If you want to run Windows PowerShell scripts first at user logon, logoff, startup, and shutdown, follow these steps. Using the Local Group Policy Editor and Registry Editor, you can prioritize Windows PowerShell scripts before non-PowerShell scripts.
All the scripts run simultaneously when a user logs on or starts up the computer. It may cause some delay in the startup or running a specific program. Running all the Windows PowerShell scripts and Group Policy Object is often required before non-PowerShell scripts.
Run Windows PowerShell scripts first at user logon, logoff, startup, and shutdown
To run Windows PowerShell scripts first at user logon, logoff, startup, and shutdown, on your Windows computer follow these steps-
- Press Win+R.
- Type gpedit.msc and hit the Enter button.
- Go to Scripts in Computer Configuration.
- Double-click on Run Windows PowerShell scripts first at user logon, logoff.
- Select the Enabled option.
- Click Apply and OK.
- Double-click on Run Windows PowerShell scripts first at computer startup, shutdown.
- Select the Enabled option.
- Click Apply and OK.
Let’s check out these steps in detail.
At first, you will have to open the Local Group Policy Editor. For that, press Win+R, type gpedit.msc, and hit the Enter button. After opening it, navigate to the following path-
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Scripts
You will see two settings called:
- Run Windows PowerShell scripts first at user logon, logoff,
- Run Windows PowerShell scripts first at computer startup, shutdown.
Double-click on each of them and select the Enabled option.
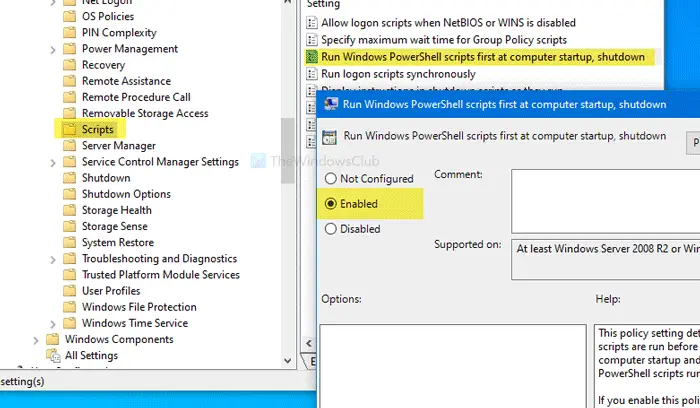
Click the Apply and OK to save the change.
Read: How to add PowerShell to Context Menu in Windows
Run Windows PowerShell scripts first at user logon, logoff, startup, and shutdown using Registry Editor
To run Windows PowerShell scripts first at user logon, logoff, startup, and shutdown using Registry Editor, follow these steps-
- Press Win+R.
- Type regedit and hit the Enter button.
- Click the Yes button.
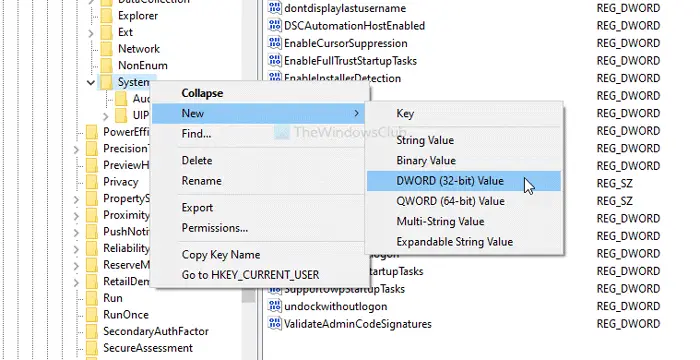
- Go to System in HKLM.
- Right-click on System > New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.
- Name it as RunUserPSScriptsFirst.
- Double-click on it and set the Value data as 1.
- Click the OK button.
- Right-click on System > New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.
- Name it as RunComputerPSScriptsFirst.
- Double-click on it to set the Value data as 1.
- Click OK to save the change.
To know more, keep reading.
Before getting started, it is recommended to backup all Registry files and create a System Restore point.
Press Win+R to open the Run prompt, type regedit, and hit the Enter button. If the UAC prompt appears, click the Yes button. After that, navigate to this path-
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System
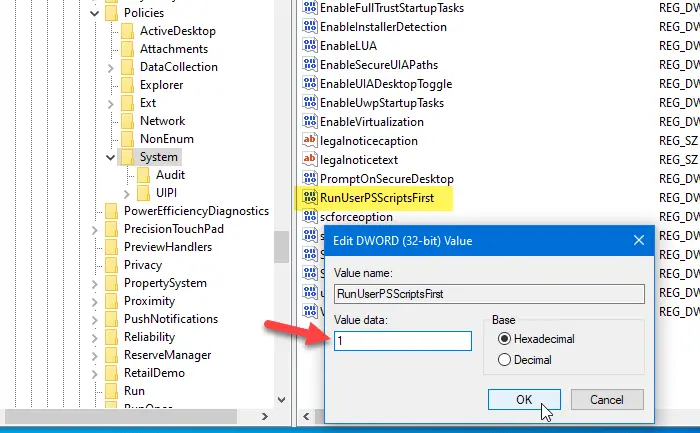
Here, you will have to create two REG_DWORD values. To do that, right-click on System > New > DWORD (32-bit) Value and name it RunUserPSScriptsFirst.
Double-click on it and set the Value data as 1.
Follow the same steps to create another DWORD (32-bit) Value and name it as RunComputerPSScriptsFirst. Then, set the Value data as 1.
RunUserPSScriptsFirst represents the Run Windows PowerShell scripts first at user logon, logoff setting, whereas RunComputerPSScriptsFirst defines the Run Windows PowerShell scripts first at computer startup, shutdown setting.
If you want to revert these changes, you can follow these steps.
If you have done it using the Local Group Policy Editor, open the same path and select the Not Configured option. If you have done it using the Registry Editor, open the same System key and delete those two REG_DWORD values. To remove them, right-click on each, select the Delete option, and confirm it by clicking the OK button.
Read: How to add PowerShell to Context Menu in Windows.
I hope it helps.
Which is the easiest way to run a PowerShell script at startup?
You can use the Task Manager to execute anything, including a PowerShell script that runs as soon as you log in to your PC. Since many programs are executed then, it is best to add delays or run it after a few minutes.
What is PowerShell used for?
PowerShell, a command-line shell and scripting language, is widely employed for automating system management tasks on Windows and other platforms. It is also utilized for creating, testing, and deploying software solutions, which play a crucial role in streamlining the software development and delivery process.
Leave a Reply