When you try to establish a remote connection or session on your Windows 11 or Windows 10 computer, you may receive the error code 0x3000046. This post is intended to help affected PC users with the most suitable solutions to apply to successfully resolve the issue. This issue usually occurs when connecting to Windows Virtual Desktop (WVD) via the Windows client (in some cases, via the web client), and you may get the error code 0x3000047 instead.
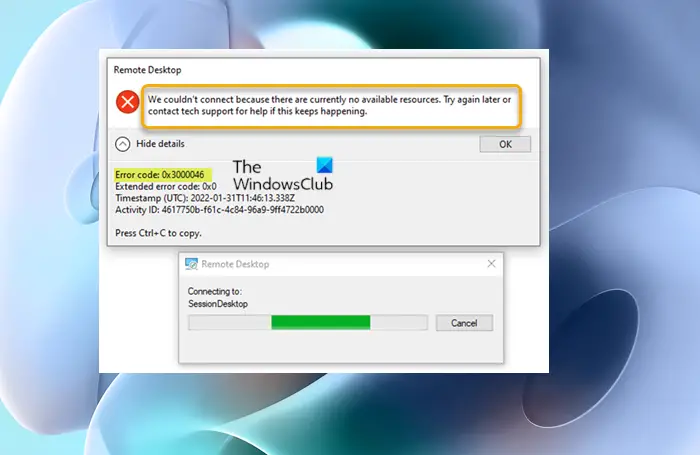
When you encounter this issue, you’ll receive the following full error message;
Remote Desktop
We couldn’t connect because there are currently no available resources. Try again later or contact tech support for help if this keeps happening.
Error code: 0x3000046
When this issue occurs, the user is not able to connect to the personal virtual desktop (with the direct assignment) when a host pool and session host is created from the new portal for Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) a.k.a WVD v2.
Fix Remote Desktop Error Code 0x3000046
If you have encountered the Remote Desktop Error Code 0x3000046 on your Windows 11/10 PC, you can try our recommended solutions below in no particular order and see if that helps to resolve the issue.
- Configure UPNs to be the same in on-prem DCs and Azure AD
- Add user to Remote Desktop Users group
- Assign user(s) to a personal desktop using PowerShell
- Assign personal desktop to user from AVD new portal
Let’s take a look at the description of the process involved concerning each of the listed solutions.
The only workaround to fix this Remote Desktop connection issue is manually starting the VM from the Azure portal, which would have been fine if the problem was not recurring or affecting only 1 or 2 users. If that’s the case for you, then continue with the solutions below.
1] Configure UPNs to be the same in on-prem DCs and Azure AD
This solution to the Remote Desktop Error Code 0x3000046 requires you to make sure the UPNs are the same in on-prem Domain Controllers and Azure AD. And also make sure the O365 UPN is the same as the User Logon Name in the local Active Directory.
To configure UPNs to be the same in on-prem DCs and Azure AD, do the following:
- Open Active Directory Domains and Trusts.
- On the left-hand side of the new window, right-click on Active Directory Domains and Trusts.
- Select Properties from the context menu.
- In the Alternative UPN suffixes field, type in the domain suffix of the user allowed to use WVD.
- Click Add.
- Next, modify the user logon name property of the respective user from (e.g:) username@contoso.local to username@domain.tld (as the user has it in O365 / AAD tenant).
- Save changes and exit.
Once done, try the remote desktop connection again. The issue should be resolved now.
2] Add user to Remote Desktop Users group
This solution requires you to add user(s) experiencing this issue to the Remote Desktop Users group. To add the user as a member of the local Remote Desktop User on the WVD computer, do the following:
- Click Start.
- Click Administrative Tools.
- Click Computer Management.
- In the console tree, click the Local Users and Groups node.
- In the details pane, double-click the Groups folder.
- Double-click Remote Desktop Users, and then click Add.
- In the Select Users dialog box, click Locations to specify the search location.
- Click Object Types to specify the types of objects that you want to search for.
- In the Enter the object names to select (examples) box, type the name you want to add.
- Click Check Names.
- When the name is located, click OK.
3] Assign user(s) to a personal desktop using PowerShell
To assign user(s) to a personal desktop using PowerShell, do the following:
- Download and Install Visual Studio Code for AVD Management.
After the installation, you will need to configure PowerShell in Visual Studio Code for AVD. Here’s how:
- Press Ctrl+P (Quick-Open) to launch the search option.
- In Quick-Open, type
ext install powershelland press Enter. - Select the Powershell Extension for Visual Studio Code (PowerShell Scripts in Visual Studio code).
- Click on the Install button to continue.
- Run the following commands one after the other from Windows Terminal.
Install-Module -Name Microsoft.RDInfra.RDPowerShell
Install-Module -Name Az.DesktopVirtualization -RequiredVersion 2.1.0
Import-Module -Name Microsoft.RDInfra.RDPowerShell
- Next, run the following commands one after the other to select the appropriate subscription:
Connect-AzAccount
Get-AzSubscription | Out-GridView -PassThru | Select-AzSubscription
Update-AzWvdHostPool -ResourceGroupName WVD-Resource-Group -Name HostPool -StartVMOnConnect:$True
- Once done, you can now run the PowerShell command below to assign user(s) to a personal desktop. Replace all the following variables with the host pool name, session hostname, resource group name, and userupn.
Update-AzWvdSessionHost -HostPoolName $hostpoolname -Name $sessionhostname -ResourceGroupName $resourcegroupname -AssignedUser $userupn
- Exit Terminal when done.
4] Assign personal desktop to user from AVD new portal
Alternative to Solution 3] above, you can assign a personal desktop to the user from AVD new portal. Here’s how:
- Login to portal.azure.com.
- Search with Azure Virtual Desktop.
- Click on the Azure Virtual Desktop icon.
- Select Personal Host Pool.
- Select personal desktop Session Hosts.
- Navigate to the right until you see the Assigned user column.
- Click on (Assign) link and select the user (direct assignment).
Now, the user can try the remote desktop connection again; this time, the connection should be successful.
That’s it!
Related post: Fix Remote Desktop Error Code 0x204 on Windows
How do I access Azure Windows Virtual Desktop?
To access Azure Windows Virtual Desktop, do the following:
- Go to the Azure portal to connect to a VM.
- Select the virtual machine from the list.
- At the beginning of the virtual machine page, select Connect.
- On the Connect to virtual machine page, select RDP.
- Select the appropriate IP address and Port number.
What is drain mode in WVD?
Drain mode in Windows Virtual Desktop simply isolates a session host when you want to apply patches and do maintenance without disrupting user sessions. When isolated, the session host won’t accept new user sessions.
Leave a Reply