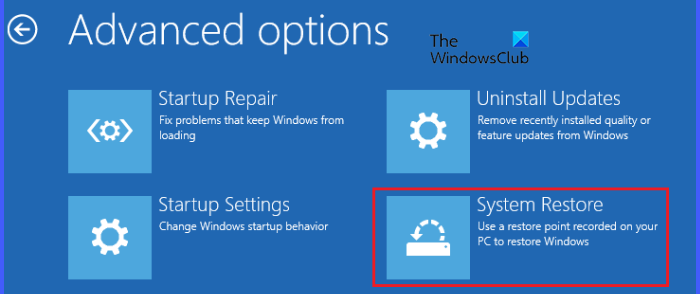
Enter Windows Recovery Environment and select Advanced options > Troubleshoot> Advanced options > System Restore. Now, select the restore point created on the date before which your system was working perfectly. Follow the on-screen instructions to restore your system.
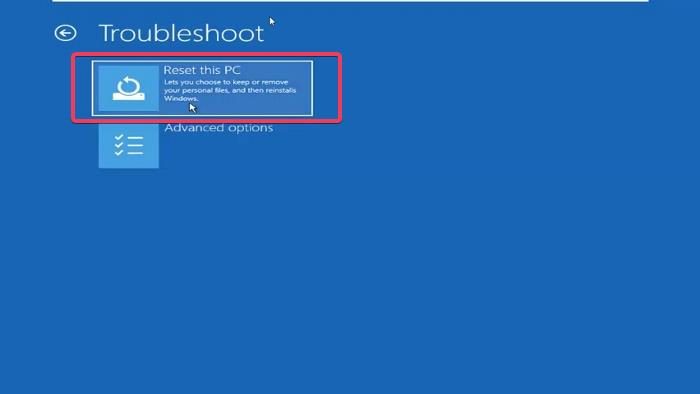
If no restore points exist on your system you will not be able to restore your system to the previous working state. In this case, you can reset your PC. Again, you have to enter the Windows Recovery Environment to do so. When you are in WinRE, select Advanced options > Reset this PC. While performing this action, select the Keep my files option. This will reset your PC to the factory default settings without deleting your data.
5] Reinstall Windows
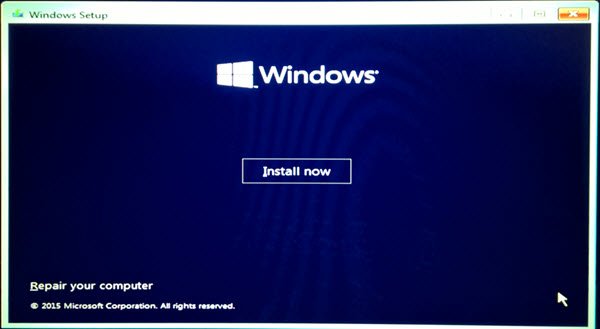
The last resort to fix the BSOD error is to perform the clean installation of Windows. This will erase all the data on the hard drive partition on which you install Windows. Therefore, select the hard drive partition carefully.
You can use the Media Creation Tool to download the Windows ISO file. After downloading the Windows ISO file, use a third-party tool like Rufus to create a bootable USB Flash drive.
I hope this helps.
Can RAM cause a blue screen error?
Yes, faulty RAM can cause a Blue Screen error on a Windows computer. A faulty RAM has some signs or symptoms. If you notice these signs or symptoms on your system, test your RAM to confirm whether the issue is with RAM or another hardware.
Read: Your computer has a memory problem.
What does maximum memory mean in msconfig?
The maximum memory feature in MSConfig limits your system’s RAM usage. Your system will not use more RAM than the value you enter here. This feature is for training and debugging purposes. Therefore, it is better to leave it to the factory default settings.
Read next: MEMORY MANAGEMENT BSOD error in Windows.
Leave a Reply