ReFS, or Resilient File System, is designed to be more scalable and reliable than the traditional NTFS file system. It can support larger local and network storage capacities and uses a digital metadata journaling system to enhance data recovery and file integrity. However, if your ReFS volume becomes inaccessible after the update, this post will help you resolve the issue.

Users commonly encounter this issue after installing Windows updates or upgrading the OS from Windows 10 to Windows 11. The primary causes of the error include:
- Incompatible or corrupted Volume Screenshot: If the Windows update ( or an OS upgrade) and the disk volume are incompatible, the file system may be unable to read or write the data correctly. Also, if the update process is interrupted multiple times or encounters errors, the volume can be inconsistent, leading to inaccessibility.
- Hardware issues: Physical damage to the hard disk can lead to Inaccessible storage sectors, which can damage file system metadata. Since the entire technology behind ReFS is centered around this metadata, such problems could disrupt file locations and attributes, making the disk volume inaccessible.
- Corrupted ReFS metadata: Damaged or improperly arranged data structure and it’s location information, in short, corrupted ReFS Metadata may occur due to abrupt system shutdowns, hardware failures, or software glitches. In such cases, the file system cannot access or manage the data stored in the device, leading to the error.
Fix ReFS volume inaccessible after update
The below-mentioned steps can be followed to resolve the said issue:
- Remove the last installed Windows update
- Upgrade ReFS volume to the latest version
- Enable Integrity Streams
1] Remove the last installed Windows update
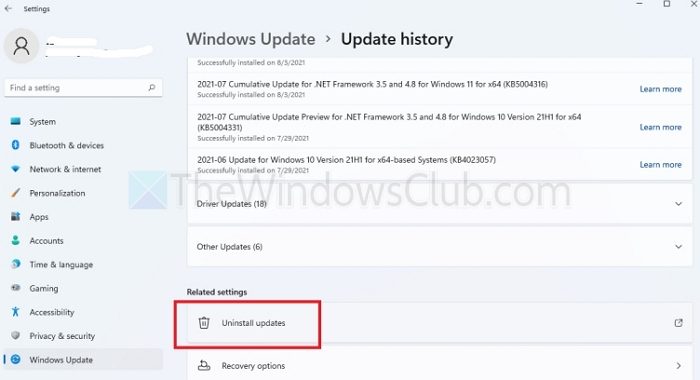
- Press the Windows +I keys together to open the Settings app.
- Select the Windows Update option from the left pane and then click on Update History on the right.
- Under the Related Settings section, click on Uninstall updates and select Uninstall next to the Update that needs to be removed.
- Restart the system once the uninstallation is completed.
Related: How to uninstall Uninstall Windows Update marked as Permanent without Uninstall Option
2] Upgrade ReFS volume to the latest version
If the system runs an older or outdated version of ReFS, it may not be compatible with the current or latest version of Windows installed on the system. For example, the ReFS 1.x support is no longer available in Windows. In such cases, updating ReFS may help resolve the said problem. We can perform an in-place upgrade to ensure that the ReFS version gets updated automatically. To perform an in-place upgrade in Windows 11:
- Download the Windows 11 ISO file
- Click to open the downloaded file and click on the setup file to continue.
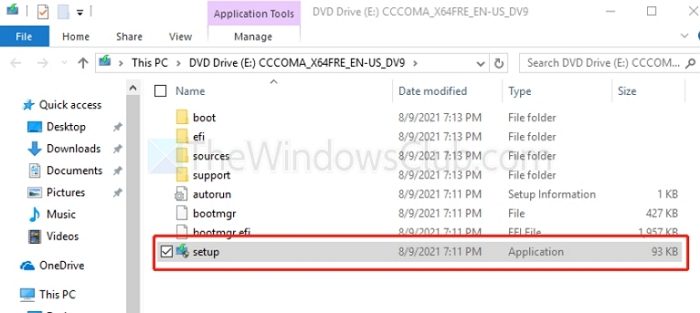
- Click on Next to continue further and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the update process
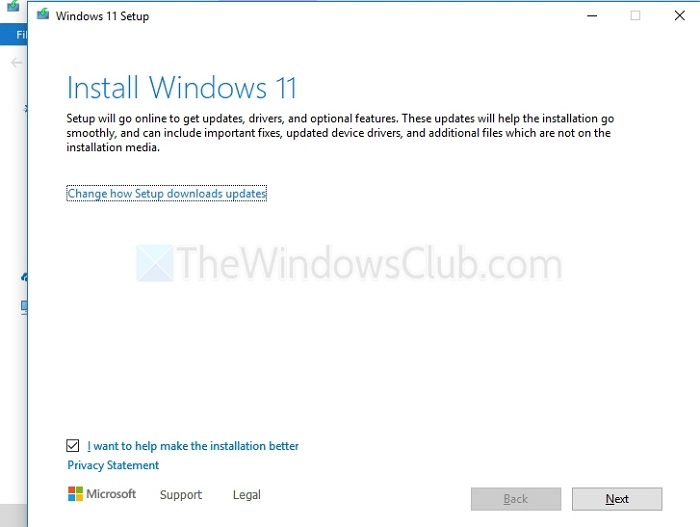
- Once the process completes, we can check the current version of the ReFS using the fsutil command in the Windows Terminal Prompt after opening it as an administrator and typing:
fsutil fsinfo refsinfo X
3] Enable Integrity Streams
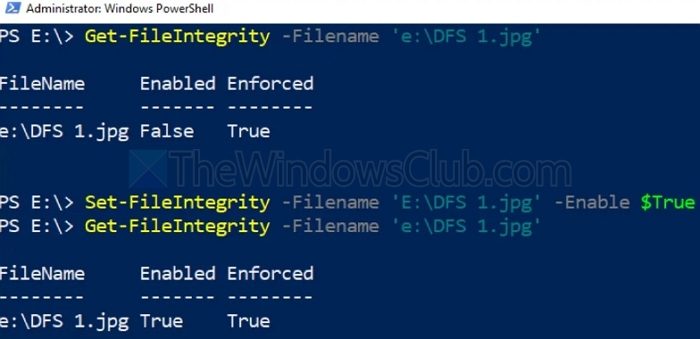
Integrity streams can identify and repair the damaged blocks or sectors if the ReFS volume is inaccessible after installing Windows updates due to data corruption. Hence, it can be considered a valuable tool to restore the functionality of the disk volume and prevent data loss. To do so:
- Open the Windows Terminal by typing cmd in the Desktop Search Bar and run it as an Administrator
- Execute the below-mentioned commands in the same order as mentioned below:
Set –FileIntegrity –Filename ‘E:\DFS 1.jpg’ –Enable $True Get –FileIntegrity –Filename ‘e:\DFS 1.jpg’
The first command enables File Integrity for all new files, while the second enables it for all the existing folders and subfolders.
Read: ReFS volume repair was not successful in Windows 11
What is the difference between NTFS and ReFS?
NTFS directly modifies file metadata, making it vulnerable to data corruption or loss in case of system failures. ReFS, on the other hand, safeguards data integrity by creating a copy of the file metadata before editing. The data is linked to its corresponding file only when the updated metadata is successfully written to disk.
Is ReFS faster than NTFS?
ReFS generally outperforms NTFS in terms of speed, especially in large-scale environments and under heavy workloads. This is primarily due to its more efficient metadata handling, which involves creating a copy of the metadata before editing and only linking the data to the updated metadata after it’s successfully written to disk. This approach reduces the likelihood of data corruption and can improve overall performance.